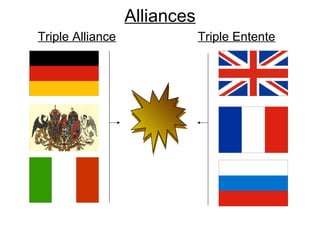
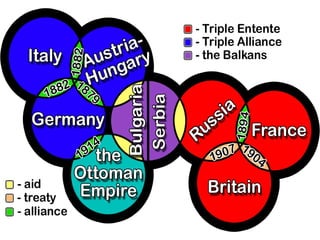
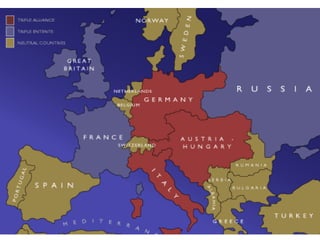
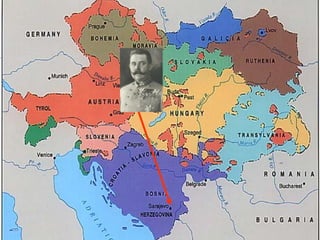
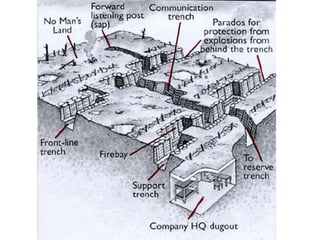
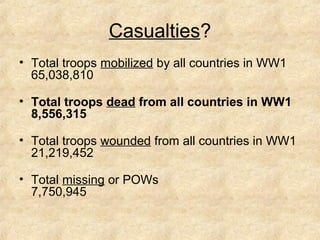
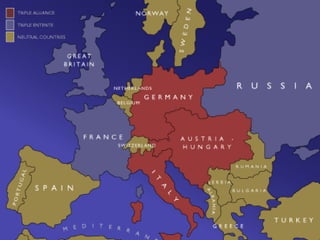
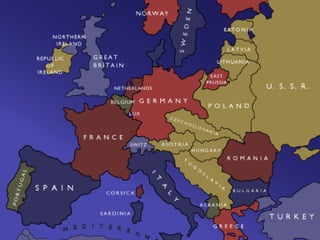
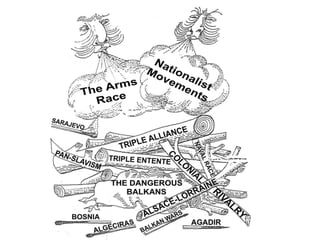
The document summarizes the key causes of World War 1, including militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism, and the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. It also discusses how new weapons like machine guns, poison gas, submarines, airplanes, and tanks led to stalemate trench warfare on the Western Front. The results of WWI included Germany's surrender, the Treaty of Versailles holding Germany responsible, reparations, and the formation of the League of Nations to prevent future wars. Total casualties from all countries exceeded 8.5 million deaths.