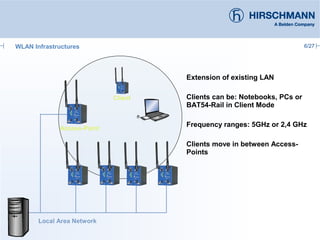
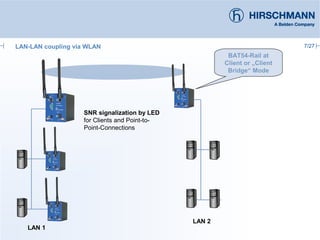
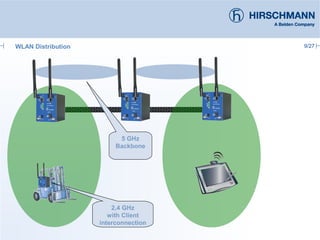
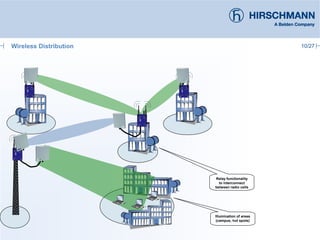
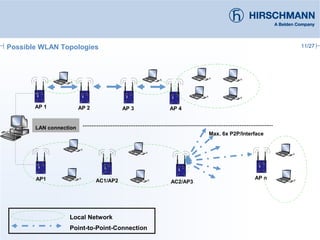
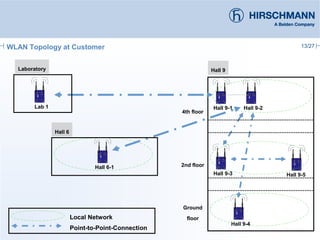
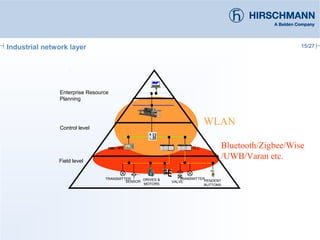
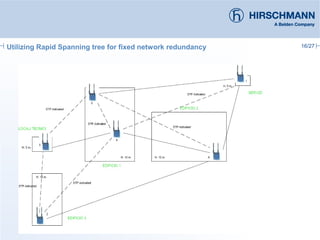
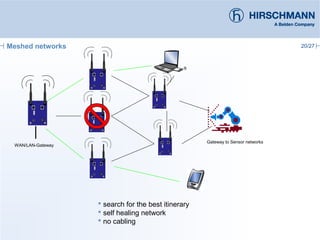
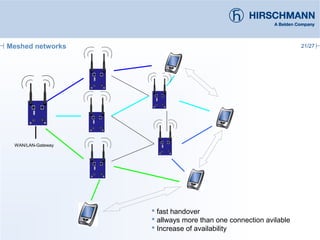
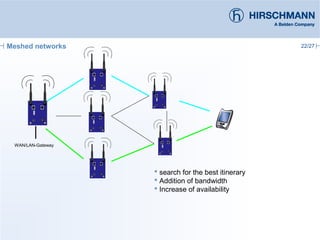
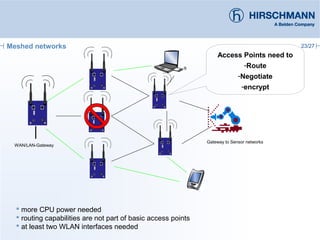
The document discusses the implementation and advantages of industrial WLAN networks, focusing on enhancing security, stability, and availability through various topologies, including meshed networks. It highlights current threats and challenges in industrial environments, proposing solutions such as redundancy and advanced routing protocols to improve performance. Additionally, it provides an overview of the features of the BAT54-rail access point, which supports complex network functionalities without requiring new hardware.