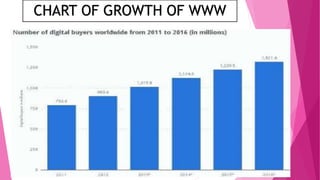
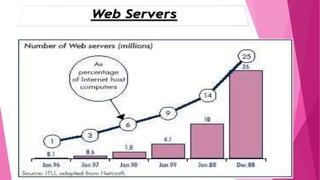
Vrushali Jaykisan Bhade has completed a 100-hour training on the World Wide Web. The document provides an overview of the history and components of the World Wide Web, which was invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. It discusses how the Web works using clients, servers, and browsers connected over the Internet. Key concepts like URLs, HTML, and hyperlinks are explained. The document also covers the advantages and growth of the Web and concludes by noting the Web's success was due to its simplicity.