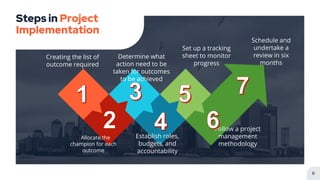
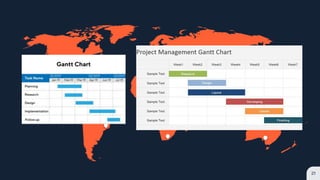
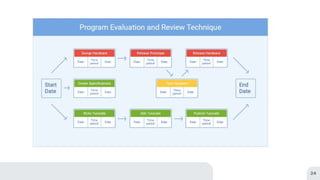
This document discusses project implementation and provides guidance on planning and tracking a project implementation plan. It begins by defining project implementation as putting plans and visions into action. It then lists the purposes of implementation as putting the action plan into operation, delivering results to achieve objectives, managing resources efficiently, and monitoring and reporting progress. Several key steps for implementation planning are outlined, including creating a list of required outcomes, allocating champions for each outcome, determining necessary actions, establishing roles and accountability, setting up a tracking sheet, following a project management methodology, and scheduling reviews. Common project implementation tracking methods like Gantt charts, critical path methods, and PERT charts are also summarized.