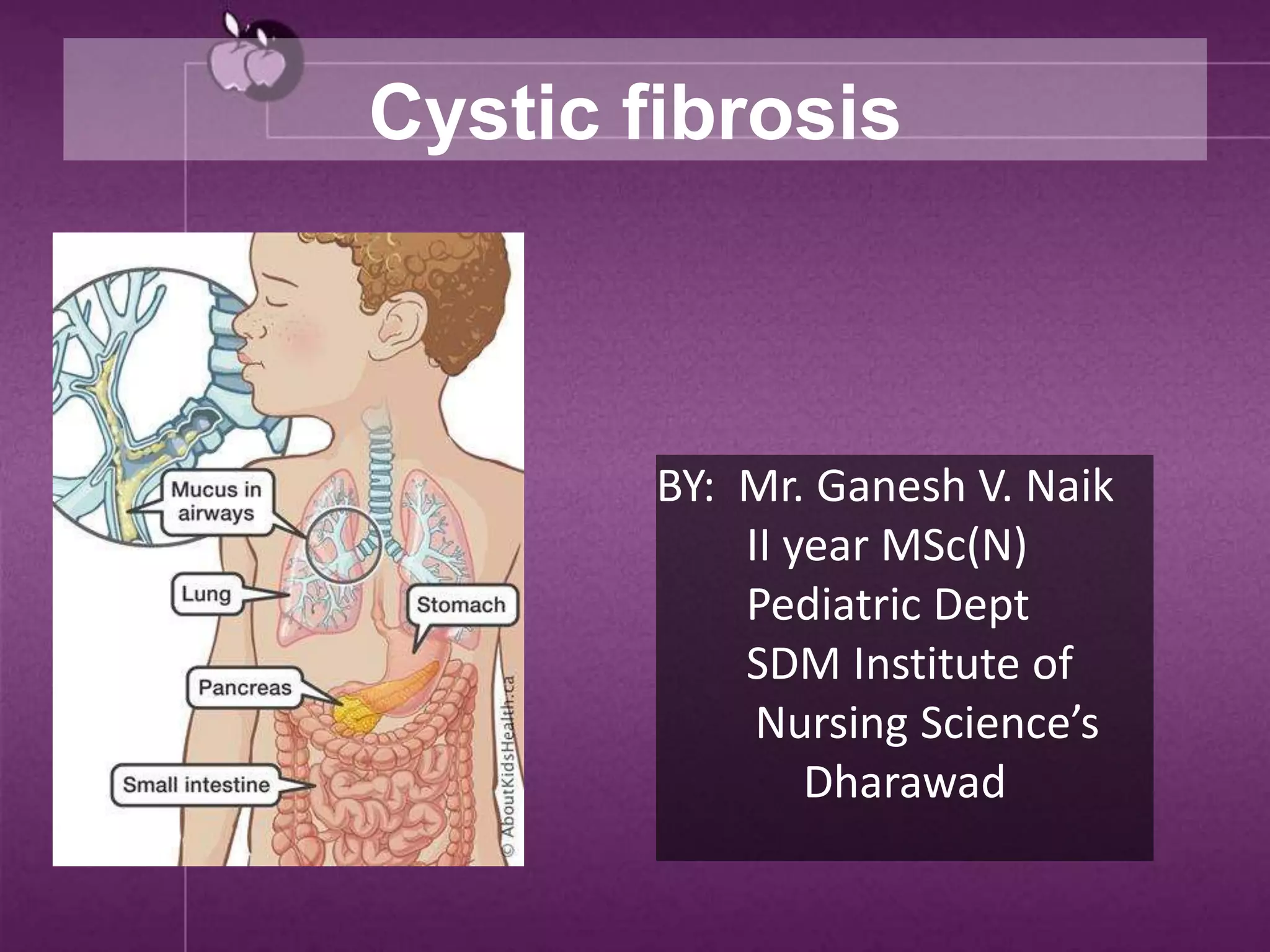
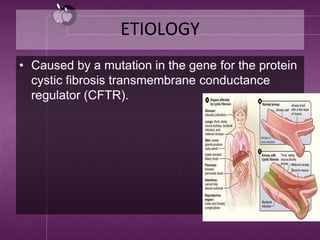
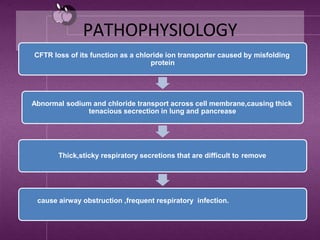
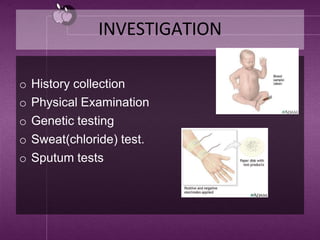
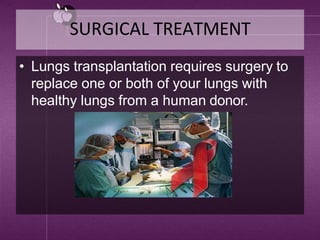
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes thick mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive tract. It is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene and results in the loss of chloride ion transport. This leads to abnormal sodium and chloride transport, causing thick secretions in the lungs and pancreas. Symptoms include cough, fatigue, infections and difficulty gaining weight in infants. Treatment involves antibiotics, airway clearance techniques, and gene therapy. Complications can affect the respiratory and digestive systems. Prevention is not possible as it is genetic, but genetic testing may help those with a family history.