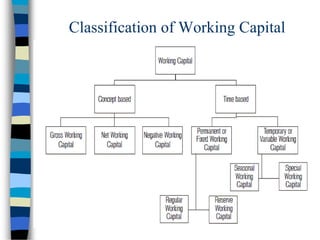
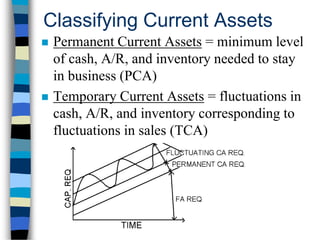
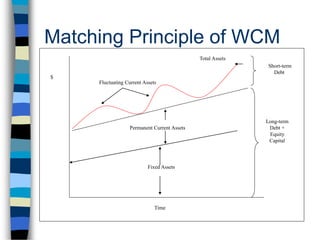
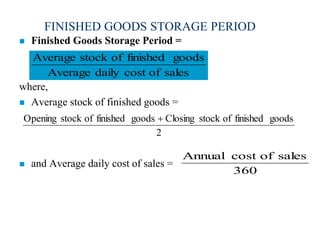
This document discusses working capital management. It defines working capital as a company's investment in short-term assets like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. It also defines concepts like gross working capital, net working capital, and operating cycle. The document emphasizes the importance of managing working capital and outlines different methods for estimating working capital needs. It also discusses the components of the operating cycle and how receivables and inventory are managed.