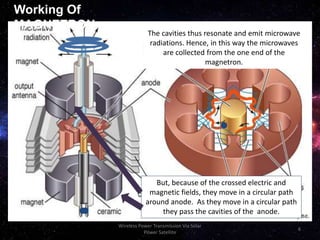
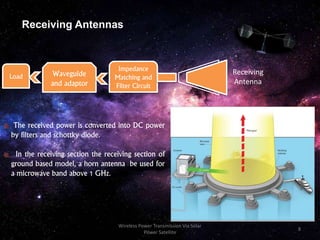
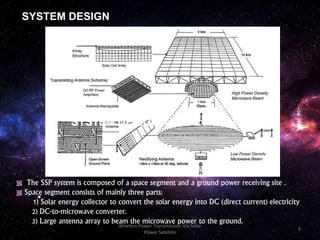
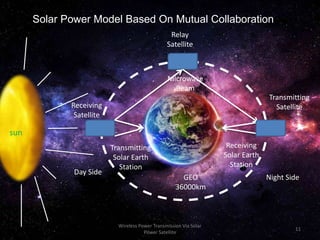
The document discusses the concept of wireless power transmission via solar power satellites (SPS), highlighting its technologies, advantages, and future potential. It describes how SPS can efficiently generate and transmit energy from space to Earth, emphasizing reduced emissions and operational costs compared to traditional energy methods. Despite challenges like biological effects from microwave transmission and high initial costs, the potential for significant energy generation positions SPS as an attractive future technology.













![Wireless Power Transmission Via Solar
Power Satellite
18
REFERENCES
[1] A. A. Nimje, S. M. Ali, “Solar Power Connectivity
Using Transmission Superhighway: Smart Grid”,
International Congress on Renewable Energy,
2010 [ICORE 2010], Tradeshow, Chandigarh,
India, 01-03 December 2010.
[2] “www.cea.nic.in/reports/yearly/lgbr_report.pdf”,
Central Electricity Authority of India.
[3] Geoffrey A. Landis, “Solar Power from Space:
Separating Speculation from Reality” XXIth Space
Photovoltaic
Research and Technology Conference (SPRAT-
2009), Cleveland, OH, October 6-8 2009.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wireless-power-transmission-using-microwave-150828030453-lva1-app6891/85/Wireless-power-transmission-using-microwave-18-320.jpg)