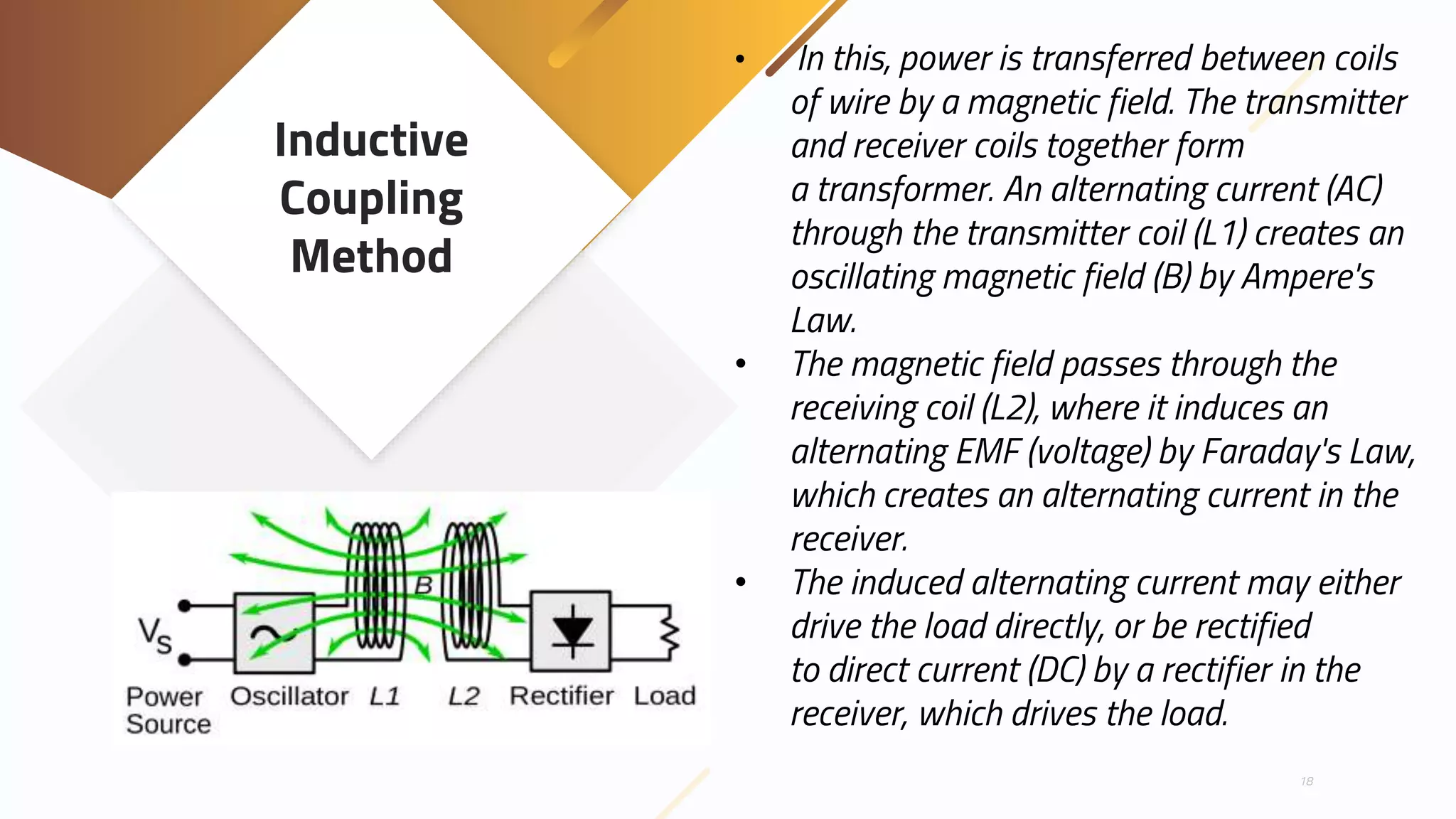
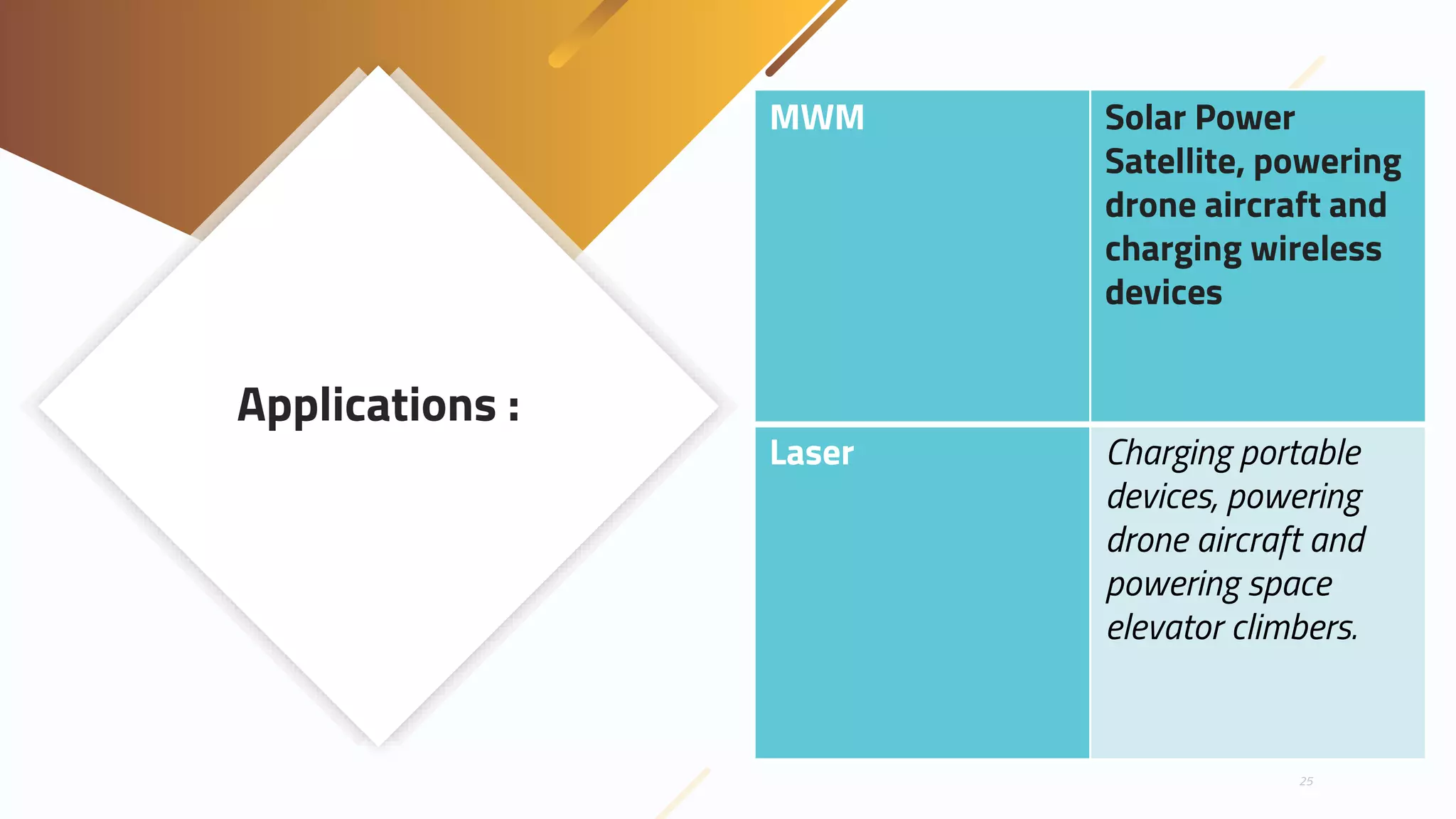
Wireless power transmission involves transmitting electrical energy through electromagnetic fields without physical connections like wires. It has been researched since the 1890s but challenges remain. Methods include resonant inductive coupling using coils, capacitive coupling using plates, and far-field radiation techniques like microwaves and lasers. Advantages are eliminating wires and losses but disadvantages include inefficiency, safety concerns, and distance limitations. Current applications include wireless phone charging and advances aim to make wireless power transfer more efficient and practical over longer ranges.