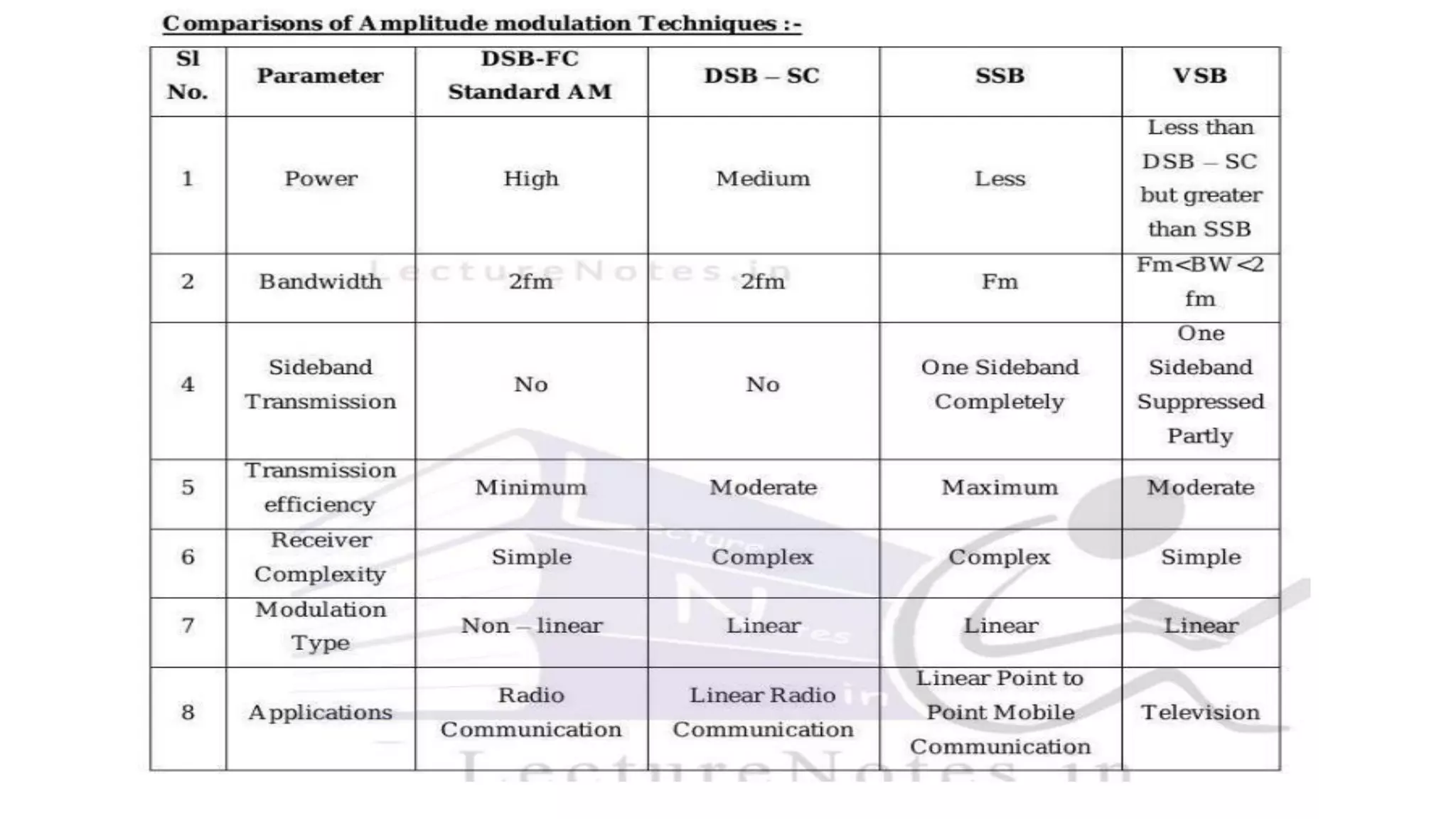
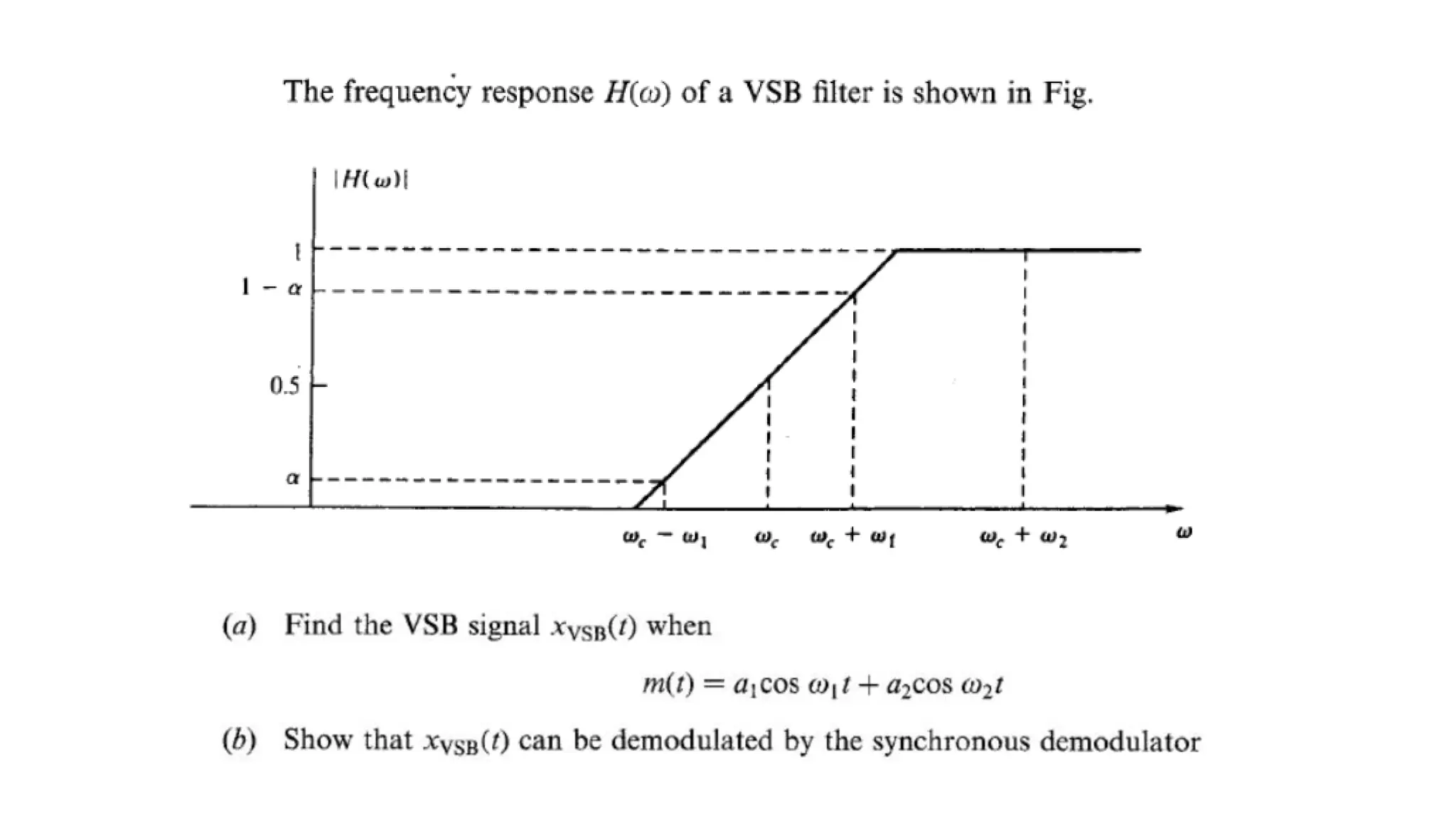
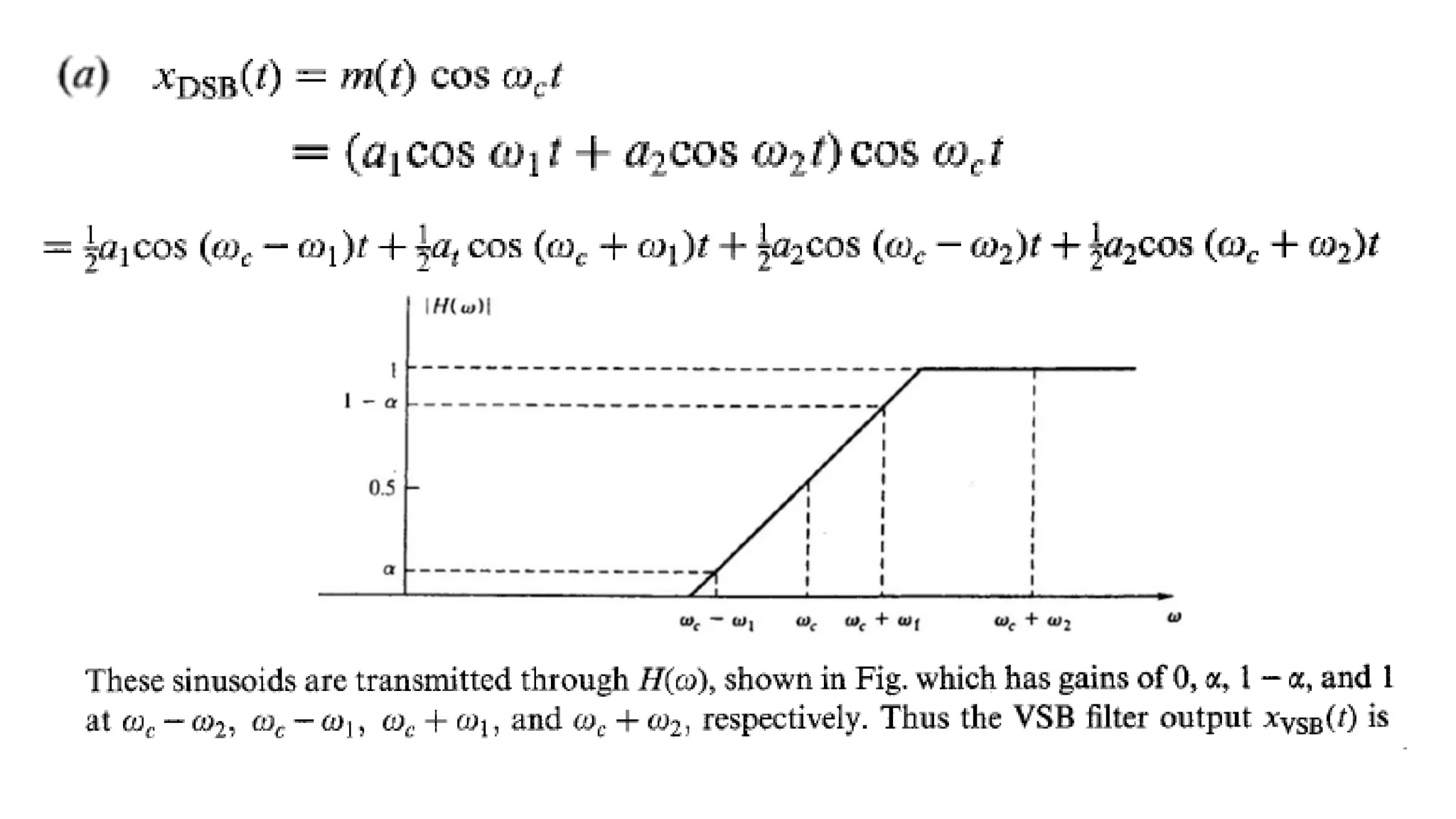
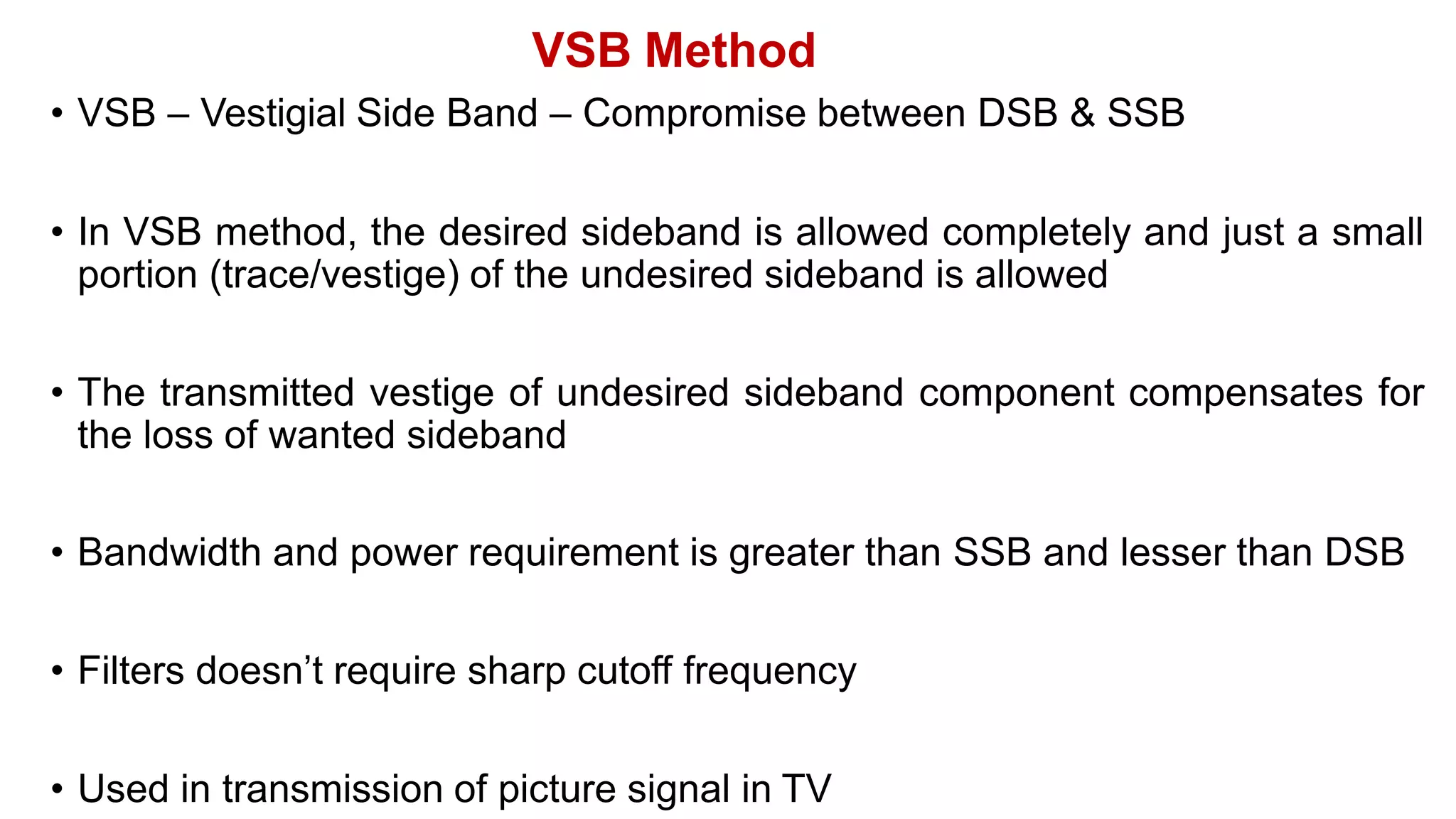
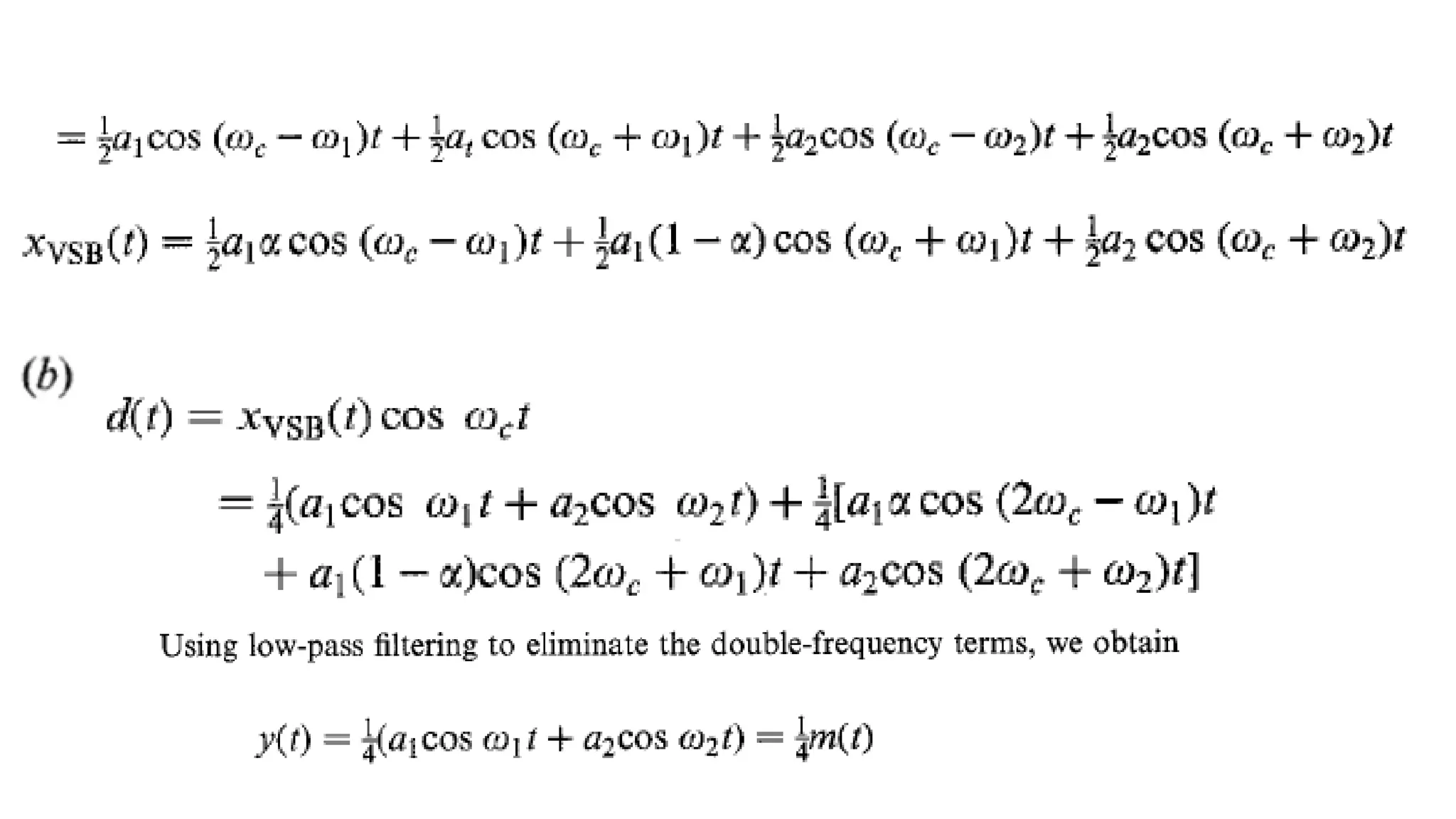VSB is a modulation technique that is a compromise between DSB and SSB. It allows the complete desired sideband along with a small vestige of the undesired sideband. This vestige compensates for loss and reduces bandwidth needs compared to DSB. In VSB modulation, the input signal is first used to generate a DSB-SC signal which is then passed through a sideband filter to obtain the VSB signal. This signal is demodulated by multiplying with a carrier and filtering to recover the original input message. VSB is used for television signal transmission due to its efficiency and easy filter design.
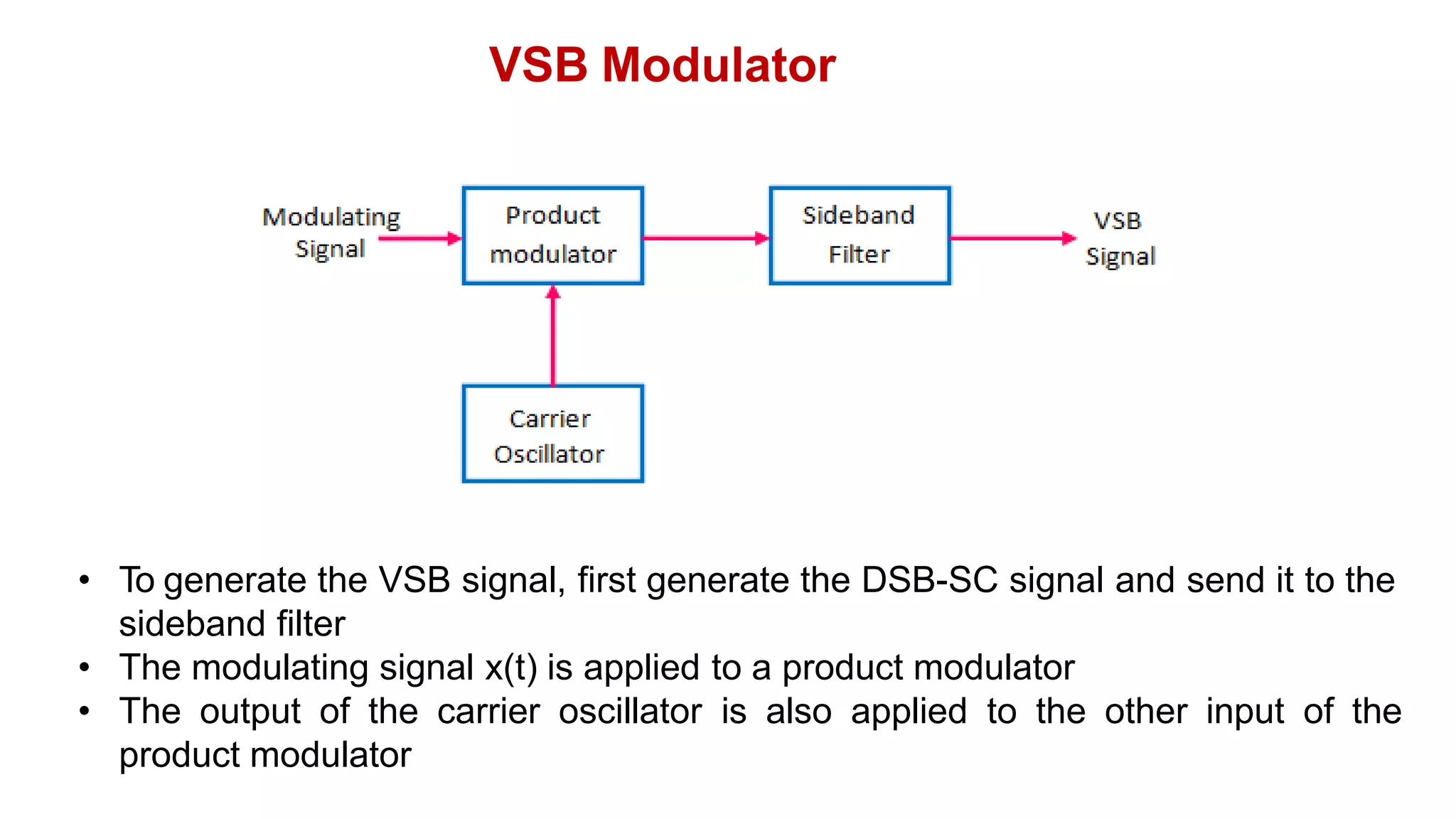
![VSB Modulator
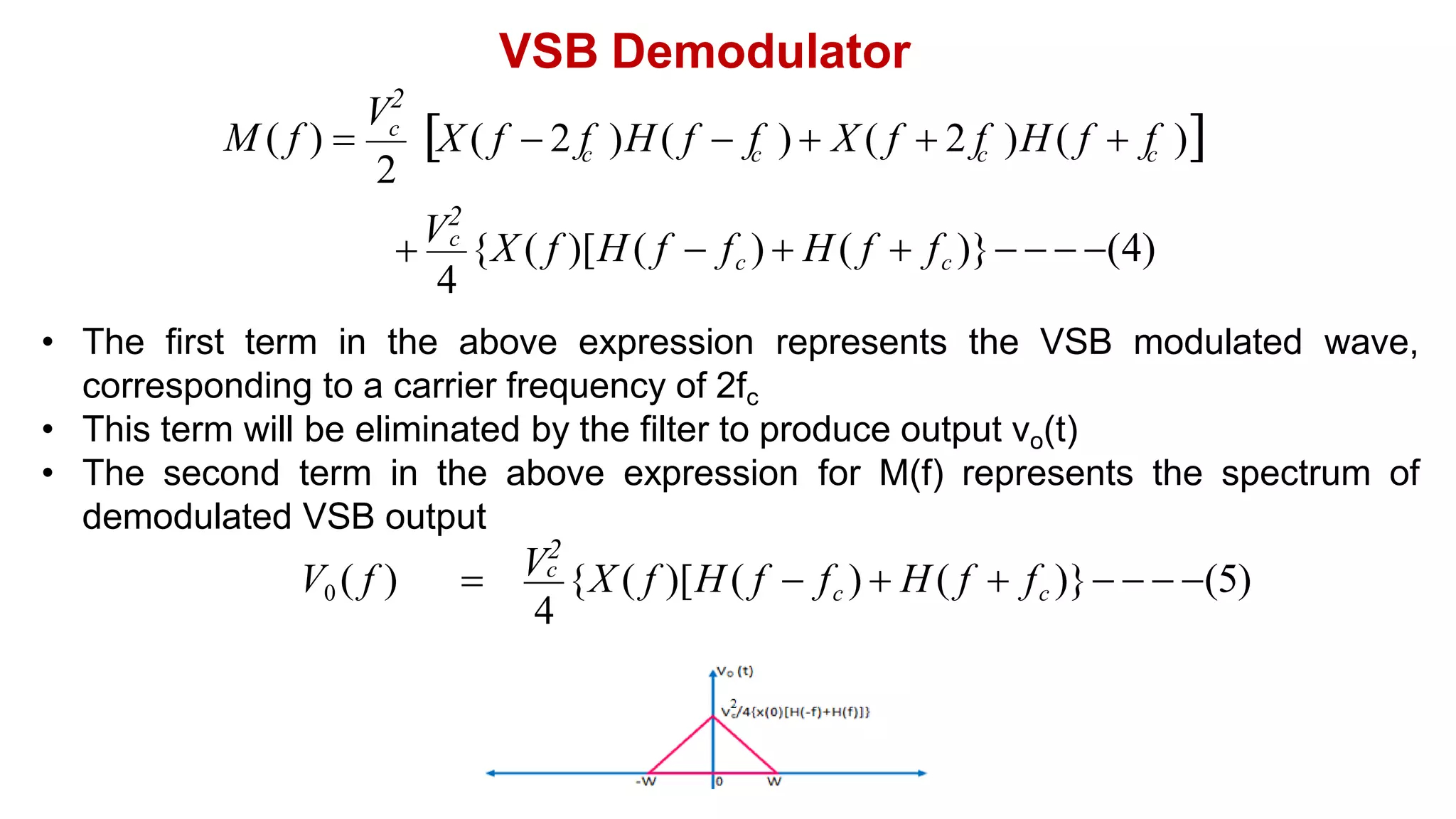
• The output of the product modulator is given as
m(t) x(t).c(t)
m(t) Vc cos2fct.x(t) (1)
Applying fourier transform on both sides
• This DSB-SC signal is given to SSB filter which pass the wanted
sideband and vestige of unwanted sideband
• Let the transfer function of the filter be H(f)
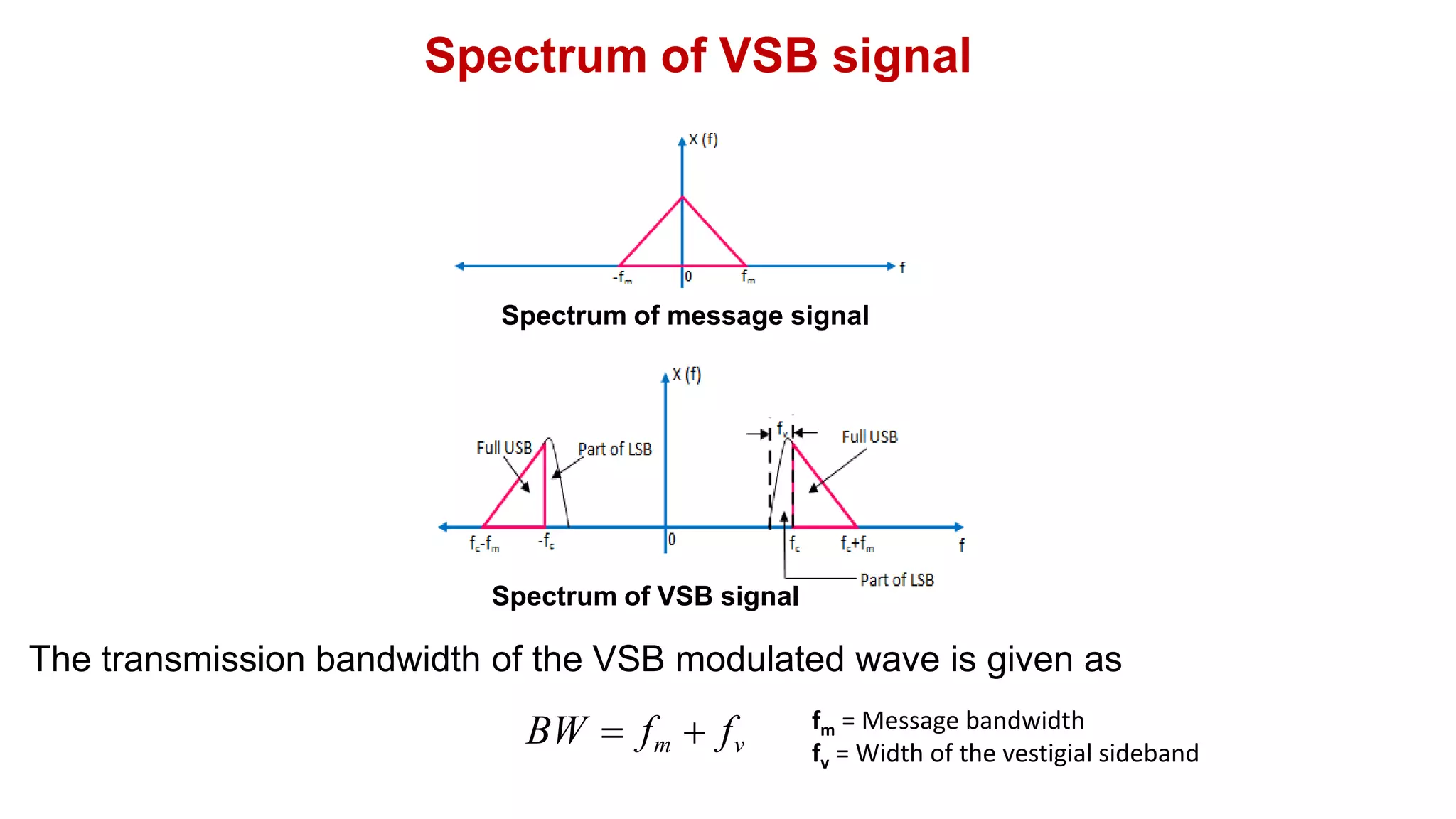
• Hence, the spectrum of the VSB modulated signal is given as
2
S( f )
V
[X ( f fc ) X ( f fc )]H ( f ) (3)
c
2
M( f )
V
[X ( f fc ) X ( f fc )] (2)
c
S( f ) M( f ) H( f )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8vsbgenerationanddetection-230528183734-c5239566/75/8-VSB_Generation_and_Detection-pdf-3-2048.jpg)
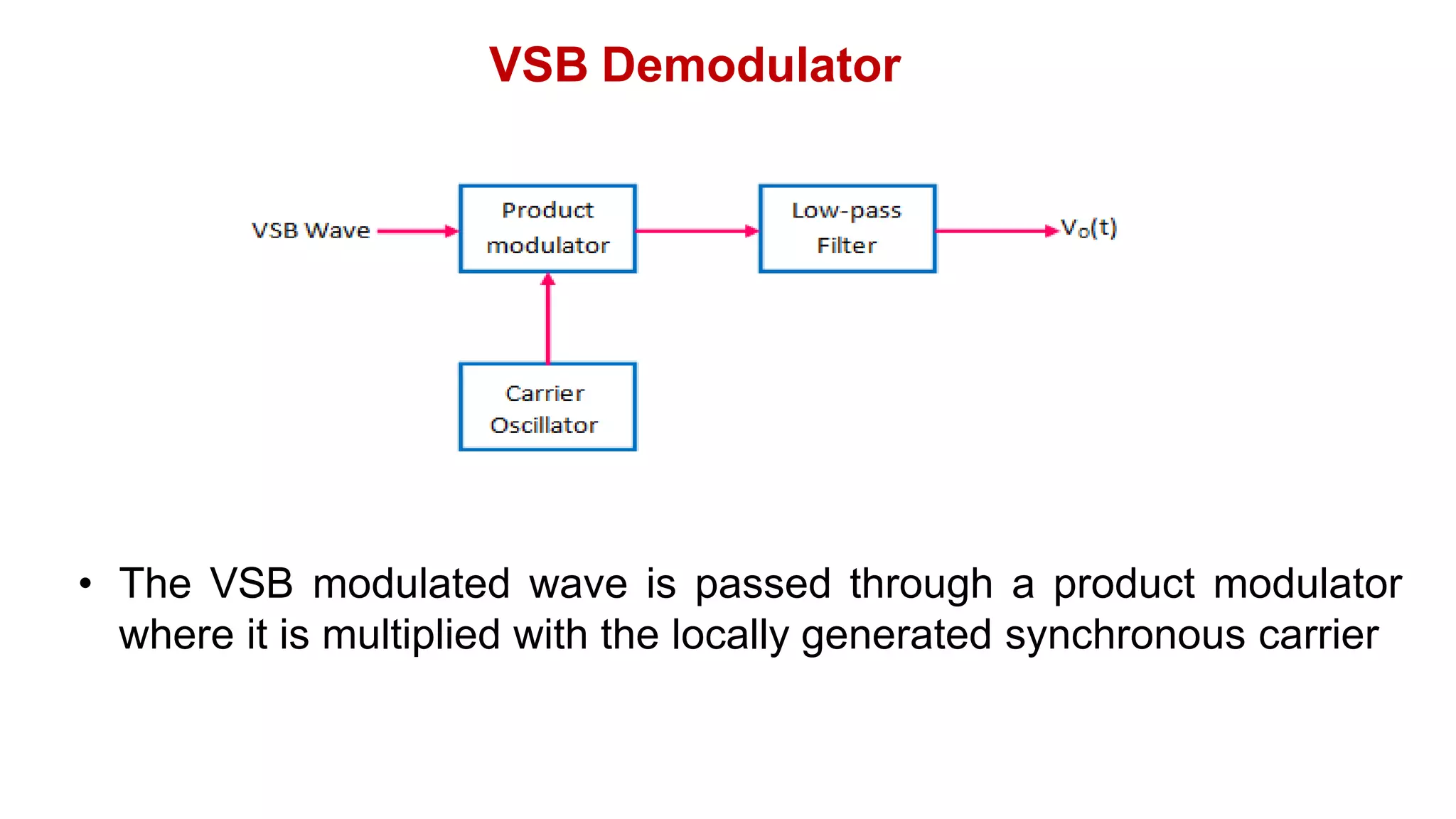
![VSB Demodulator
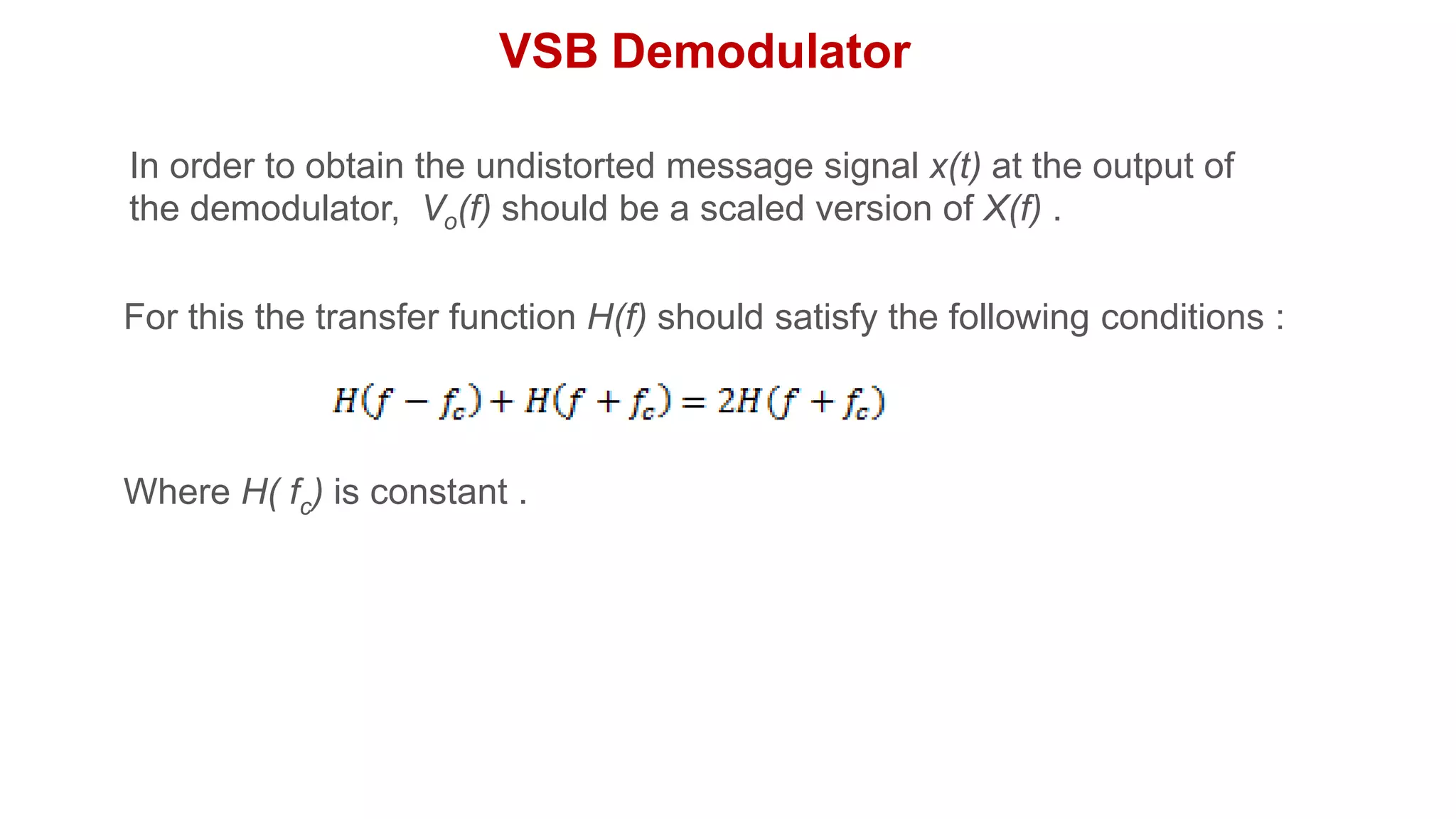
• The output of the product modulator is given as
m(t) s(t).c(t)
m(t) Vc cos2fct.s(t) (1)
• Taking Fourier transform on both sides, we get
• Sub Eq.(3) in Eq.(2)
2
S( f )
V
[X ( f fc ) X ( f fc )]H ( f ) (3)
c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8vsbgenerationanddetection-230528183734-c5239566/75/8-VSB_Generation_and_Detection-pdf-6-2048.jpg)