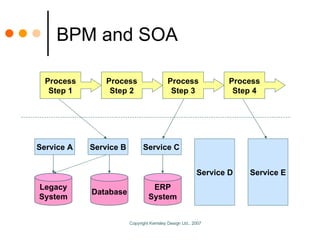
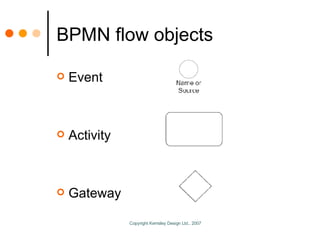
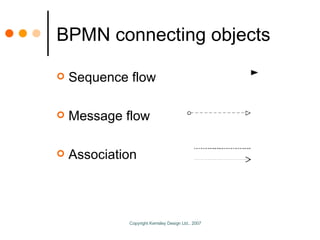
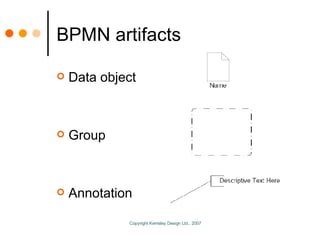
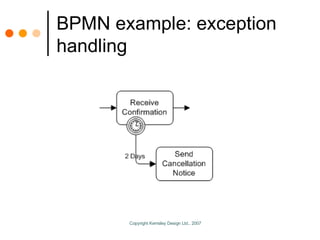
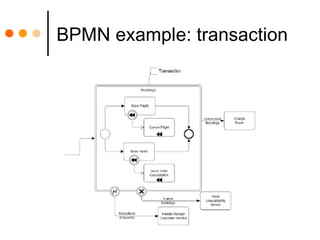
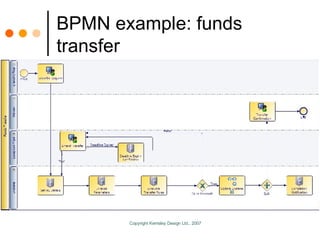
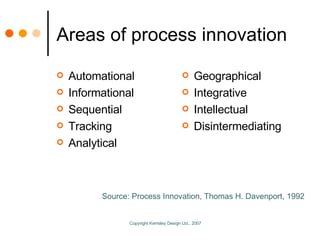
The document by Sandy Kemsley discusses business process modeling (BPM) and the integration of service-oriented architecture (SOA) to enhance organizational efficiency and adaptability. It outlines the importance of utilizing BPMN standards for effective communication of processes, the potential ROI from process innovation, and the implications of BPM on job roles and organizational change. The document emphasizes the collaborative nature of BPM and SOA in orchestrating business processes while addressing common challenges and strategies for successful implementation.