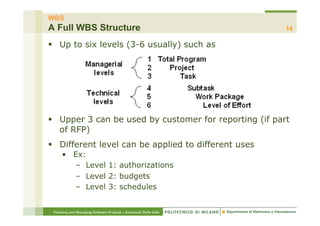
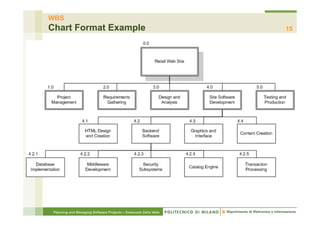
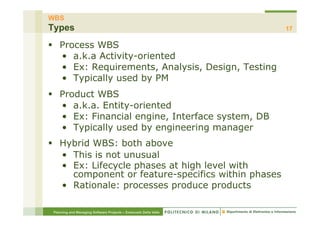
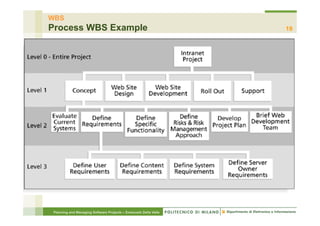
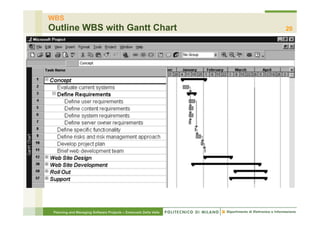
The document focuses on planning and managing software projects, specifically highlighting the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) as a crucial tool for project organization and management. It covers project phases, estimation processes, and scheduling techniques, emphasizing the importance of breaking down projects into manageable tasks to improve planning accuracy. Additionally, the document outlines various WBS types, techniques for creating a WBS, and guidelines for effective project management.