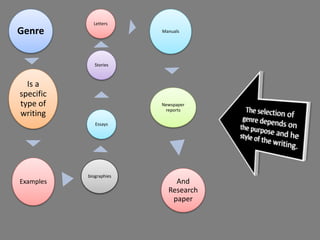
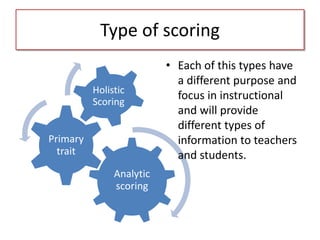
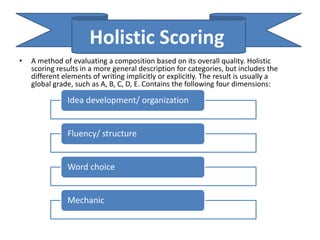
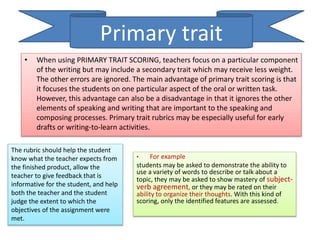
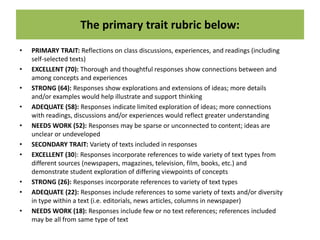
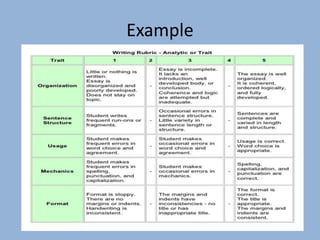
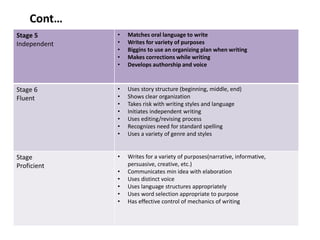
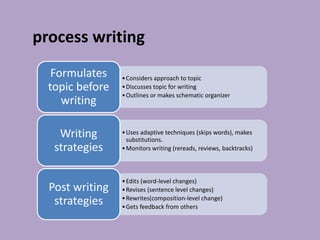
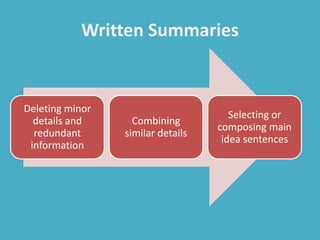
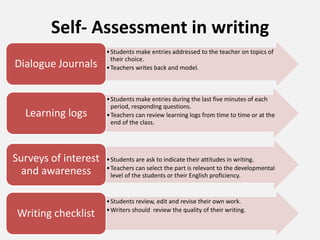
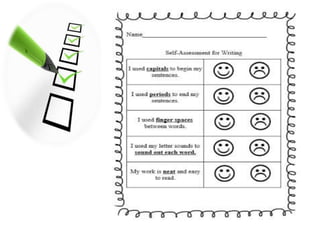
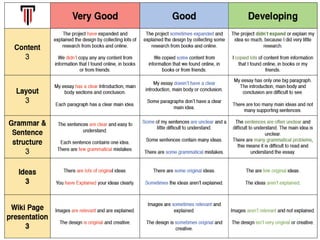
The document discusses various aspects of writing assessment including: the writing process, purposes and genres of writing, authentic assessment through prompts and rubrics, stages of writing development, monitoring student progress, and strategies like summaries, self-assessment, and peer assessment. Key points include that writing is a process, assessment should be authentic through meaningful prompts and clear rubrics, and strategies like conferencing and sharing rubrics can help connect assessment to instruction.