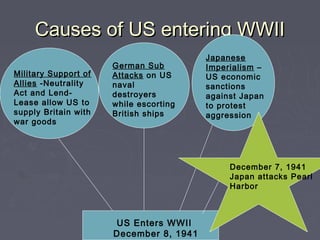
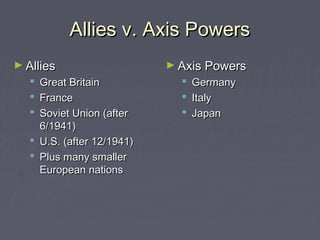
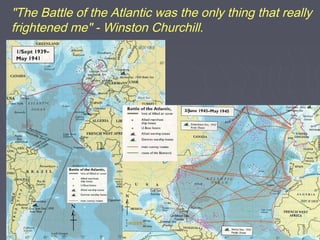
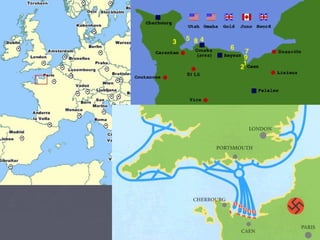
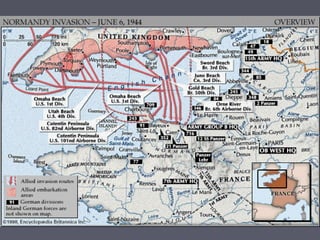
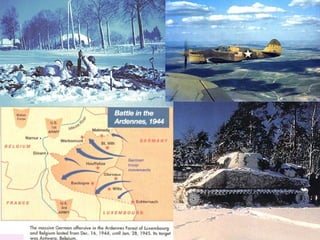
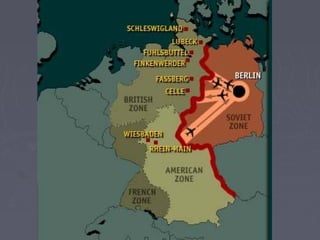
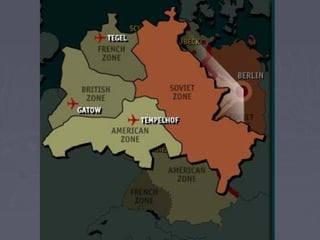
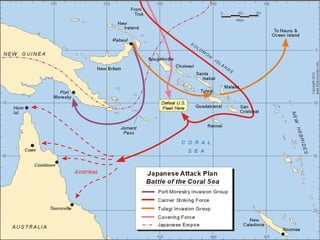
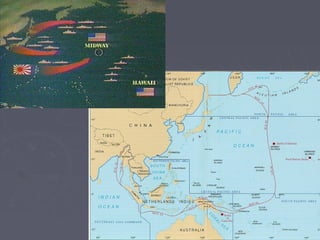
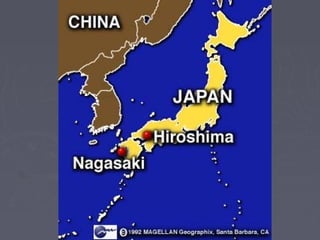
World War 2 began after Germany invaded Poland in 1939. The US initially remained neutral but entered the war after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941. Over the next several years, major battles were fought across Europe, North Africa, and the Pacific as the Allied forces that included the US, Britain, Soviet Union, and others battled the Axis powers of Germany, Italy, and Japan. The war concluded in 1945 with the Allied victories in Europe and the Pacific, including the US dropping atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki leading to Japan's surrender.