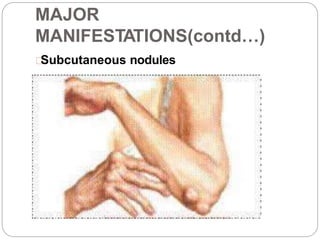
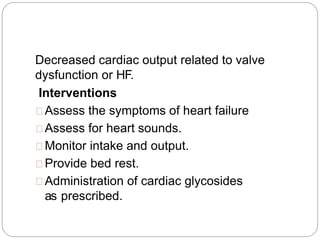
Rheumatic fever is an immunological disorder caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, primarily affecting children aged 6 to 15. It can lead to severe complications involving the heart and joints, with a higher risk in individuals from poor socio-economic backgrounds and those with previous infections. Diagnosis relies on the modified Jones criteria, and management includes anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, and potential surgical interventions for severe cases.