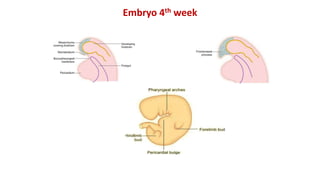
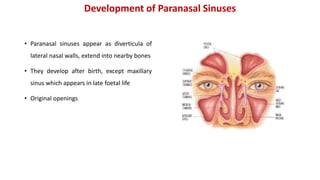
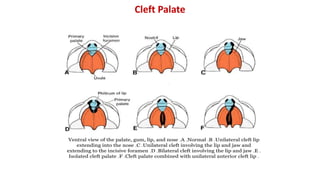
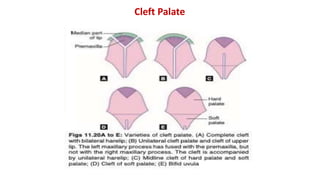
The document discusses the development of the face, nose, and palate between 4-12 weeks of gestation. It summarizes that:
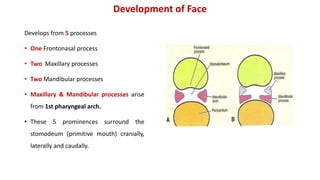
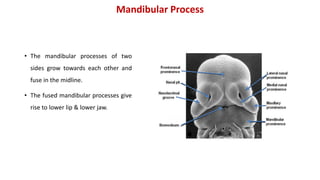
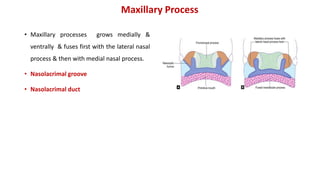
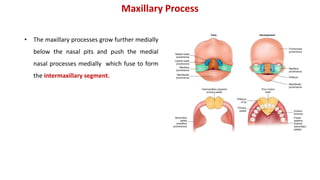
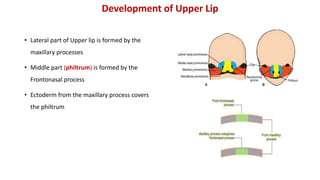
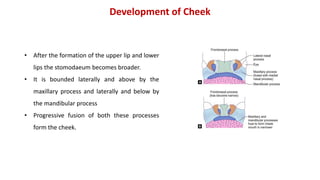
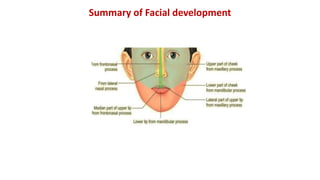
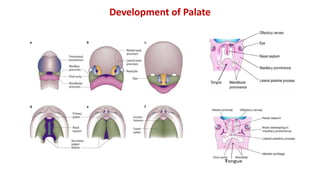
1) The face develops from 5 processes - the frontonasal, two maxillary, and two mandibular processes. These processes fuse to form structures like the upper and lower lips.
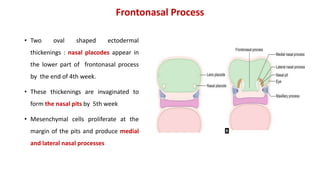
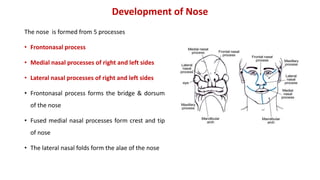
2) The nose develops from the frontonasal process, medial and lateral nasal processes, which fuse to form structures like the bridge and tip of the nose.
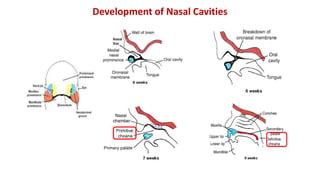
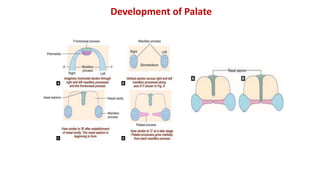
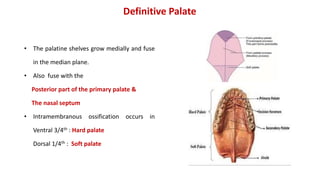
3) The palate develops from the lateral palatine processes which elongate and fuse above the tongue to form the primary and secondary palate. This separates the oral and nasal cavities.