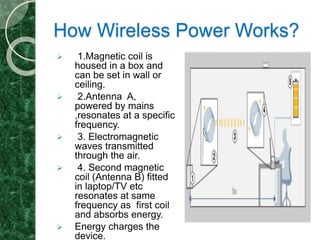
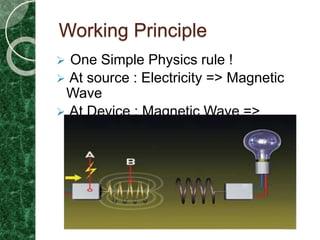
Wireless power transmission involves transmitting electric power through the air without wires. In 1899, Nikola Tesla proposed a method of wireless power but achieved only 15% efficiency due to using radiative transmission. In 2007, MIT engineers developed a method using resonant induction that powered a 60W lightbulb from 7 feet away at 40% efficiency, demonstrating practical wireless power transfer. Wireless power works by powering a magnetic coil that transmits electromagnetic waves to a receiving coil which absorbs the energy and uses it to charge a device. While wireless power eliminates wires, its range is limited to a few meters and efficiency is around 40%.