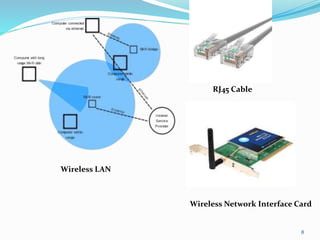
The document outlines a group presentation on networking, specifically focusing on wireless networking, its types, requirements, and technologies. It covers the characteristics of wireless LAN, MAN, WAN, and PAN, along with security measures and IEEE standards for wireless networks. Key technologies such as RF signals, Wi-Fi, and cellular generations (2G to 4G) are discussed, emphasizing the advantages and drawbacks of wireless networks.