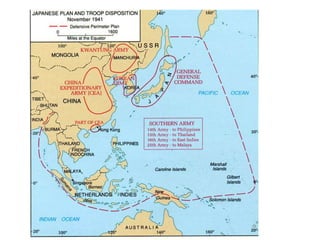
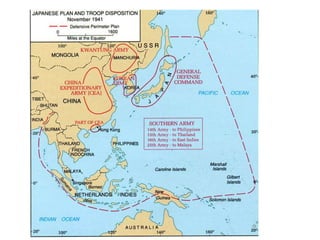
The Japanese attacked the Philippines hours after bombing Pearl Harbor. US forces under Douglas MacArthur retreated to Bataan Peninsula but later surrendered, resulting in the brutal Bataan Death March. The Doolittle Raids on Tokyo boosted American morale. The Battle of Midway was a major turning point, after which Japan was on the defensive. Manhattan Project scientists developed the atomic bomb, which the US dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, leading to Japan's surrender and the end of WWII.