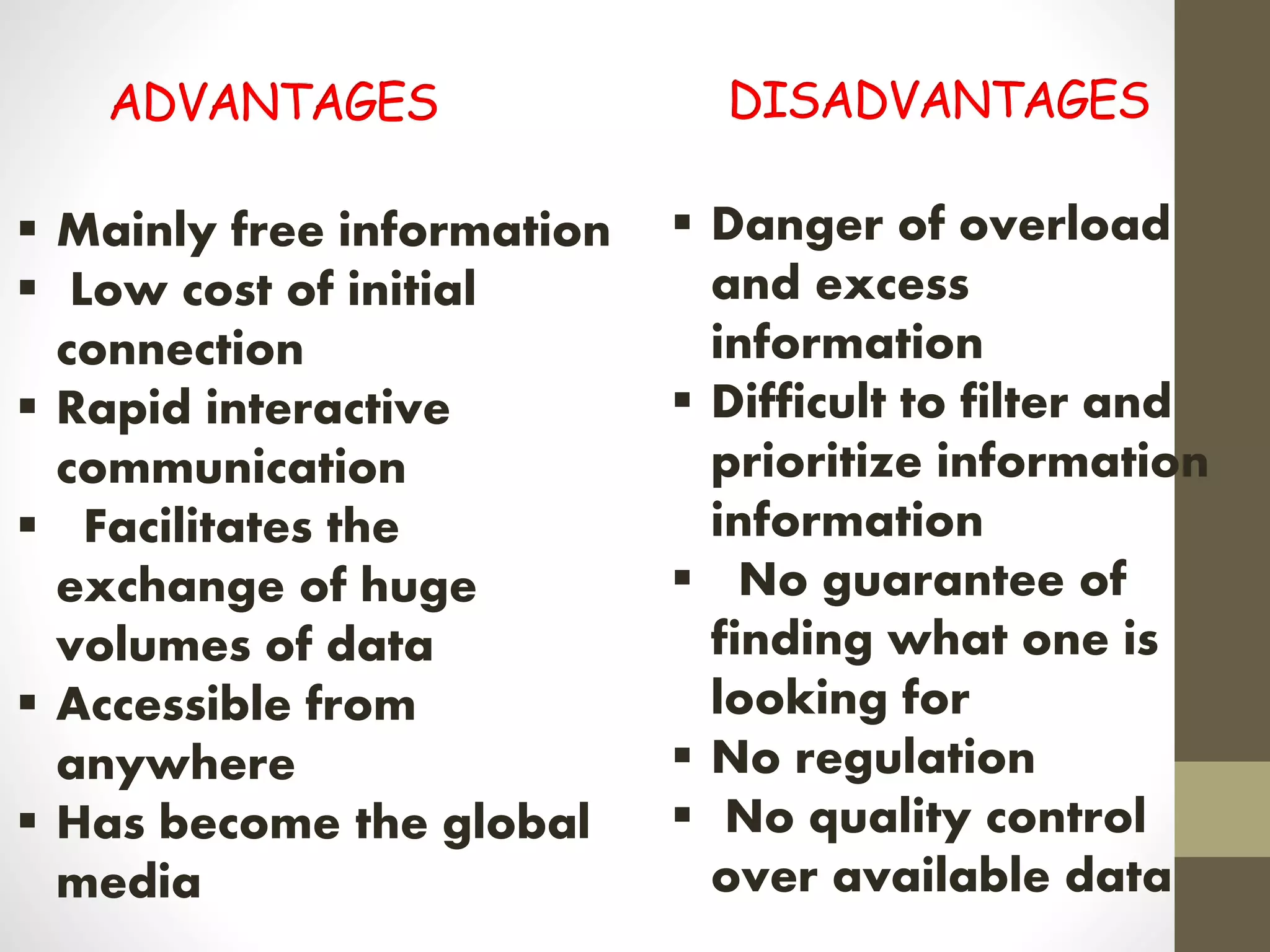
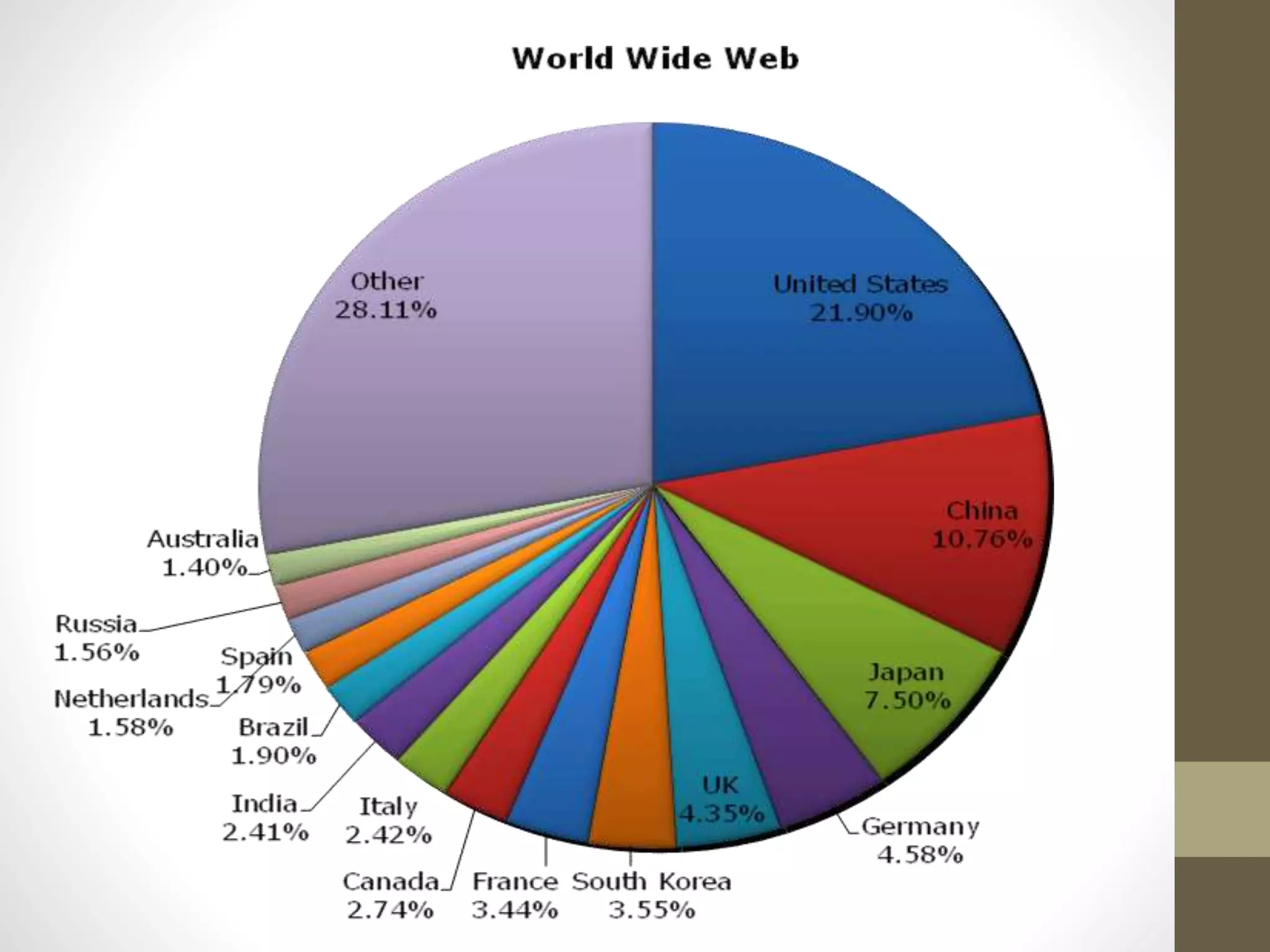
Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web (WWW) in 1989-1990 at CERN as a way to transfer text and graphics simultaneously over the Internet. The WWW is constructed using HTML and consists of web pages with text, graphics, sounds and other files. It is built upon several technologies including HTTP, HTML, URLs and works by clients using browsers to send requests to servers for web pages.