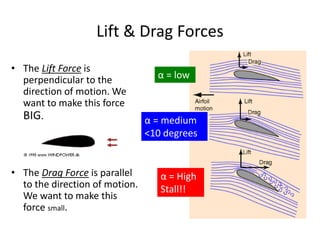
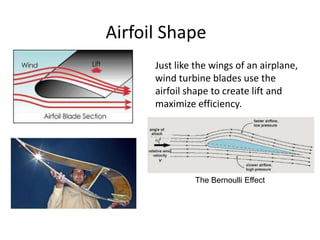
Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into electrical power. They are designed using aerodynamic modeling to determine the optimal tower height, control systems, number of blades, and blade shape for the location. Conventional horizontal axis turbines have three main components: the rotor, generator, and structural support tower. Most use three blades for balance and slower rotation to reduce costs and increase efficiency. The airfoil shaped blades create lift and drag forces, with lift being maximized for efficiency. Small wind turbines can provide energy in off-grid areas, while wind power is becoming increasingly competitive with other sources and can power irrigation and desalination.



![Continued :
Wind turbines convert wind energy to electricity for
distribution. Conventional horizontal axis turbines
can be divided into three components:
• The rotor component,
• The generator component - includes the electrical
generator,[29][30] the control electronics, and most likely a
gearbox (e.g. planetary gearbox),[31] adjustable-speed
drive[32] or continuously variable transmission[33]
component for converting the low speed incoming rotation
to high speed rotation suitable for generating electricity.
• The structural support component includes the tower and
rotor yaw mechanism.[34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tr-140807150930-phpapp02/85/Wind-Turbines_Brief-4-320.jpg)