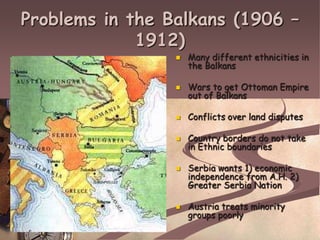
The document summarizes the key causes and events leading up to World War 1. Militarism and nationalism in European powers increased tensions, as did imperial and ethnic disputes in the Balkans. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand set off a chain reaction of diplomatic failures and military mobilizations that escalated into a continental war by August 1914. Major powers formed the Allied and Central Power alliances and fought brutal trench warfare for four years until Germany's defeat in November 1918. Over 10 million soldiers and civilians lost their lives making it one of the deadliest conflicts in history.