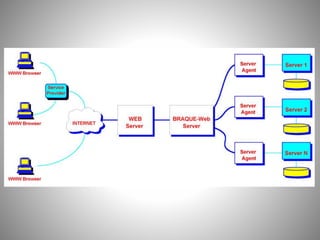
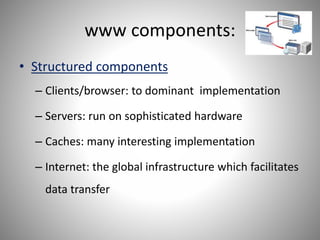
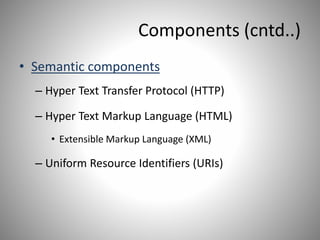
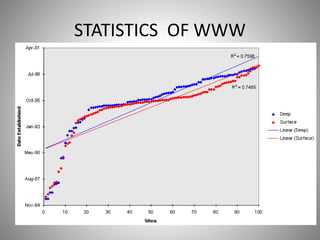
Tanvi Wadekar completed a 100-hour IT training course and project on the World Wide Web (WWW). The document defines WWW as an information system accessed via the internet that allows for the exchange of hypertext documents and other digital resources. It discusses the history of WWW, invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, and its key components like browsers, servers, caches, and protocols. The working of WWW involves connecting to a server via HTTP, requesting an HTML page, and receiving a response before closing the connection. Common elements on WWW are discussed like web pages, bookmarks, directories, sites and URLs. [/SUMMARY]