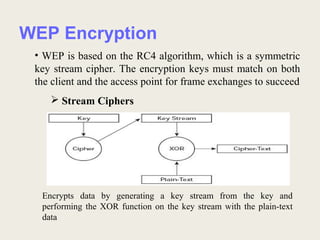
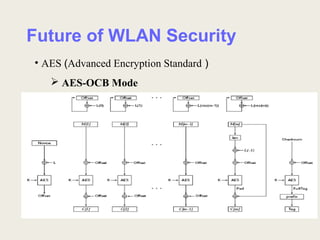
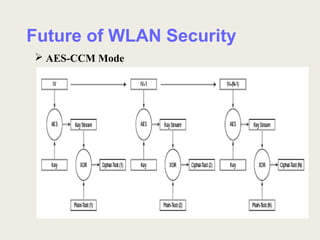
This document discusses security issues and solutions for wireless LANs (WLANs). It outlines vulnerabilities in common WLAN authentication and encryption standards like open authentication and WEP. Specifically, it notes that open authentication provides no validation of clients and that WEP encryption can be cracked with statistical analysis of packets. The document then presents improvements like 802.1X/EAP authentication and dynamic WEP keys to address these issues. Finally, it recommends the AES encryption standard as a more robust solution and emphasizes that WLAN deployments should implement security features to the fullest extent possible given device limitations.