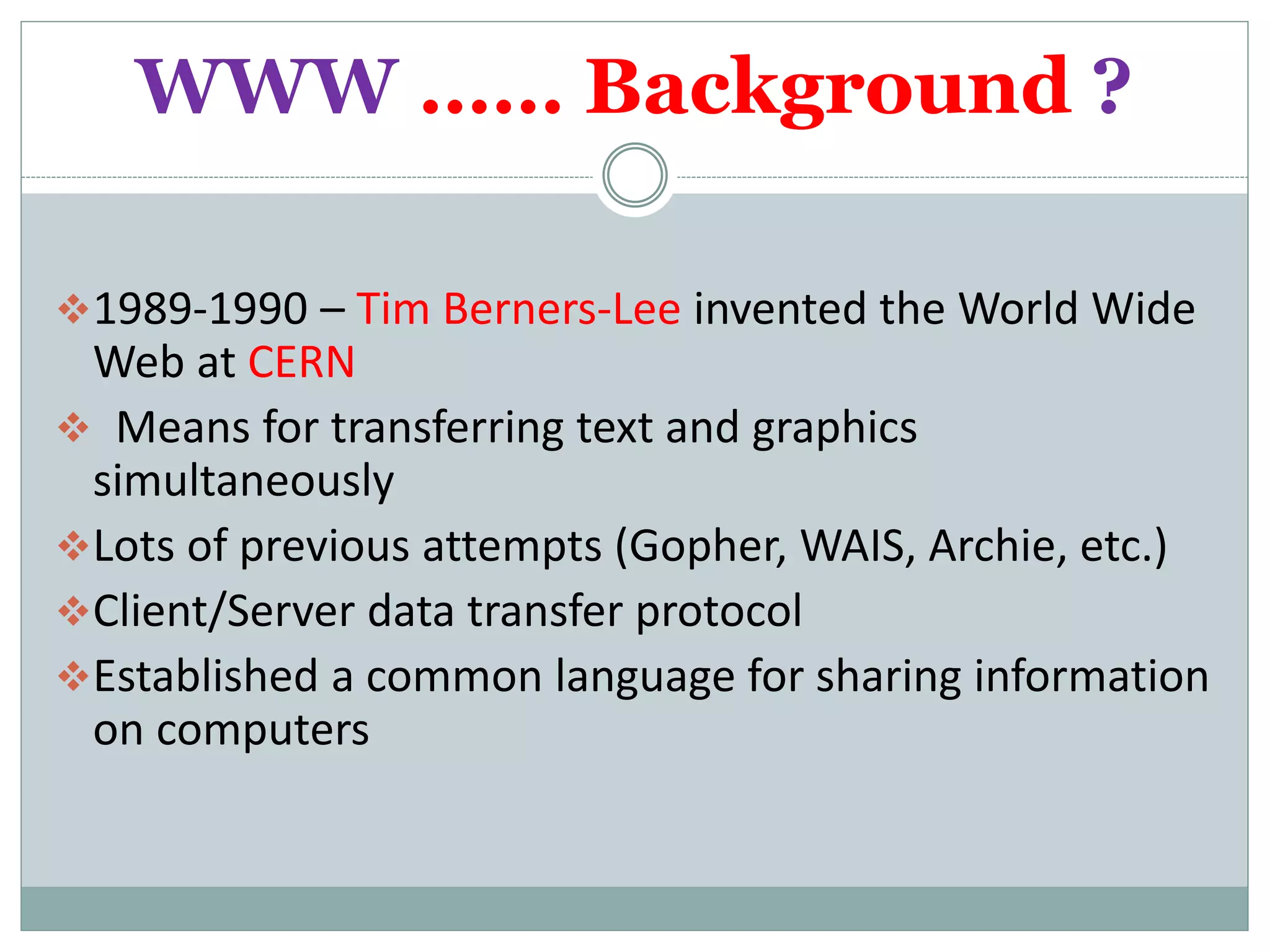
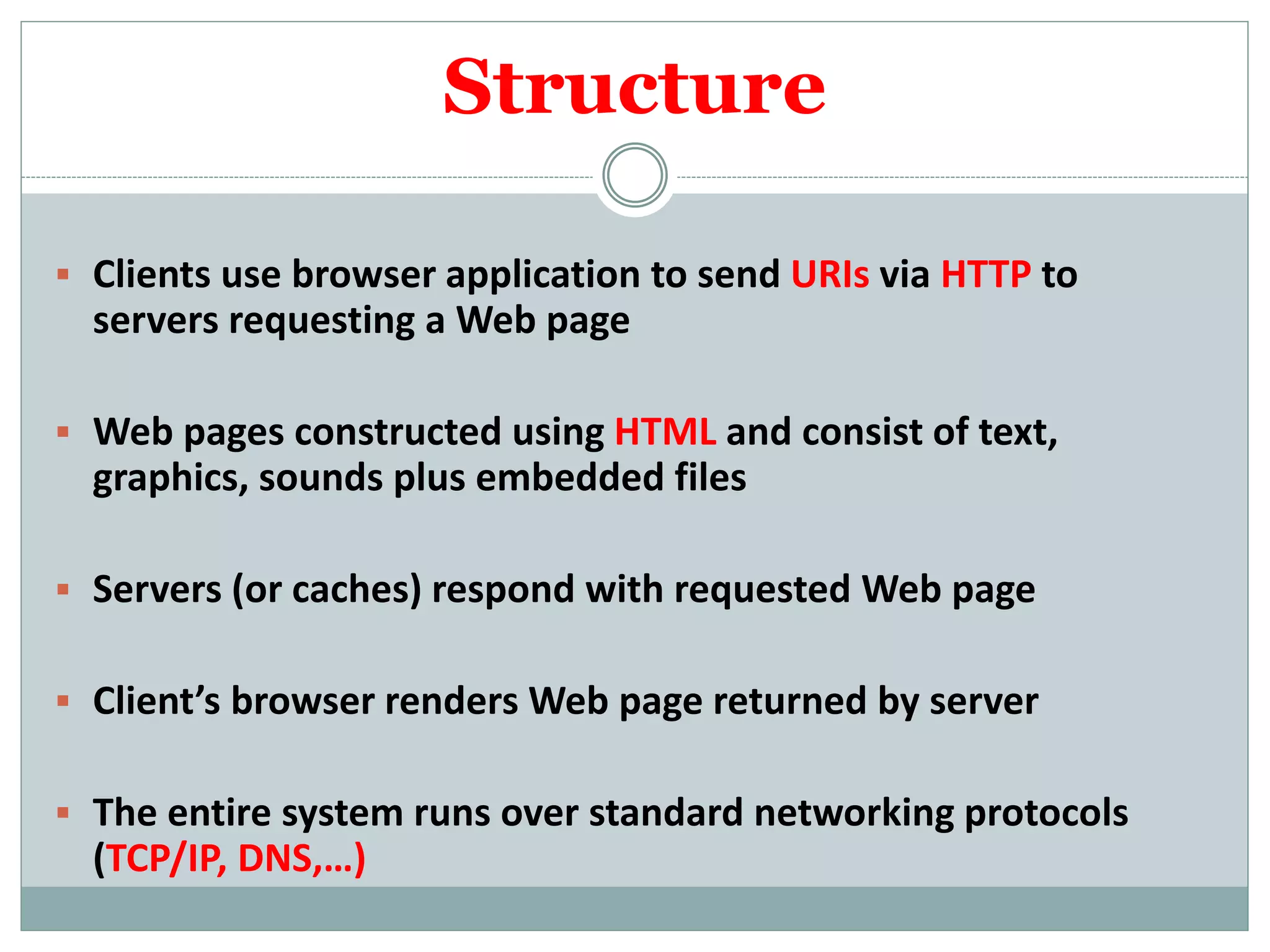
This presentation introduces the topic of the World Wide Web (WWW). It discusses that the WWW allows for the exchange of information between computers on the Internet using browsers. Key points include that Tim Berners-Lee invented the WWW in 1989 at CERN to allow for simultaneous transfer of text and graphics. The structure of the WWW involves clients using browsers to send requests via HTTP to servers, which respond with web pages rendered by the client's browser. Components include clients, servers, caches, protocols, HTML, URIs, and HTTP. The presentation concludes by noting the visionaries who created the early WWW.