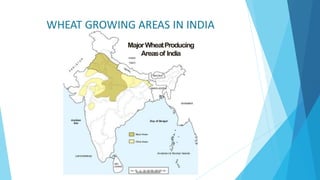
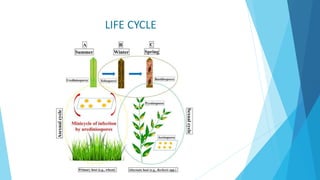
This document discusses stem rust of wheat, a fungal disease caused by Puccinia graminis that affects wheat and other cereal crops. It provides an introduction to stem rust and the parts of wheat affected. The life cycle of the fungus is described in five spore stages. Symptoms include reddish brown pustules and production of urediospores and telia. Favorable conditions for the fungus are temperatures around 23-25 degrees C and hosts including barberry and mahonia plants. Management strategies discussed include fungicide use, resistant varieties, and cultural practices like early wheat maturation.