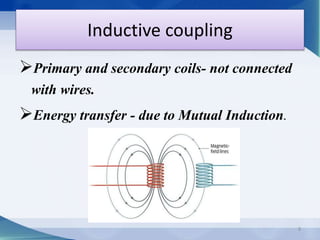
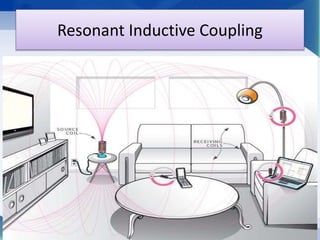
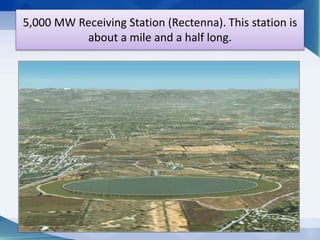
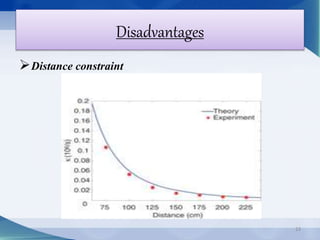
Nikola Tesla proposed wireless power transmission in 1899 and successfully lit over 200 lamps from over 40 km away in his Colorado Springs experiment using resonant induction and high frequency currents transmitted through the ground. In 2007, MIT engineers revived interest in wireless power by demonstrating resonant inductive coupling to transmit 60W of power over 2 meters without wires. Wireless power transmission systems use techniques like inductive coupling, resonant inductive coupling, microwave power transmission, and laser power transmission to transfer energy through the air or ground without wires. Potential applications include wirelessly charging electric vehicles and powering devices without plugging them in.