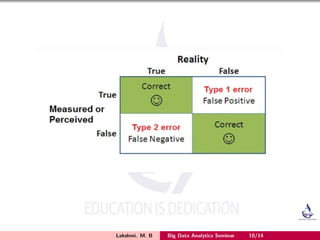
The document discusses the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test, a non-parametric hypothesis test that checks if two populations are identically distributed. It assumes the two populations are identically distributed and their ordering would be evenly intermixed. The test ranks all observations from both groups as if they come from one large group, then sums the ranks for at least one population's sample. It also discusses Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing, where a Type I error rejects the null hypothesis when it is true, and a Type II error accepts the null hypothesis when it is false. The probabilities of each are denoted by alpha and beta, respectively.