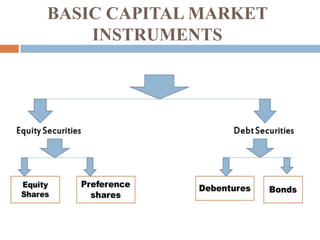
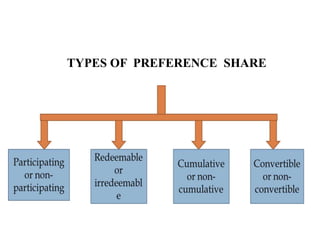
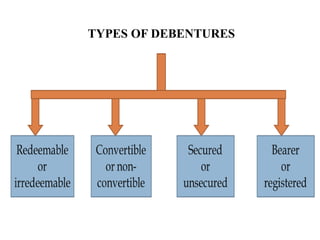
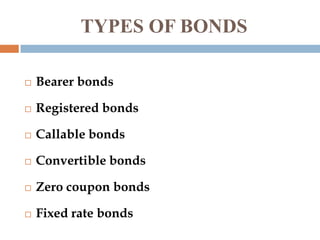
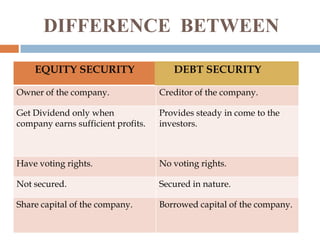
This document provides information about a student group project on capital market instruments. It includes the names and roll numbers of the group members, a table of contents for the project, and sections describing different capital market instruments like equity shares, preference shares, debentures, and bonds. It also discusses the differences between equity and debt securities and concludes that the capital market plays an important role in economic development.