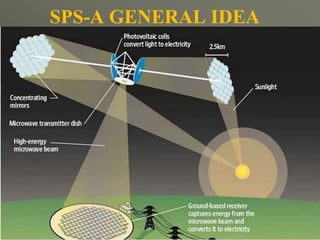
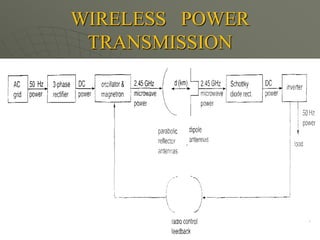
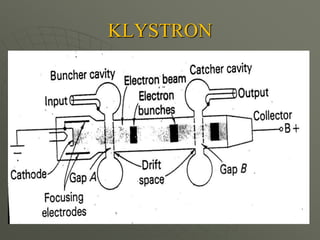
The document presents a technical seminar on solar power satellites (SPS), detailing their function of capturing solar energy in geosynchronous orbit and transmitting it via microwave to Earth. It discusses the advantages of SPS such as constant solar exposure and energy availability while addressing challenges like high costs and radiation hazards. Recent developments in Japan's efforts to create demonstration satellites are highlighted, emphasizing the potential and obstacles for SPS in energy technology.









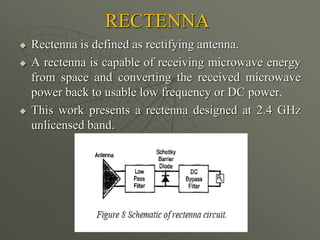
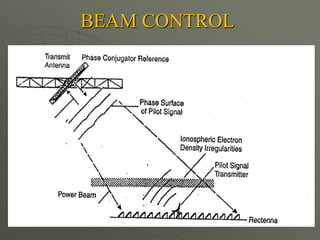


![ADVANTAGES
The full solar irradiation would be available at all times expect
when the sun is eclipsed by the earth.
The power could be directed to any point on the earth’s
surface.
The zero gravity and high vacuum condition in space would
allow much lighter, low maintenance structures and collectors
[14].
The power density would be uninterrupted by darkness,
clouds, or precipitation, which are the problems encountered
with earth based solar arrays.
The realization of the SPS concept holds great promises for
solving energy crisis
No moving parts & also No fuel required.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2gb19me4041-230407045456-e228e8c2/85/2GB19ME404-1-ppt-18-320.jpg)



