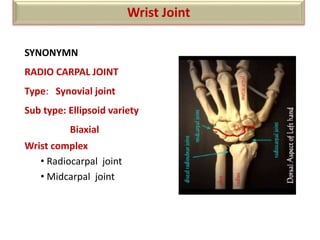
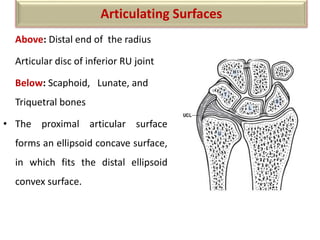
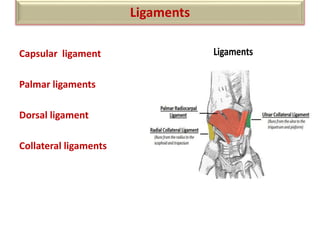
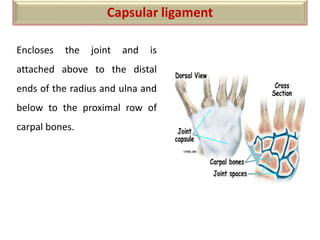
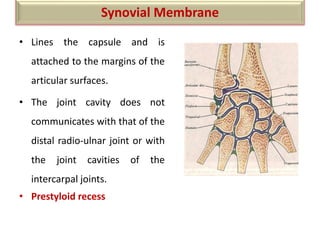
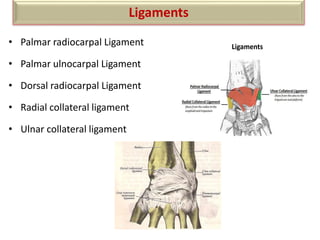
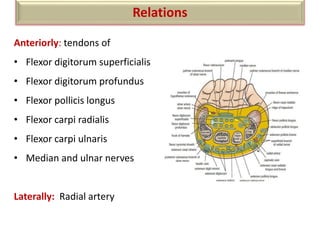
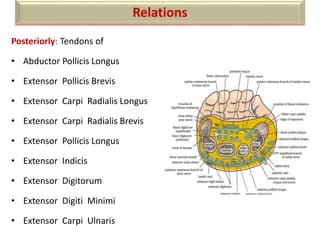
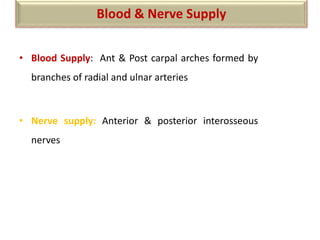
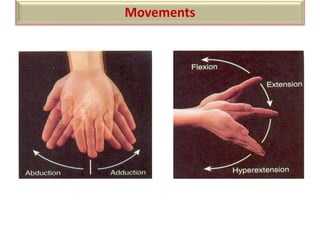
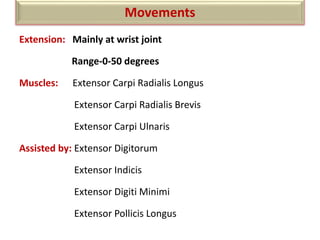
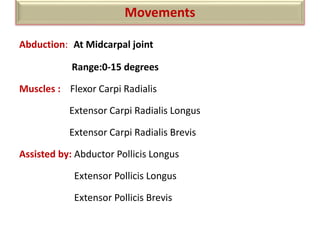
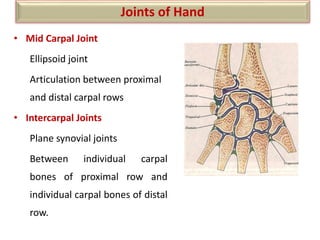
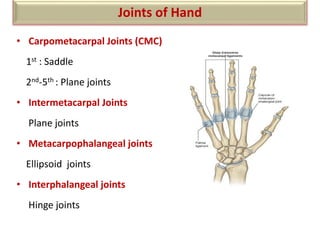
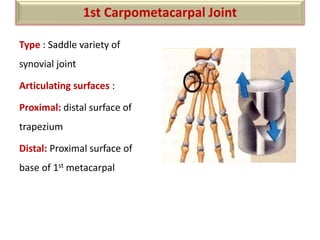
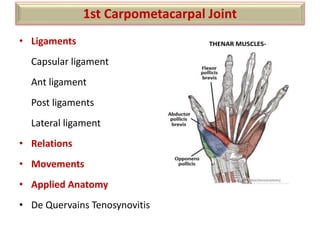
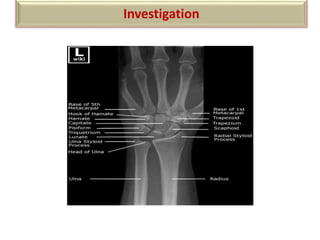
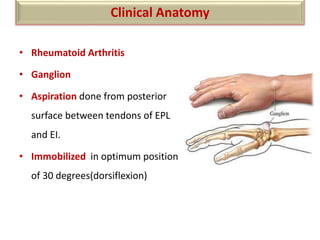
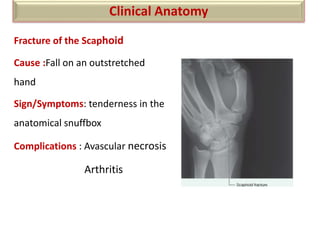
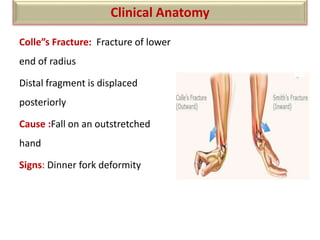
The document summarizes the wrist joint and joints of the hand. It describes the wrist joint as an ellipsoid synovial joint between the radius and carpal bones. It then discusses the ligaments, movements, blood supply, and relations of the wrist joint. It also provides an overview of the joints in the hand, including the midcarpal joint, intercarpal joints, carpometacarpal joints, intermetacarpal joints, and interphalangeal joints. It concludes with brief discussions of the clinical anatomy of some wrist and hand injuries.