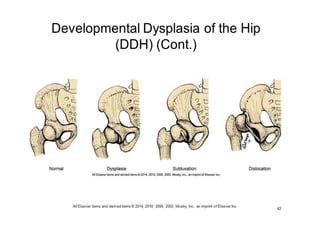
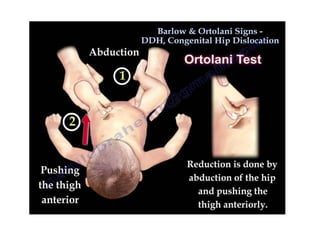
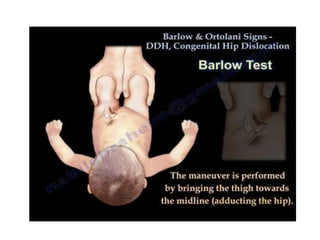
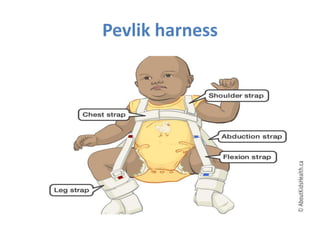
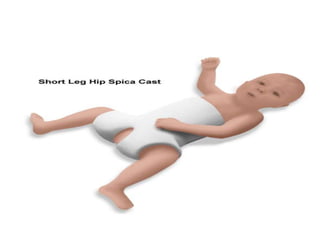
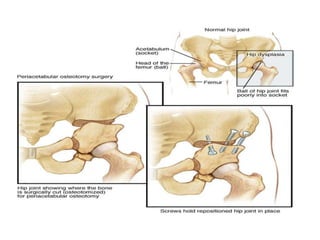
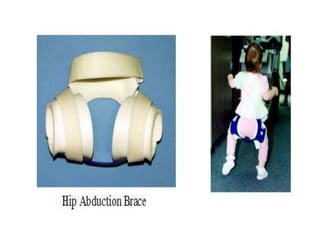
Dislocation of the hip is a congenital or acquired deformity where the head of the femur is improperly aligned with the acetabulum cavity. It can range from mild acetabular dysplasia to complete dislocation. Risk factors include female sex, breech presentation, and family history. Clinical features depend on age but may include leg length discrepancy, limited hip motion, or abnormal gait. Diagnosis involves physical exam, ultrasound, and x-rays. Treatment varies by age but may include use of pelvic harnesses, skin traction, surgery, and casting to relocate the femoral head.