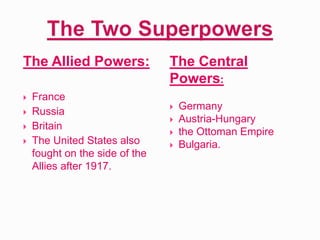
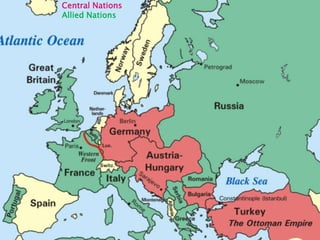
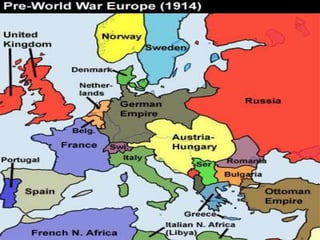
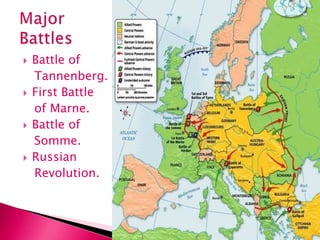
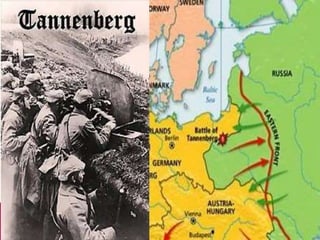
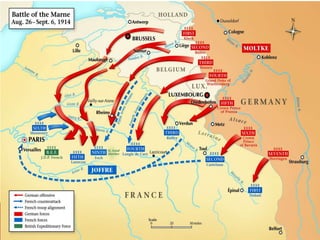
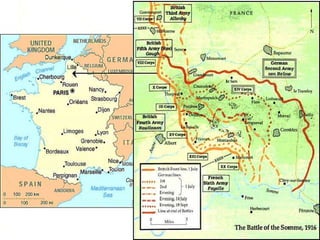
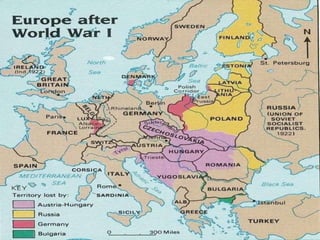
World War I, fought from July 28, 1914, to November 11, 1918, involved two main factions: the Allied Powers (including France, Russia, Britain, and the U.S.) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria). The war was primarily ignited by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and was characterized by intense nationalism, militarism, and an intricate system of alliances. The conflict concluded with the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed heavy reparations and territorial losses on Germany.