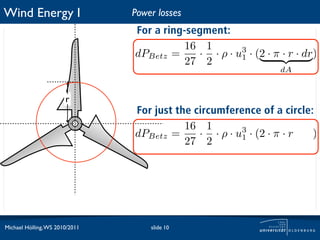
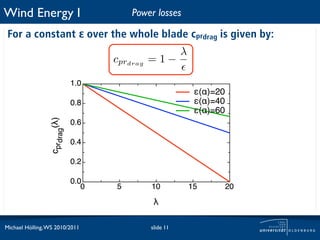
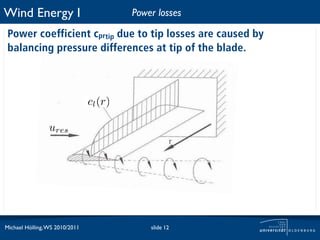
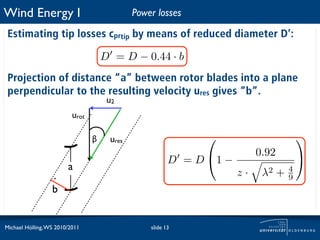
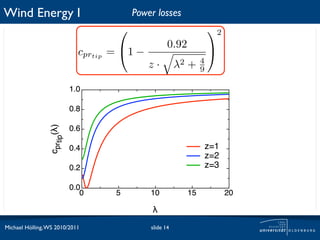
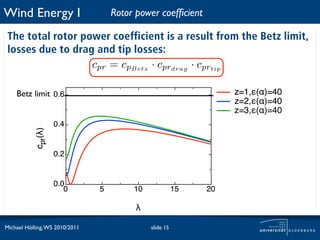
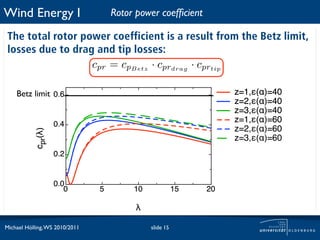
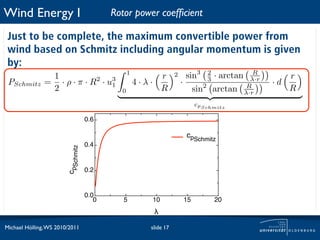
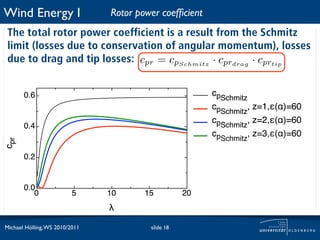
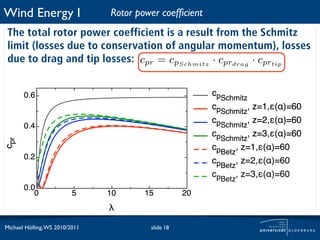
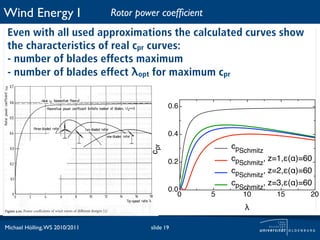
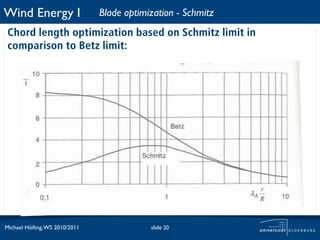
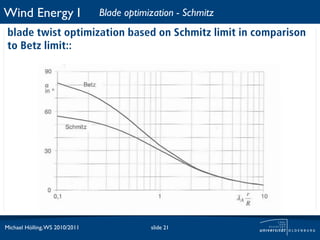
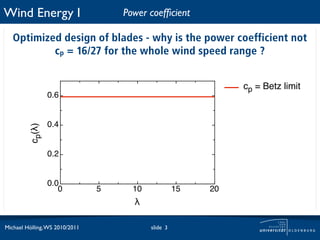
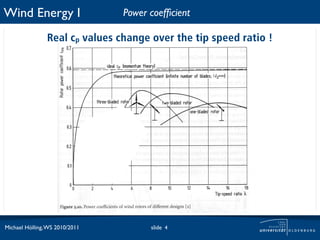
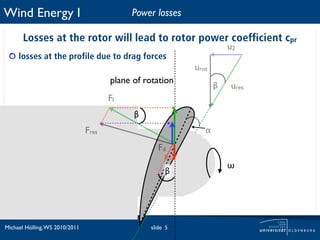
The document discusses power losses that occur at the rotor blades of a wind turbine. It explains that the rotor power coefficient is lower than the theoretical Betz limit due to drag and tip losses. Drag losses are caused by friction on blade surfaces and tip losses occur at the ends of blades due to vortex shedding. The rotor power coefficient can be calculated as the product of coefficients for the Betz limit, drag losses, and tip losses. Graphs show how the different loss coefficients and the total rotor power coefficient vary with tip speed ratio.


![Wind Energy I Power losses
Possible behavior of cprdrag over blade radius r for different ε
and λ:
70 1.0
!(r) !=4
!=7
60 ! = 10
0.9
cprdrag(r)
!(r)
50
40 0.8
30 0 10 20 30 40 50
0 10 20 30 40 50
r [m] r [m]
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18thlesson-111024033706-phpapp01/85/Wind-energy-I-Lesson-8-Power-losses-at-rotor-blade-8-320.jpg)