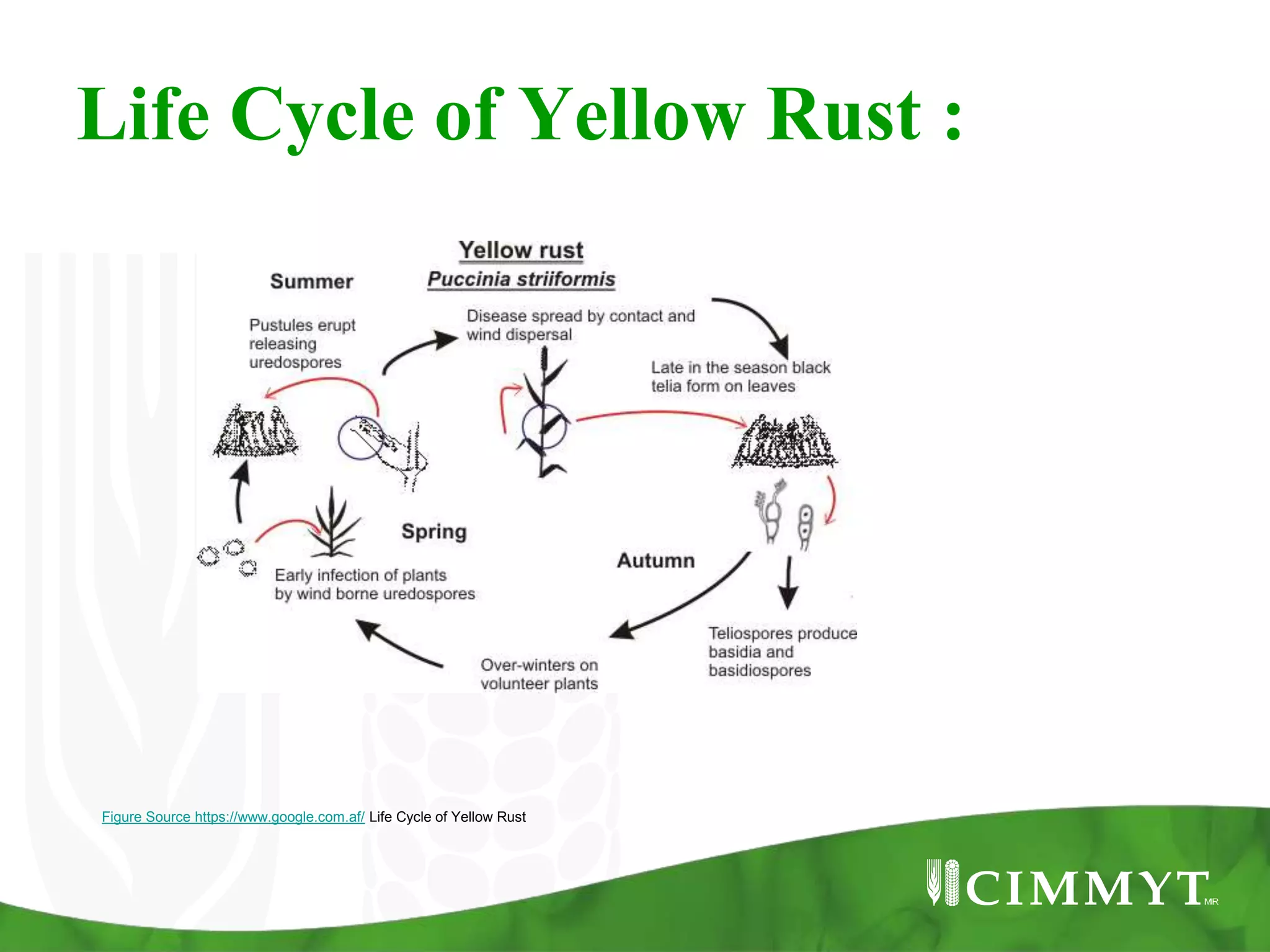
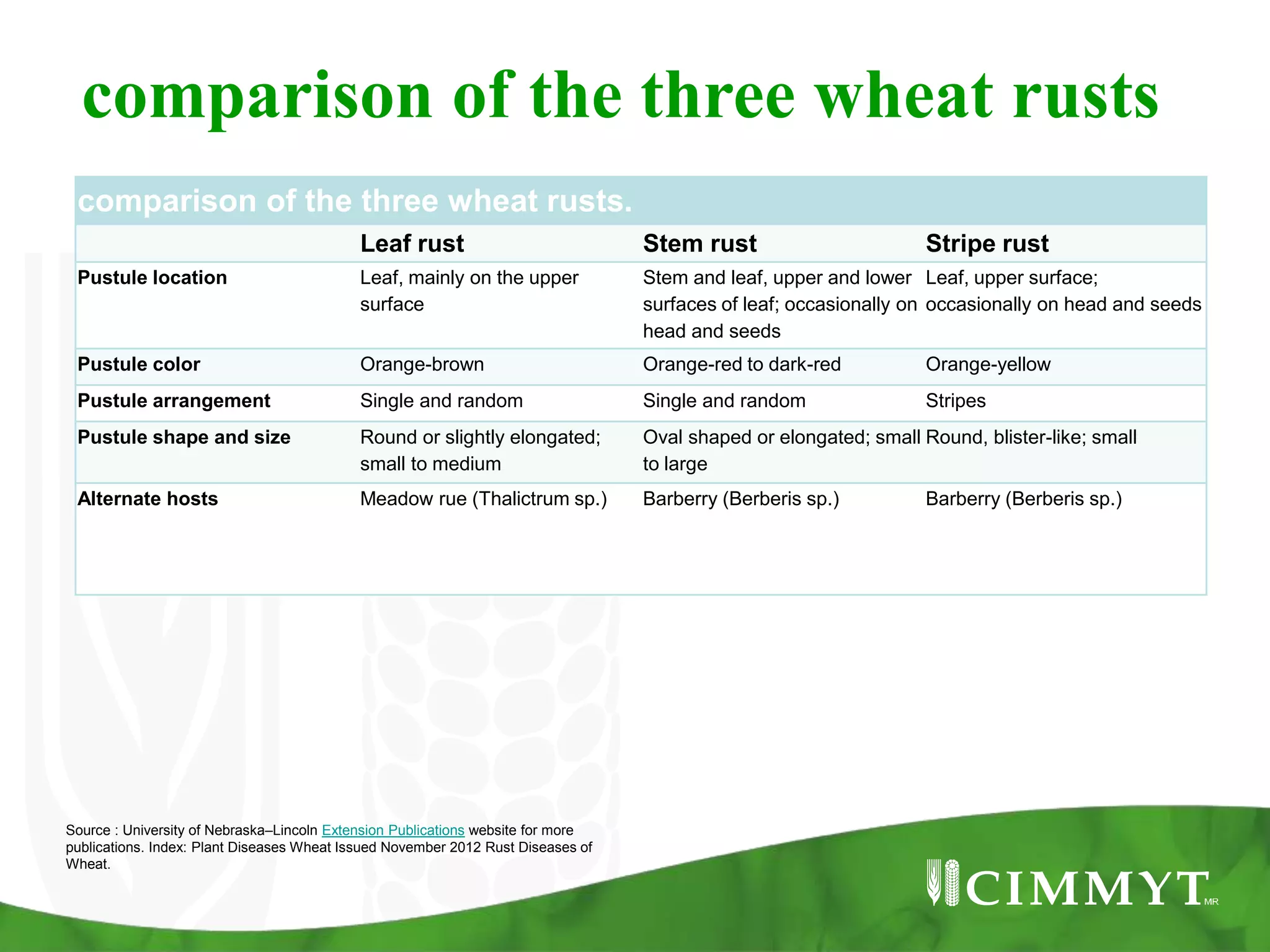
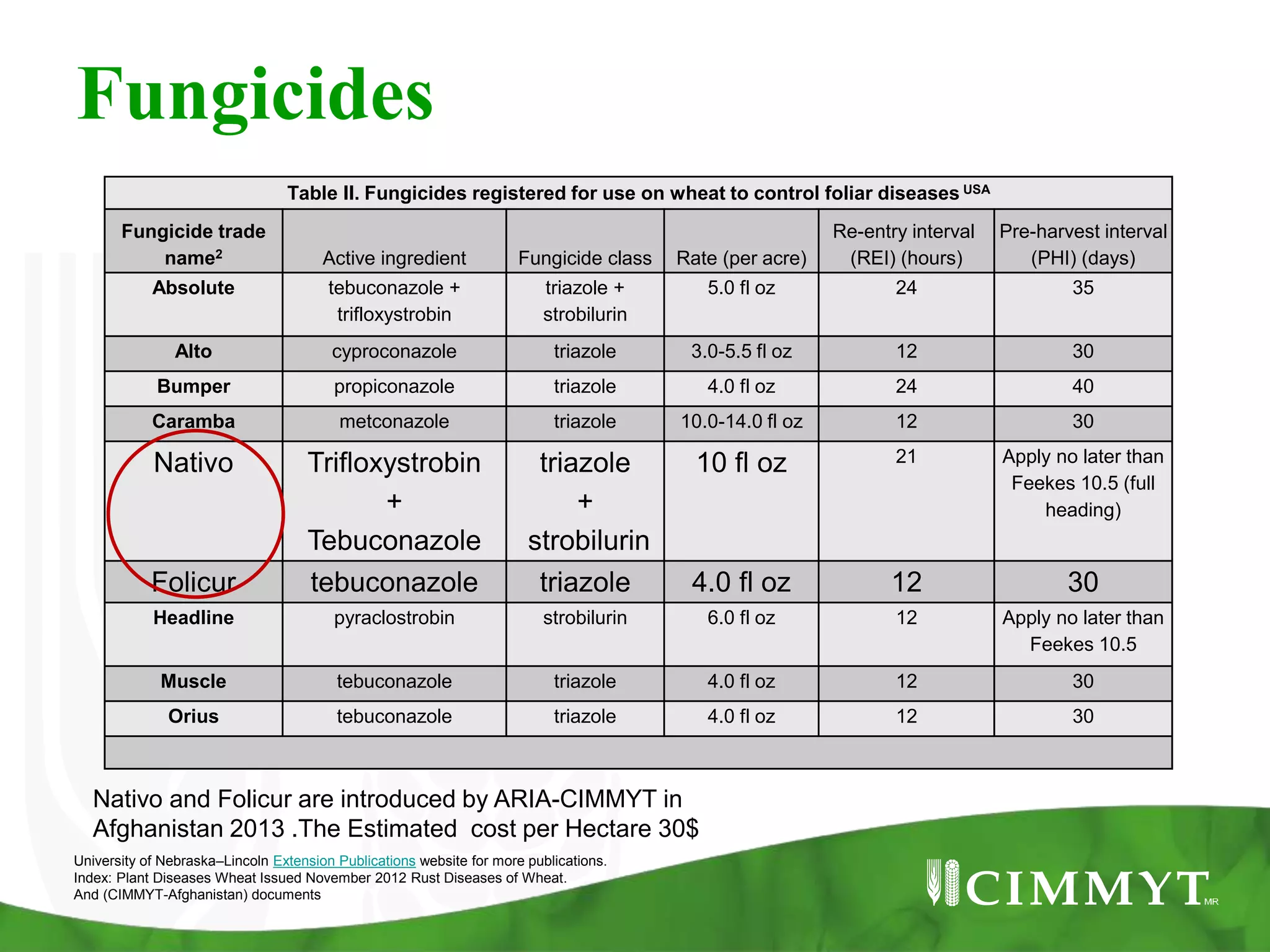
This document discusses three types of wheat rust: stem rust, stripe rust, and leaf rust. It provides information on the causal fungi, symptoms, life cycles, importance, and management strategies. The three rusts are among the most important fungal diseases of wheat worldwide due to their wide distribution and ability to develop new races that can overcome resistance. Effective management requires sustained investment in surveillance, capacity building, and developing resistant wheat varieties.