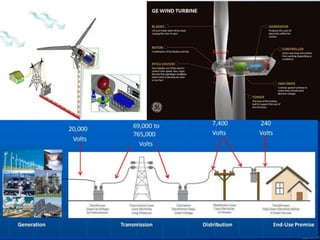
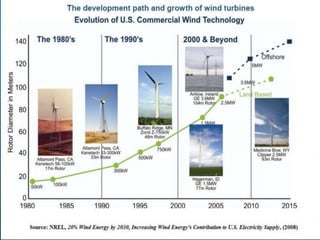
Offshore wind farms provide a green source of energy and have significant advantages over onshore wind farms. The document discusses the history and types of wind turbines and wind farms, including horizontal-axis and vertical-axis turbines. Offshore wind farms are located at sea and Europe leads in offshore wind power development. Challenges of offshore wind farms include difficulties building structures in deep water and risks from waves and hurricanes. Both offshore and onshore wind farms provide pollution-free energy but also have ecological impacts that must be considered.