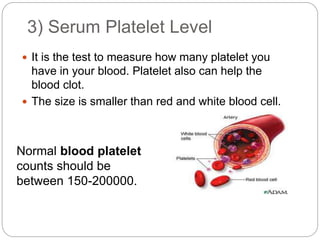
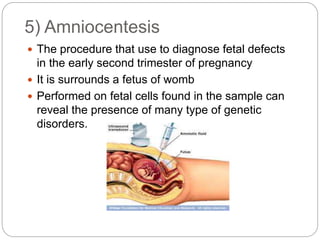
Hemophilia is a group of inherited bleeding disorders caused by deficiencies in clotting factors, leading to impaired blood clotting. There are several types of hemophilia including Hemophilia A, Hemophilia B, and von Willebrand's disease. Symptoms include bleeding into joints, easy bruising, and prolonged bleeding from minor injuries. Treatment involves replacing the deficient clotting factor through products like fresh frozen plasma or specific clotting factor concentrates. Nursing care focuses on preventing and treating bleeding episodes, avoiding risk factors, managing pain, and providing patient education.