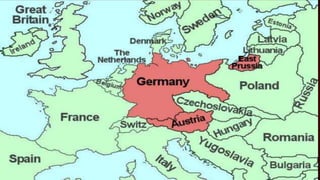
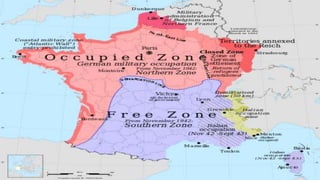
The document provides a detailed overview of the key events of World War II from 1939-1945. It describes how the political and economic instability in Germany following WWI led to the rise of Hitler and the Nazis. It then outlines Germany's aggression across Europe in the late 1930s that precipitated the start of WWII. The document discusses the major military campaigns and battles across Europe and in the Pacific theater between the Allied and Axis powers. It also describes the implementation of the Holocaust by Nazi Germany and its allies that resulted in the genocide of approximately 6 million European Jews.