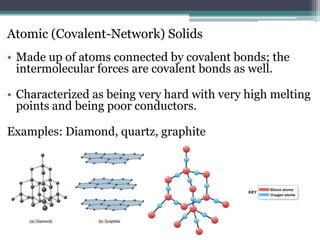
Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles that are tightly packed and not easily compressible. The particles vibrate about fixed positions and have strong intermolecular forces. At the melting point, vibrations overcome interactions holding particles in fixed positions, transforming the solid to a liquid. Sublimation is the direct transition from solid to gas without an intermediate liquid phase. Crystalline solids have an orderly repeating structure while amorphous solids lack order. Different types of crystalline solids include ionic held by electrostatic forces, molecular held by dispersion forces, and metallic held by delocalized electrons.