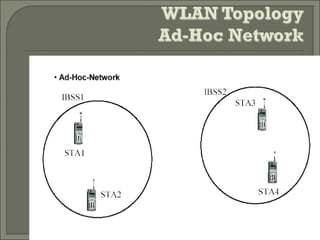
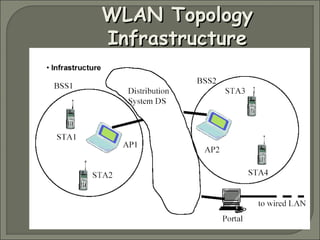
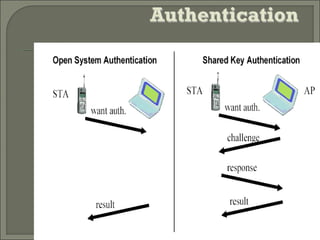
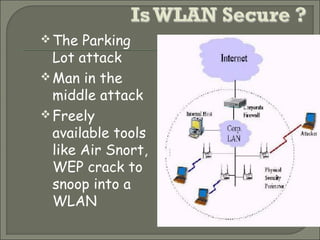
Wireless LANs (WLANs) provide flexibility, portability and mobility by allowing connectivity without physical cables. The IEEE 802.11 standard defines the specifications for WLANs and addresses differences from wired LANs such as power management and security. WLANs use infrastructure and ad-hoc modes for connectivity. Security in WLANs is currently provided by WEP which has proven vulnerabilities. Improved security standards are needed to allow wider adoption of WLANs, especially in environments with sensitive data.