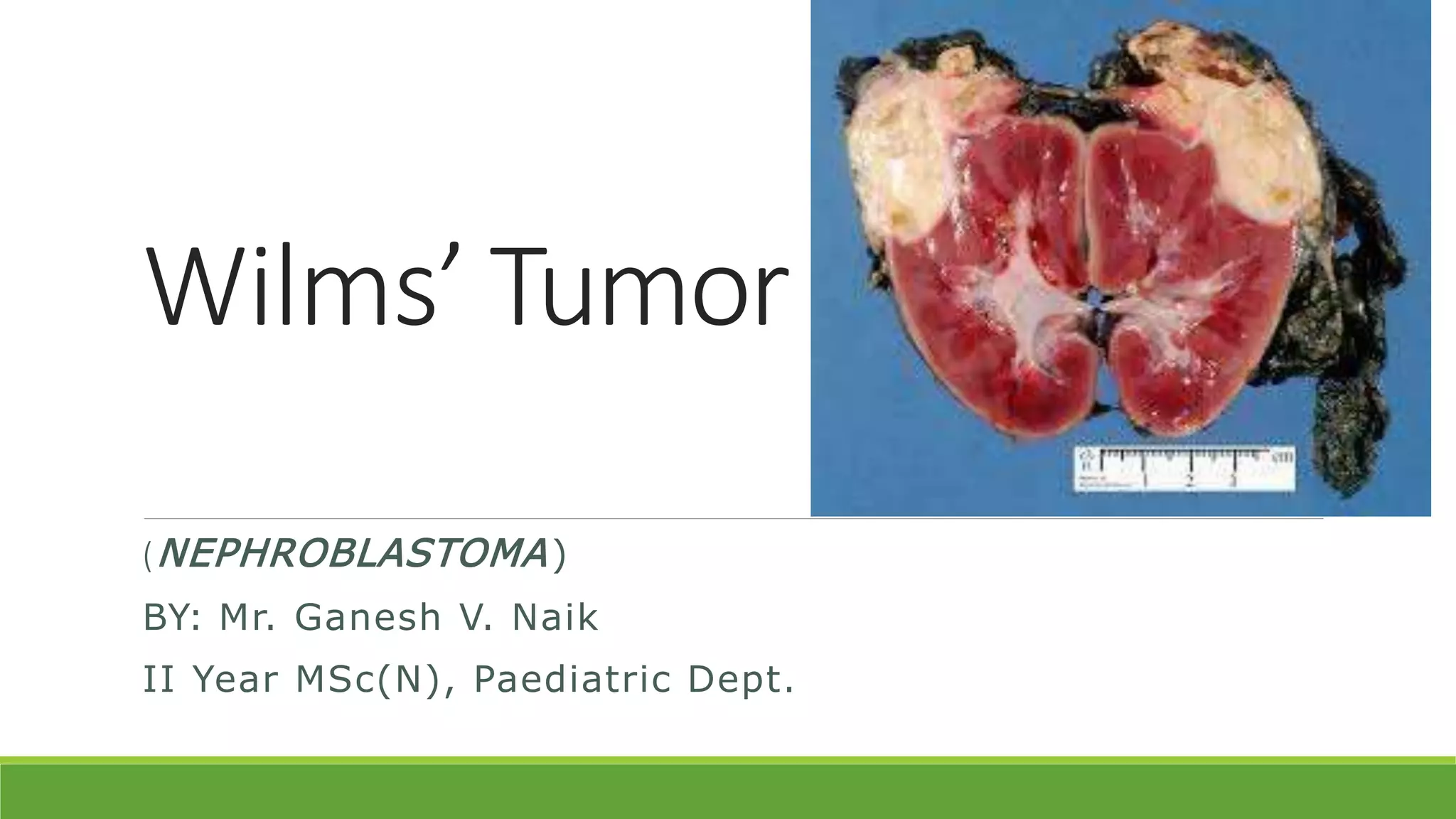
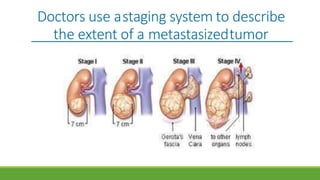
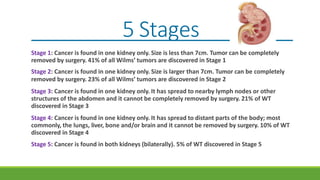
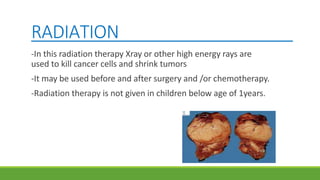
Wilms' tumor is a rare, malignant kidney tumor that is most common in children under 5 years old. It makes up about 90% of all kidney tumors diagnosed in children. While the exact cause is unknown, risk factors include family history and certain birth defects. Symptoms can include an abdominal mass, swelling, pain, and high blood pressure. Diagnosis involves imaging tests, blood tests, biopsy and assessing the tumor stage. Treatment involves chemotherapy, surgery to remove the tumor and possibly the kidney, and sometimes radiation therapy. With treatment, about 90% of patients survive at least 5 years.