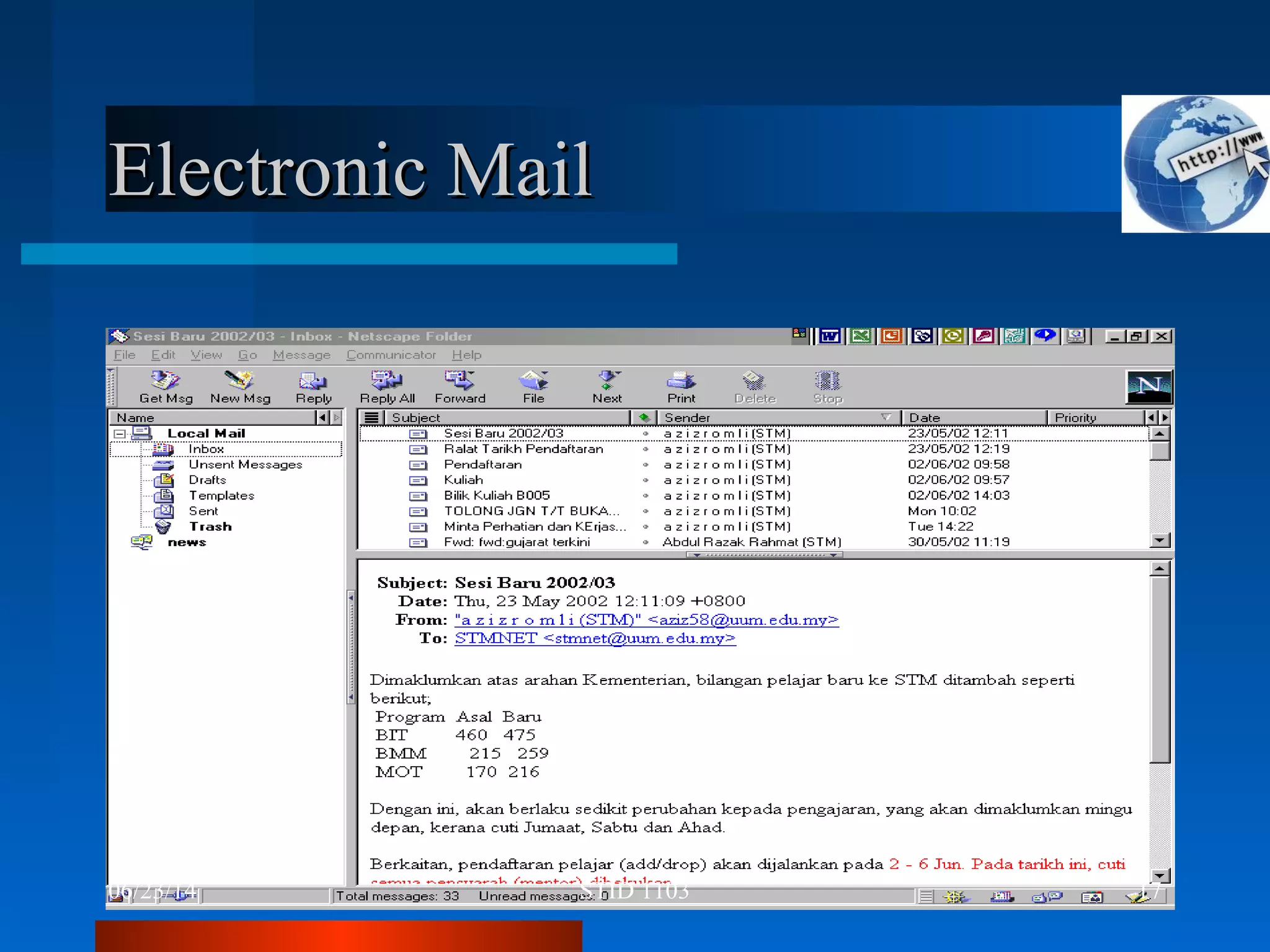
The document provides an overview of the internet, detailing its history, functionality, and various components such as web browsers and protocols. It discusses the advantages of the internet in communication, research, education, and financial transactions, while also highlighting the potential disadvantages like privacy theft, malware threats, and social isolation. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of using the internet effectively and understanding the challenges associated with it.