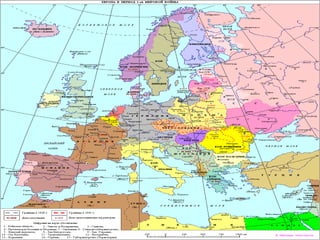
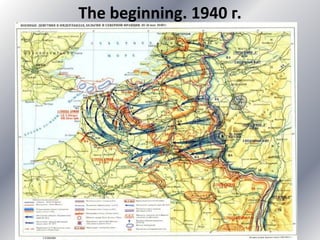
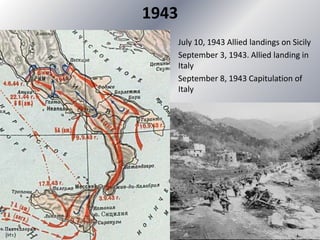
This document provides information about World War 2 from 1939 to 1945. It details the key dates and events of the war, including the countries involved on both the Allied and Axis sides. The document discusses the leaders of the major participating countries and outlines some of the major battles that took place over the six year period. It also describes the genocide committed by Nazi Germany, including the Holocaust that resulted in approximately six million Jewish deaths. The concluding sections discuss the consequences of the war, including the Nuremberg and Tokyo war crime tribunals held after the war.