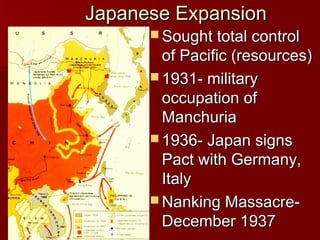
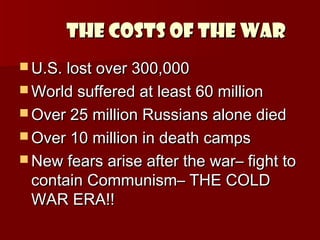
World War II was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved most of the world's nations who split into two military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. The war resulted in over 60 million casualties, including around 25 million Russian deaths. It ended in 1945 after the United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, prompting Japan's surrender. The war had enormous social and political consequences as it marked the end of fascism in Europe and the emergence of the Cold War between Western allies and the Soviet Union.