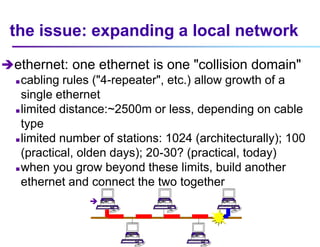
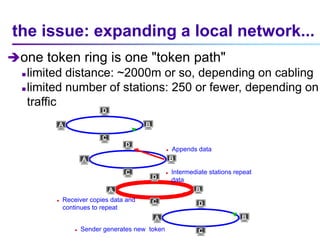
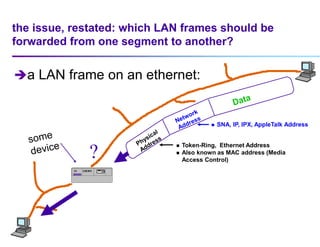
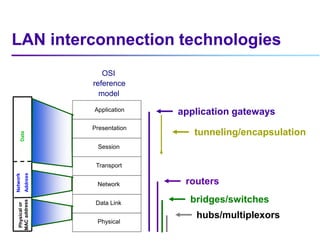
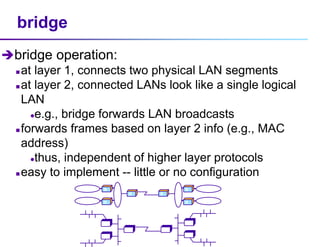
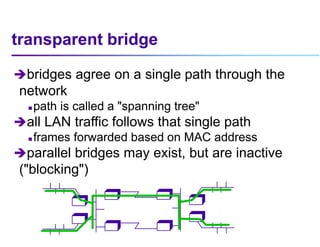
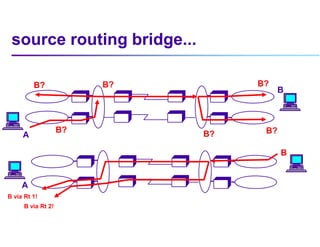
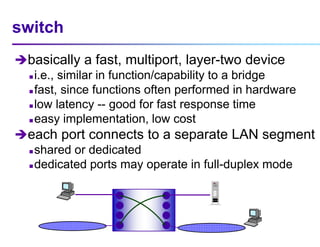
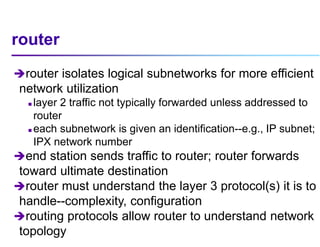
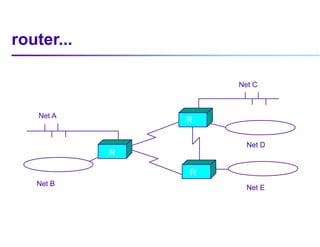
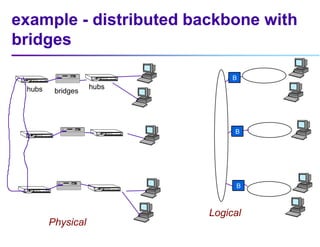
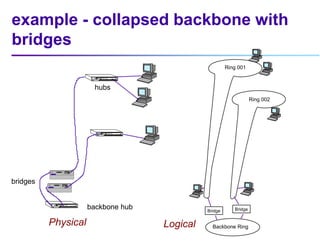
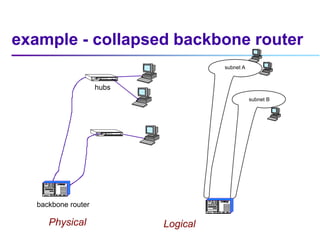
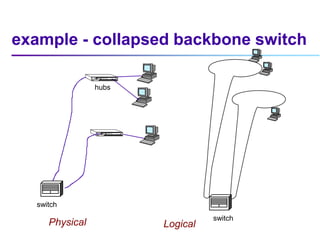
This document discusses options for interconnecting local area networks (LANs) in a campus network. It describes bridges, switches, and routers that operate at the data link layer and can be used to connect multiple LAN segments. Switches are preferred within campus networks today as they provide fast connection speeds with low latency and easy administration. The document also discusses using higher speed backbone technologies like Fast Ethernet, FDDI, or ATM to connect LAN segments at higher speeds while still requiring interconnection devices like switches or routers.