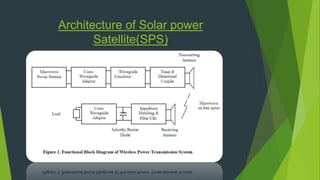
This document discusses wireless power transmission (WPT) and compares microwave and laser transmission methods. It describes how a rectenna works to receive microwaves with 85% efficiency within 5km. Solar power satellites that transmit power via microwaves from space are also discussed, including their advantages over earth-based solar like constant sunlight. Current development of a low-cost Japanese demonstration project by 2025 and potential applications of WPT like electric vehicles are mentioned.