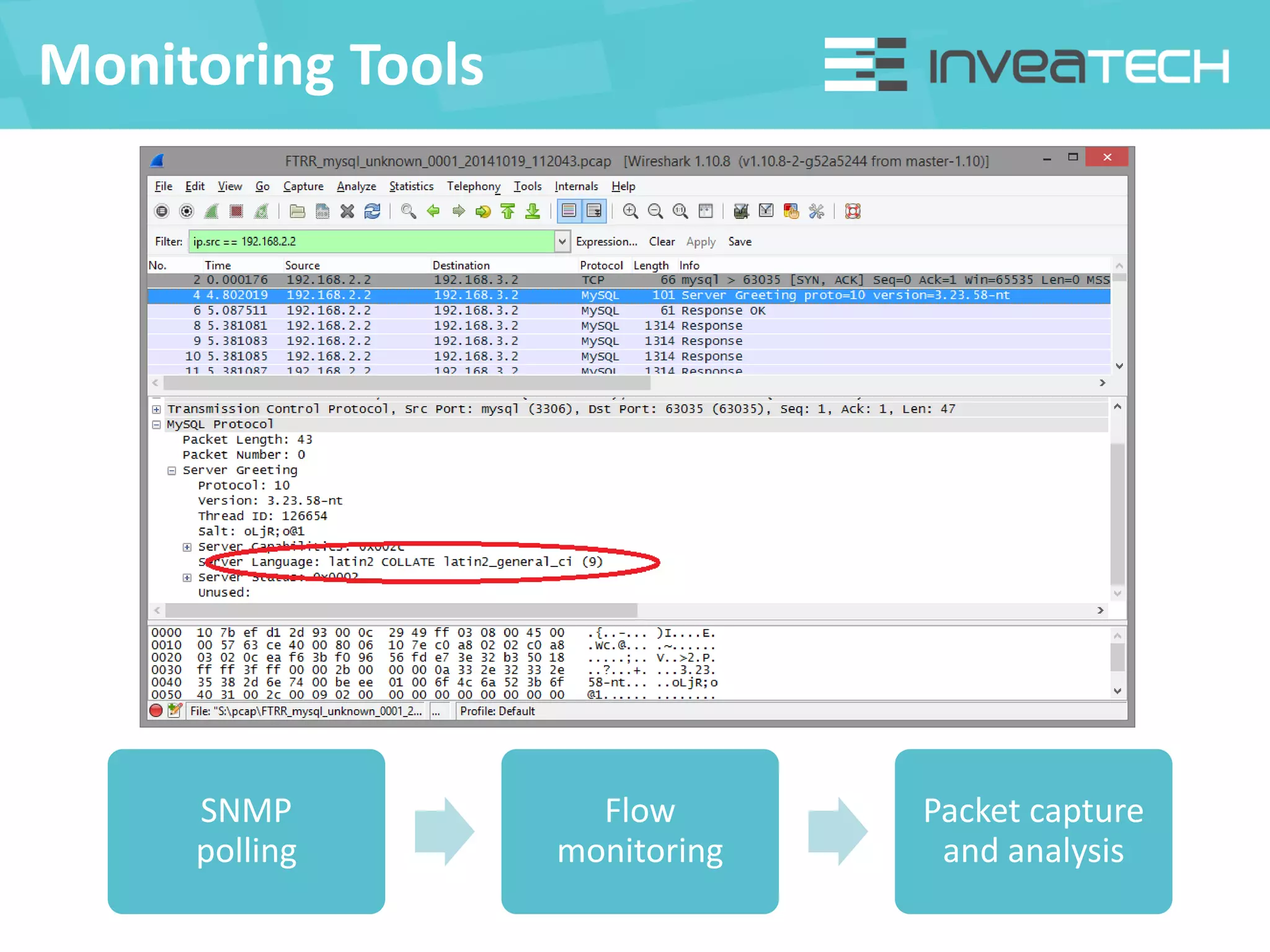
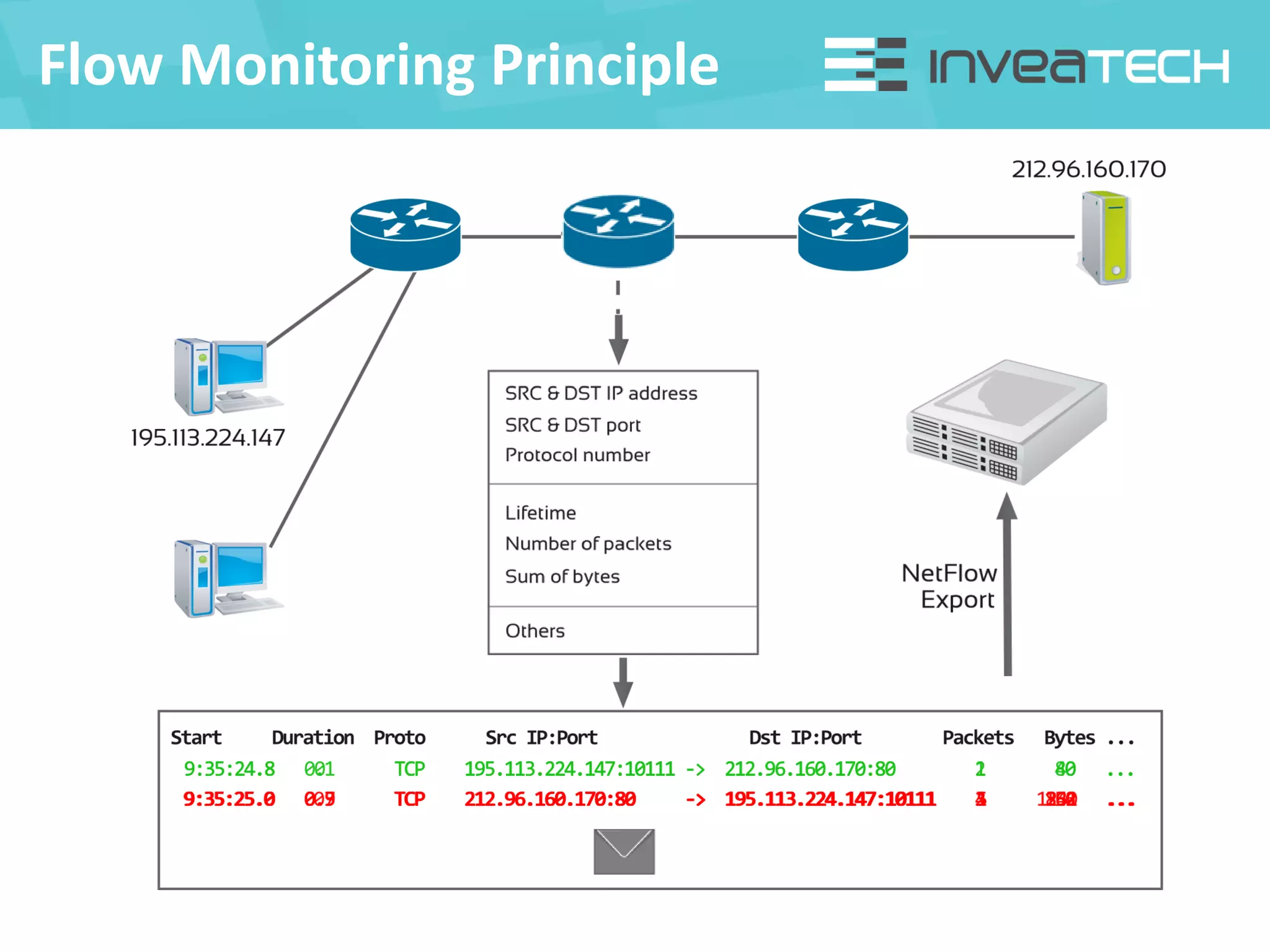
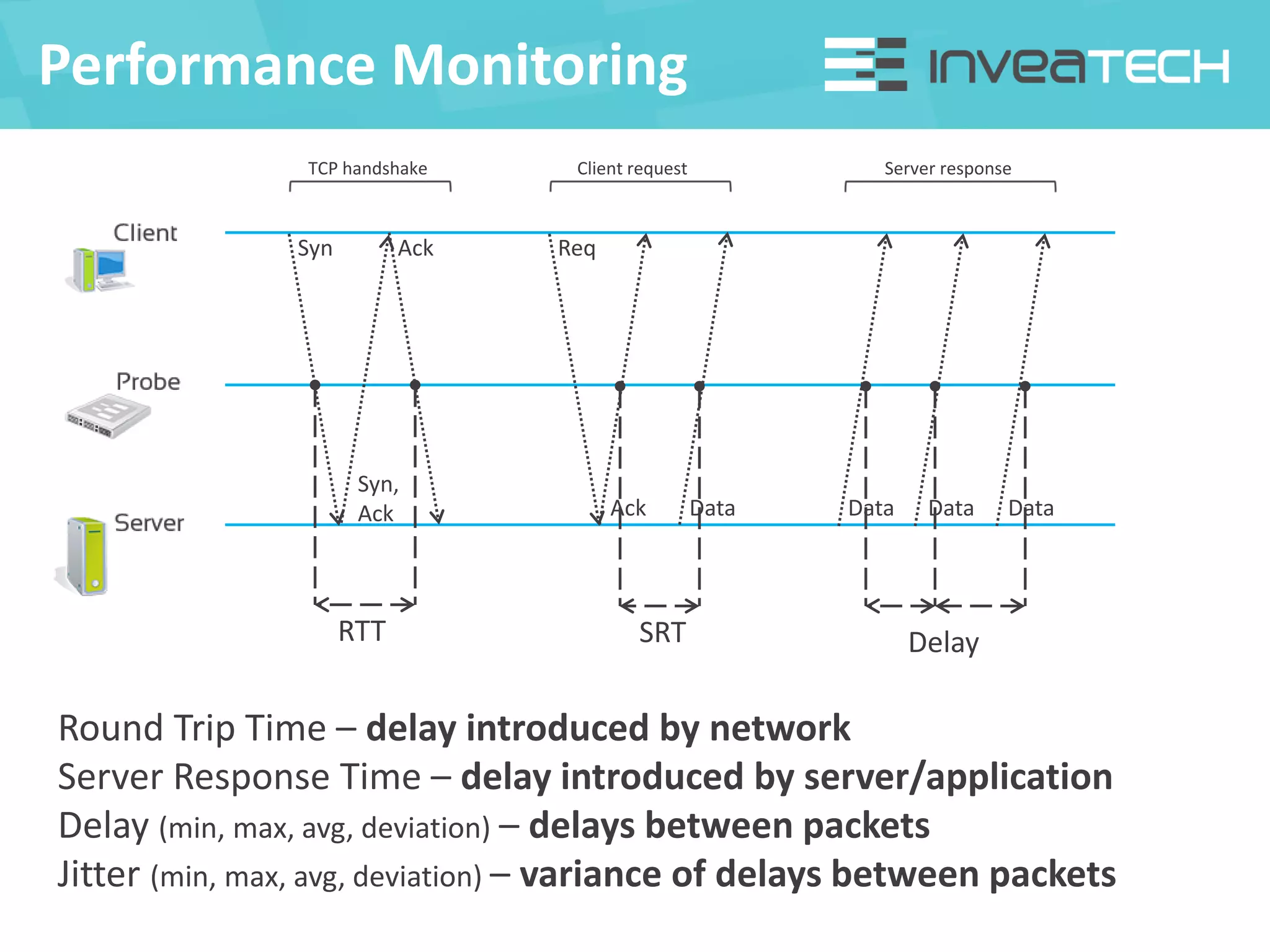
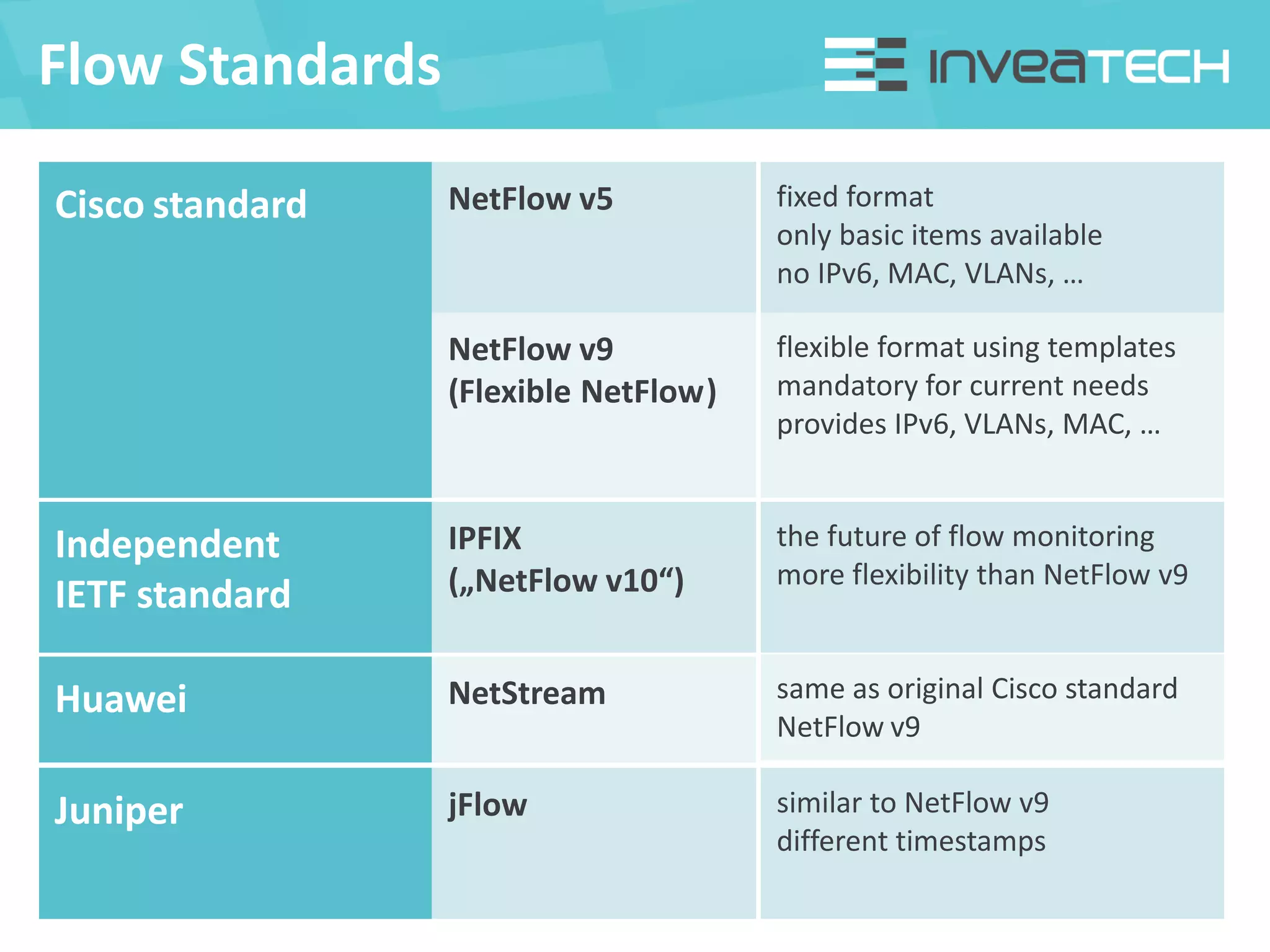
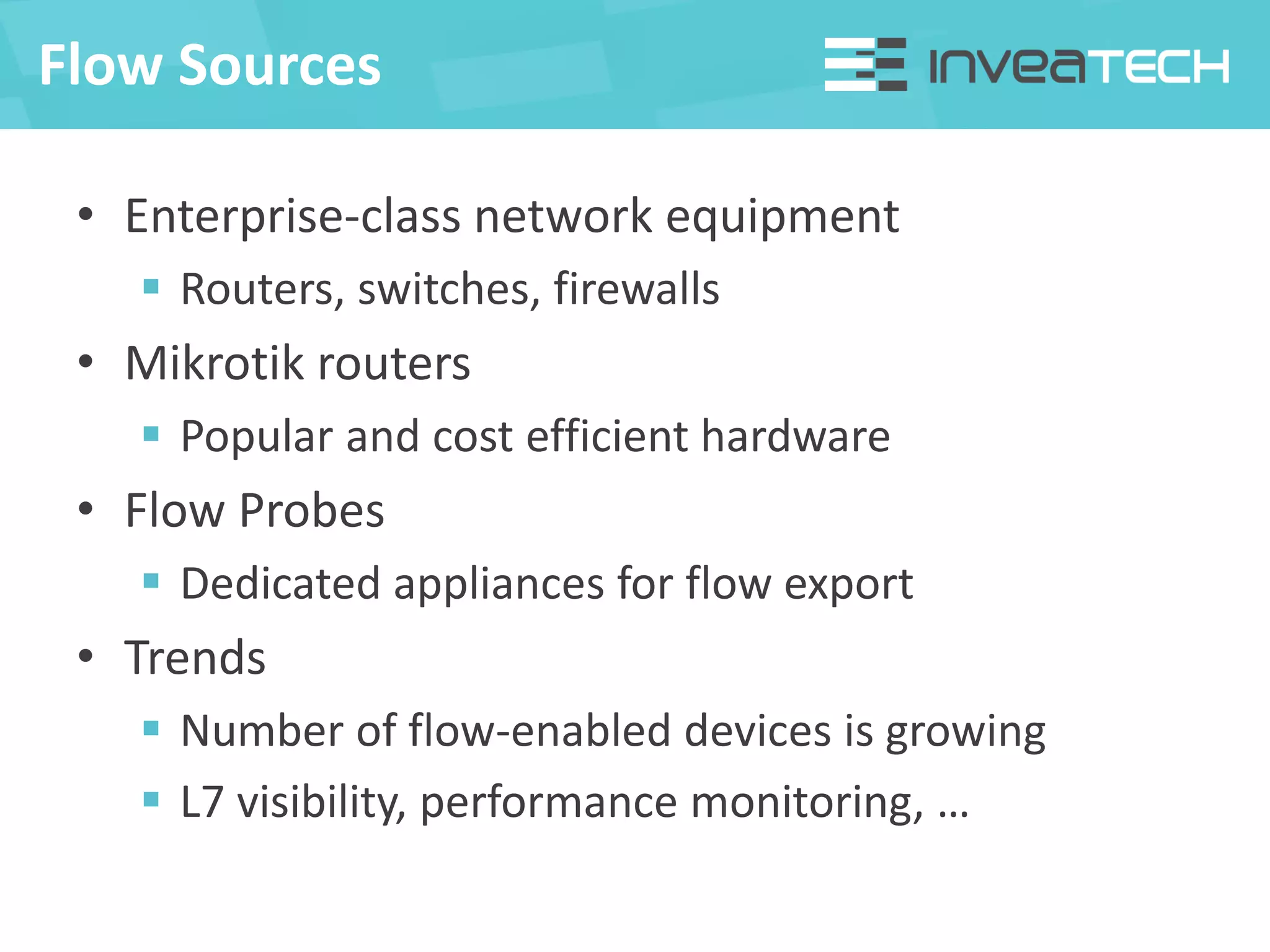
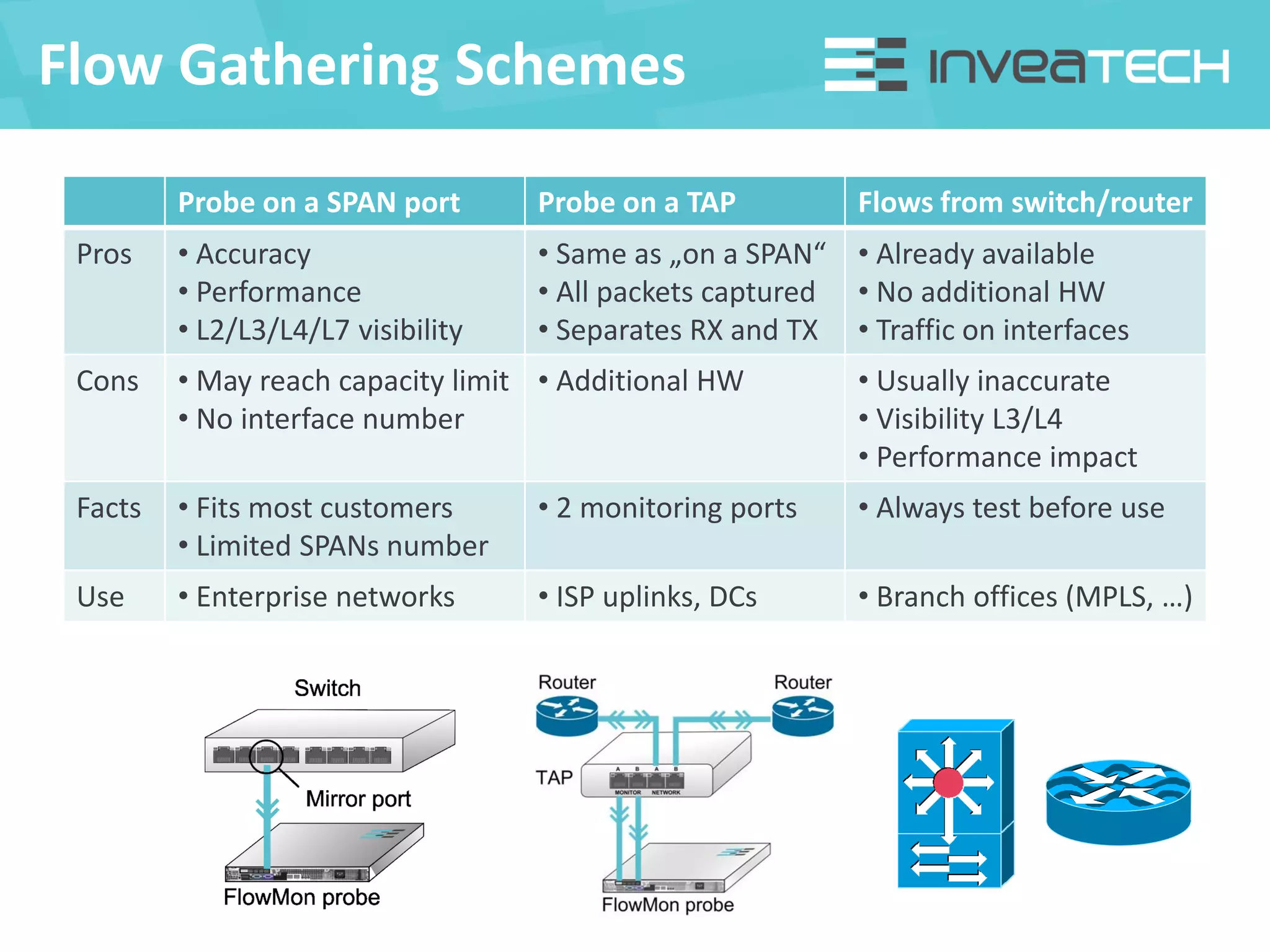
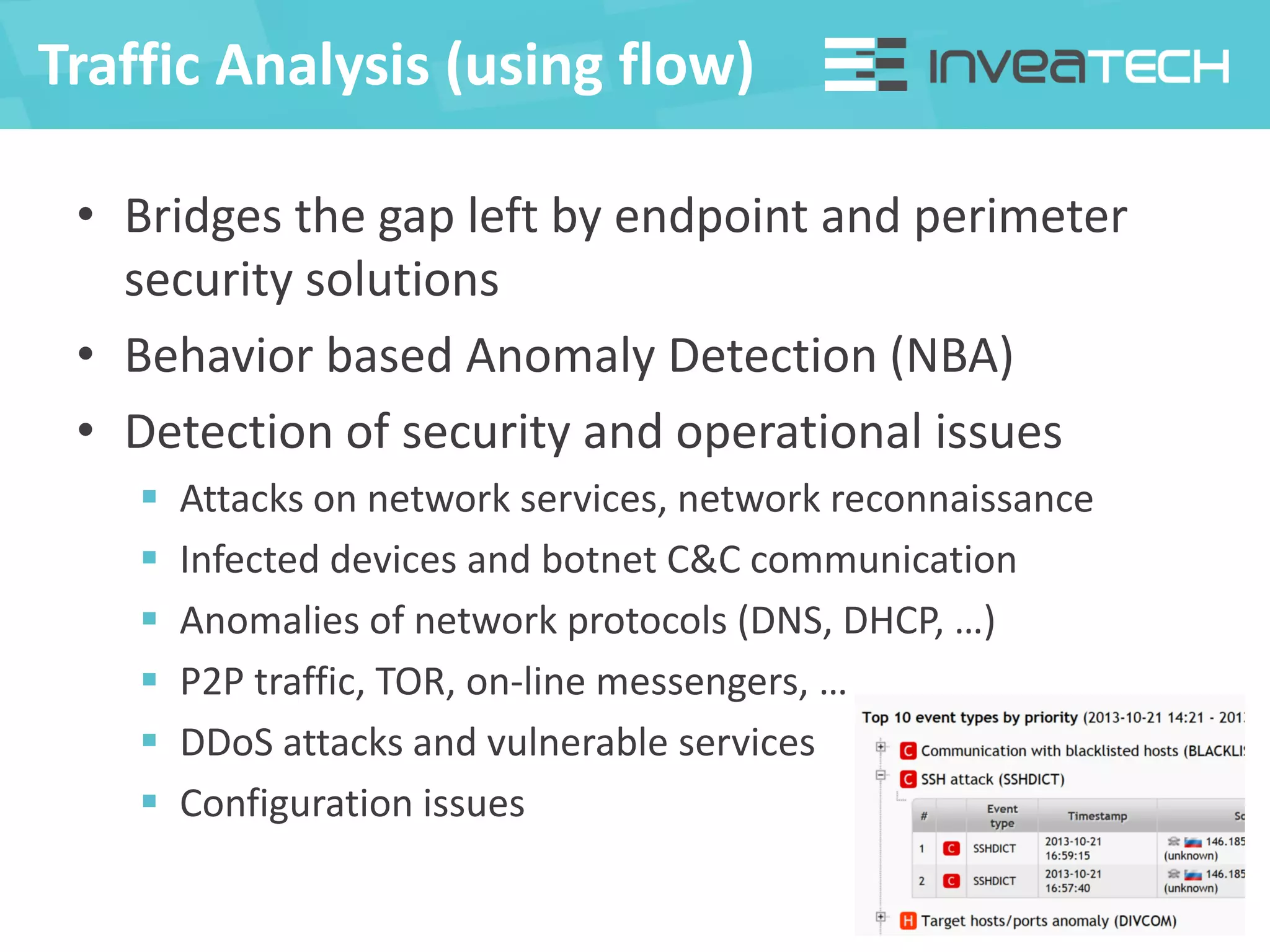
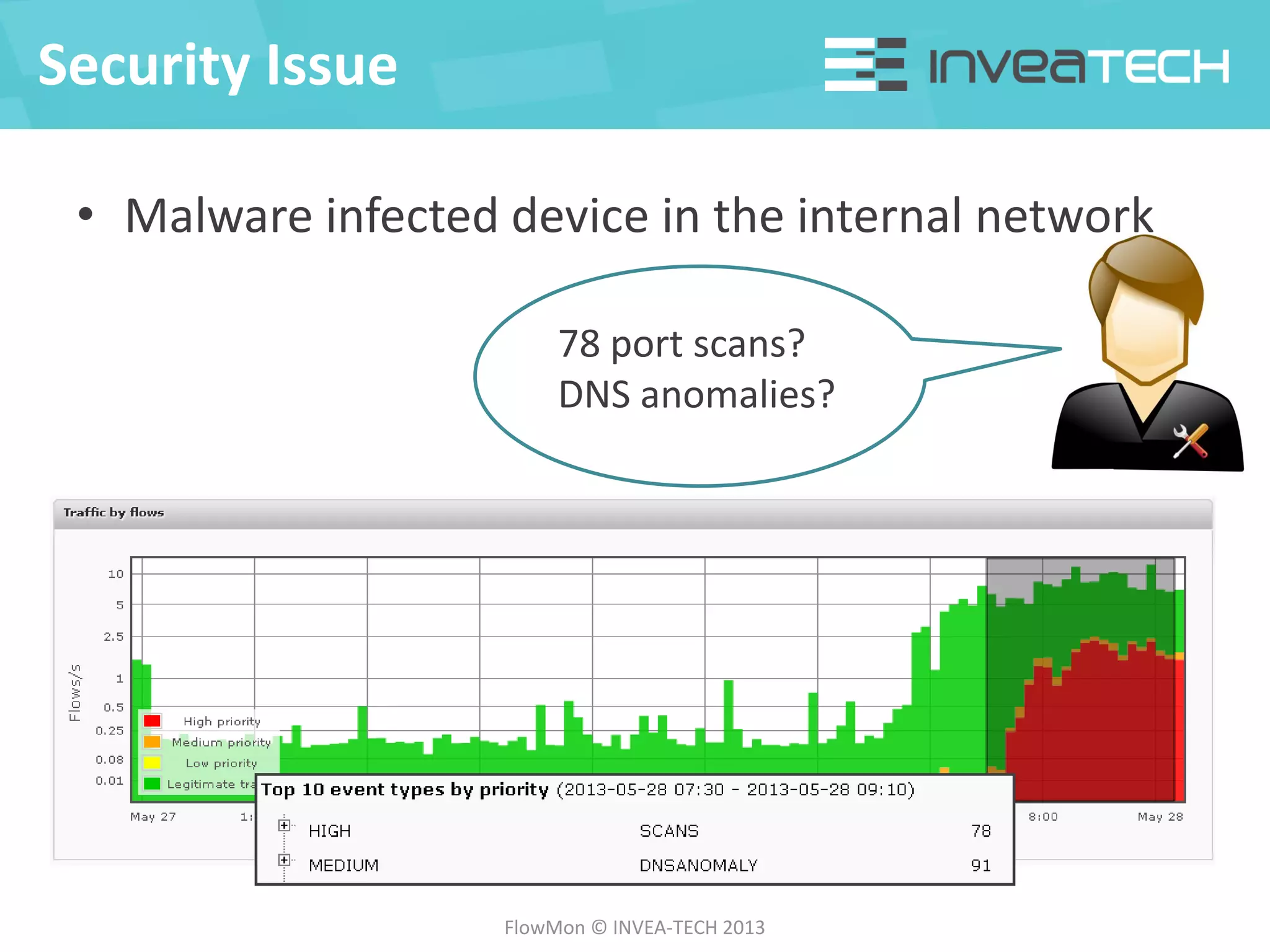
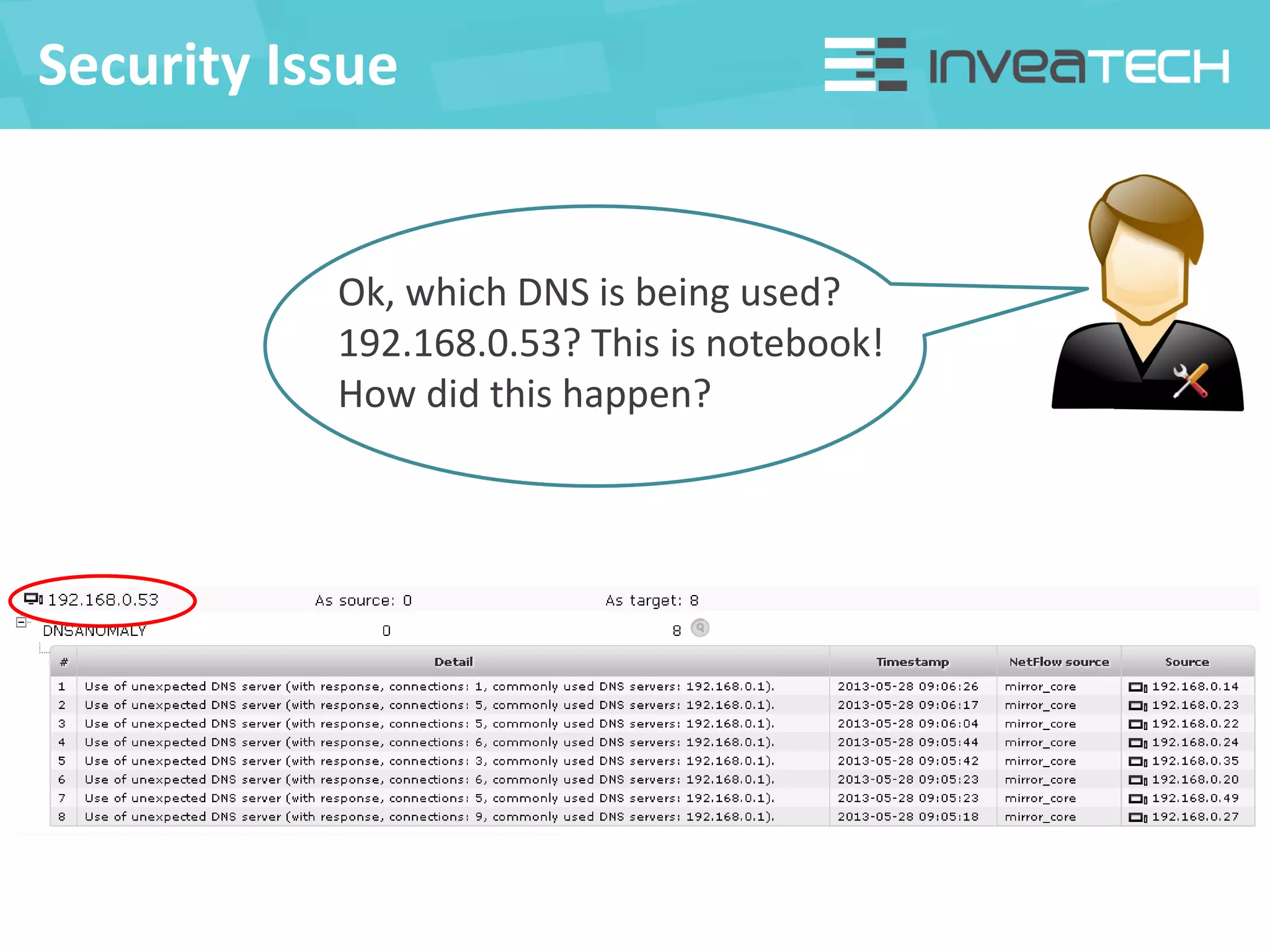
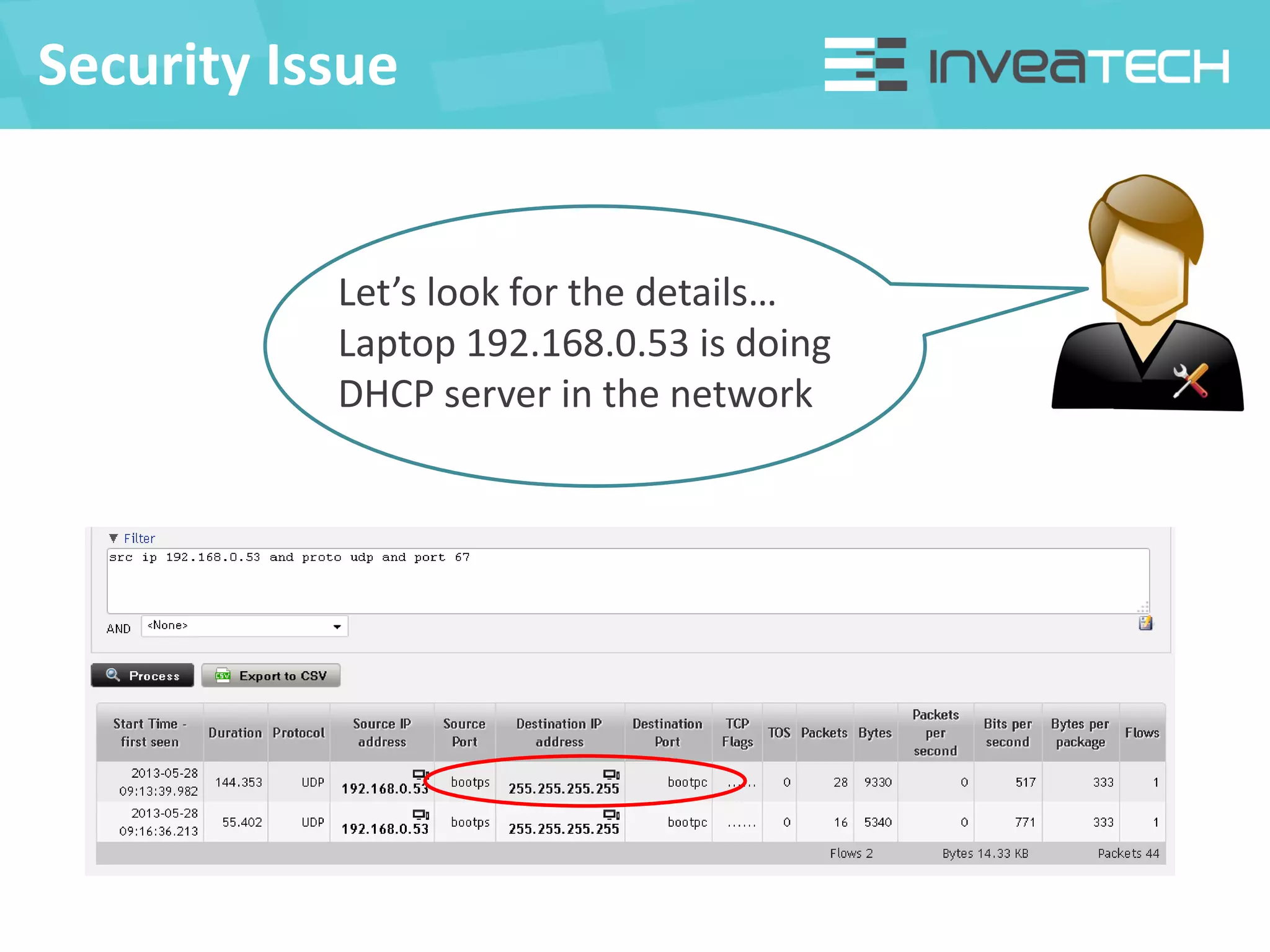
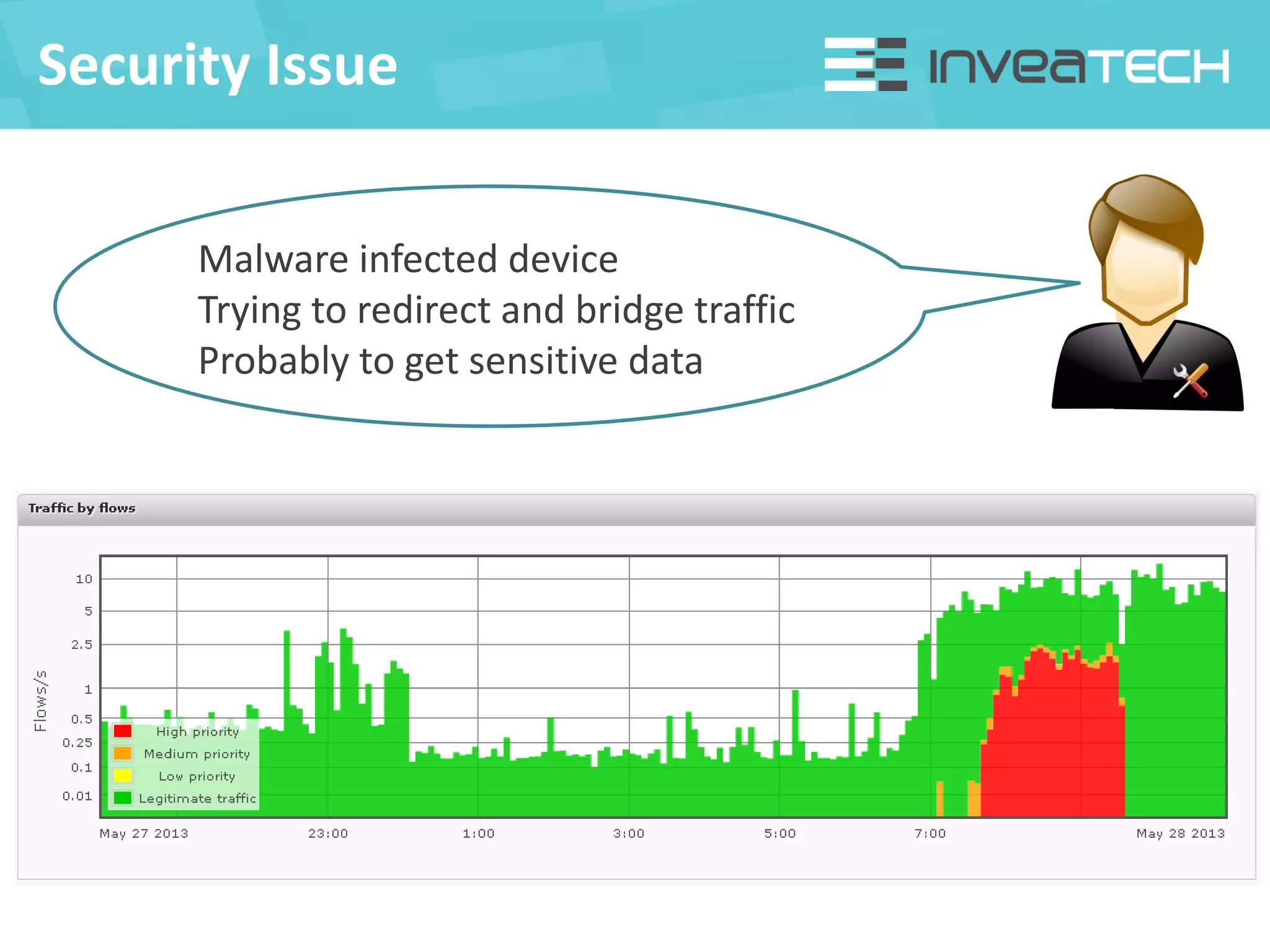
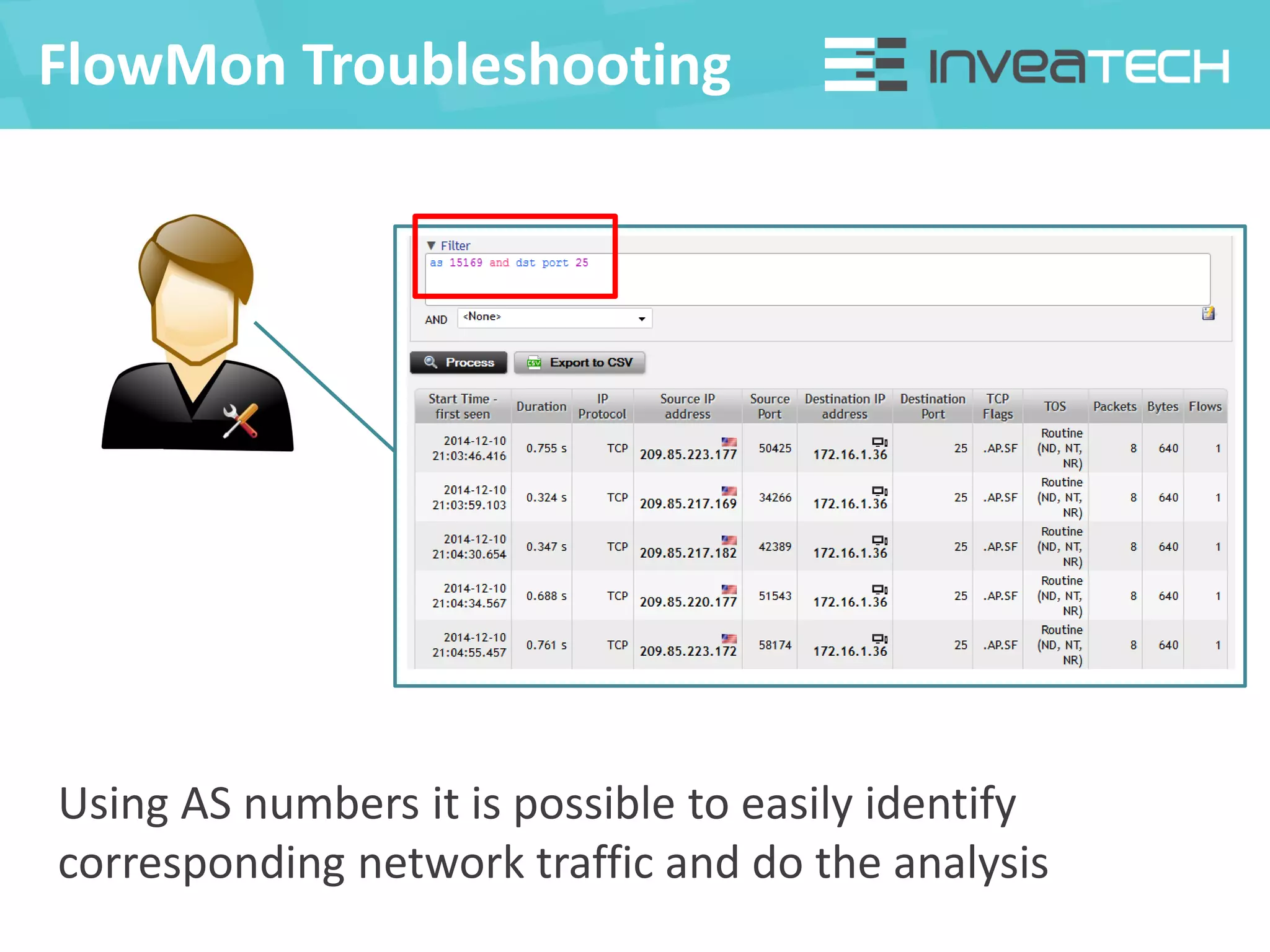
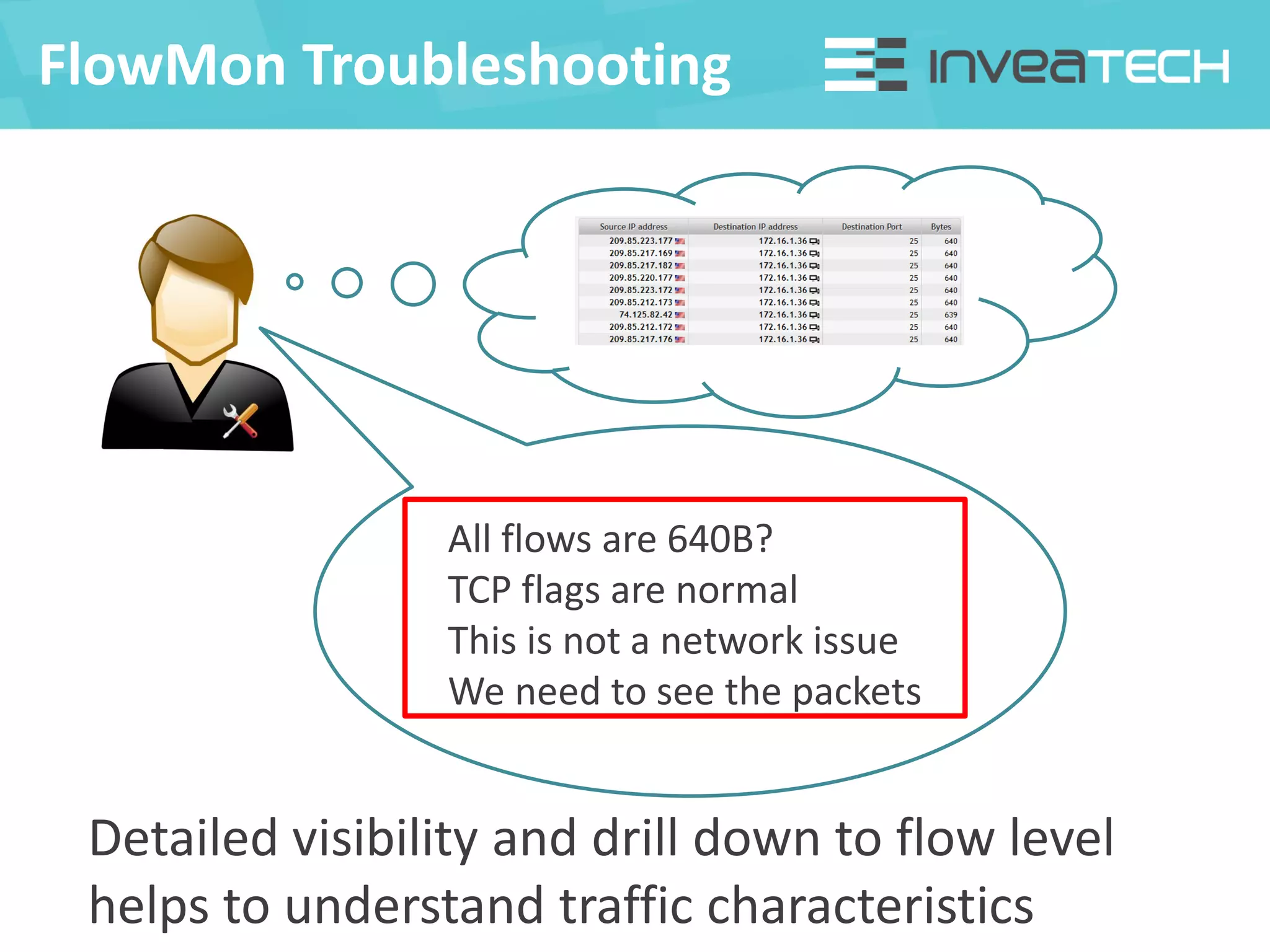
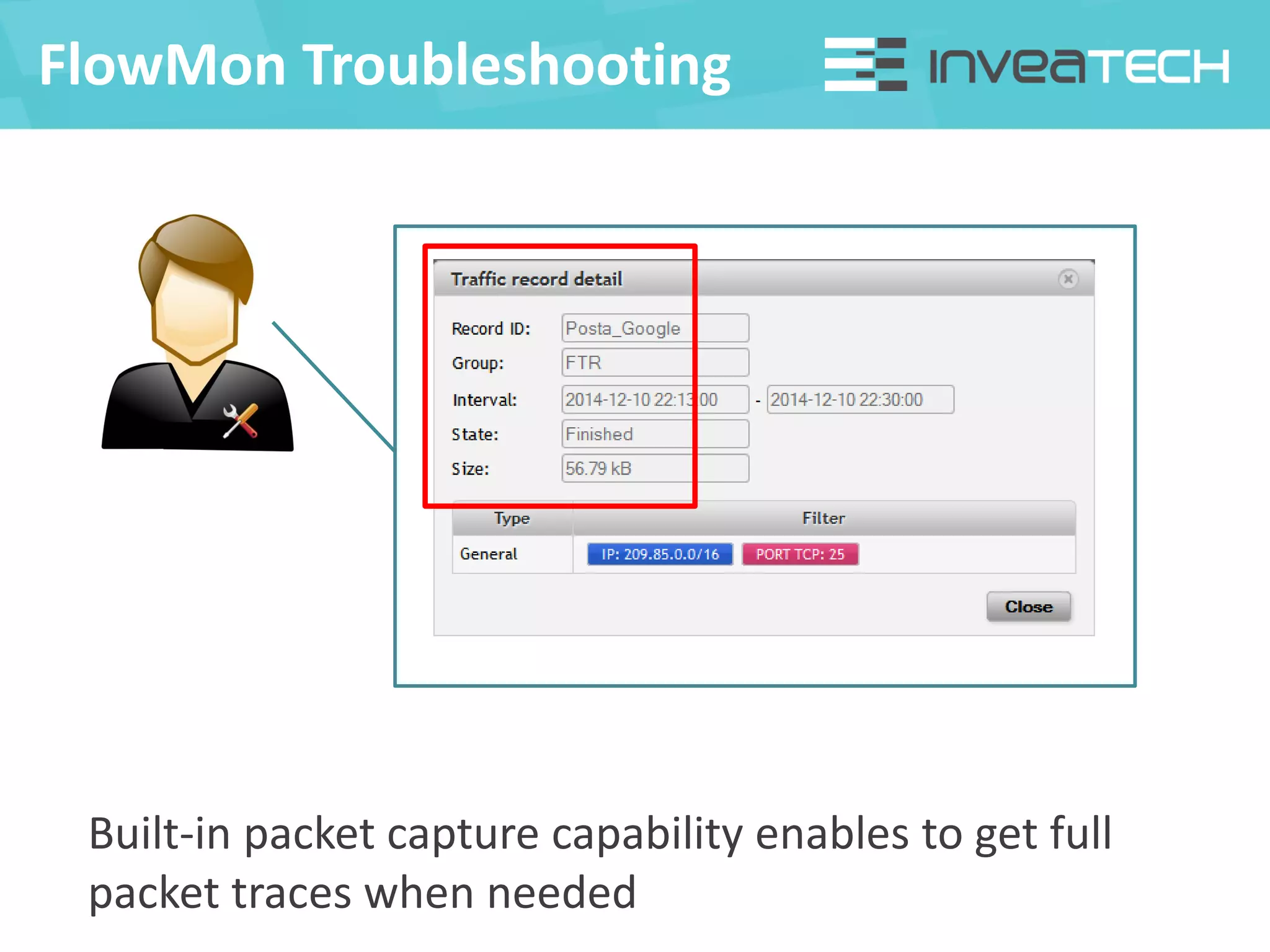
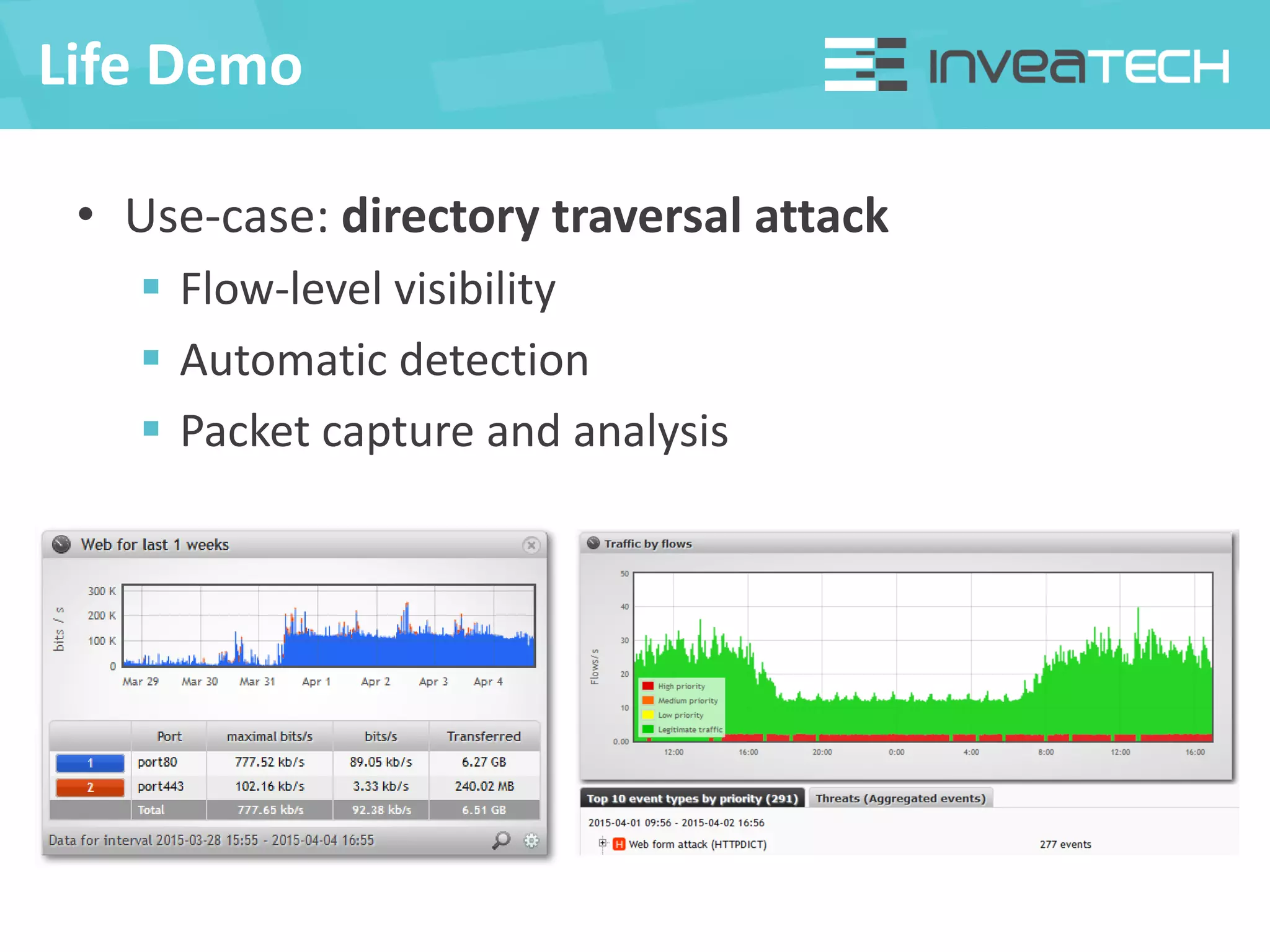
This document summarizes a presentation about network traffic monitoring and analysis. It discusses traditional monitoring tools like SNMP and newer tools that provide deeper traffic visibility. It explains how flow monitoring works and standards like NetFlow. The presentation also demonstrates how tools can analyze flow data to detect security issues, troubleshoot problems, and capture packets for forensic analysis. Real examples are shown of using these techniques to identify a malware infection and resolve a email delivery problem.