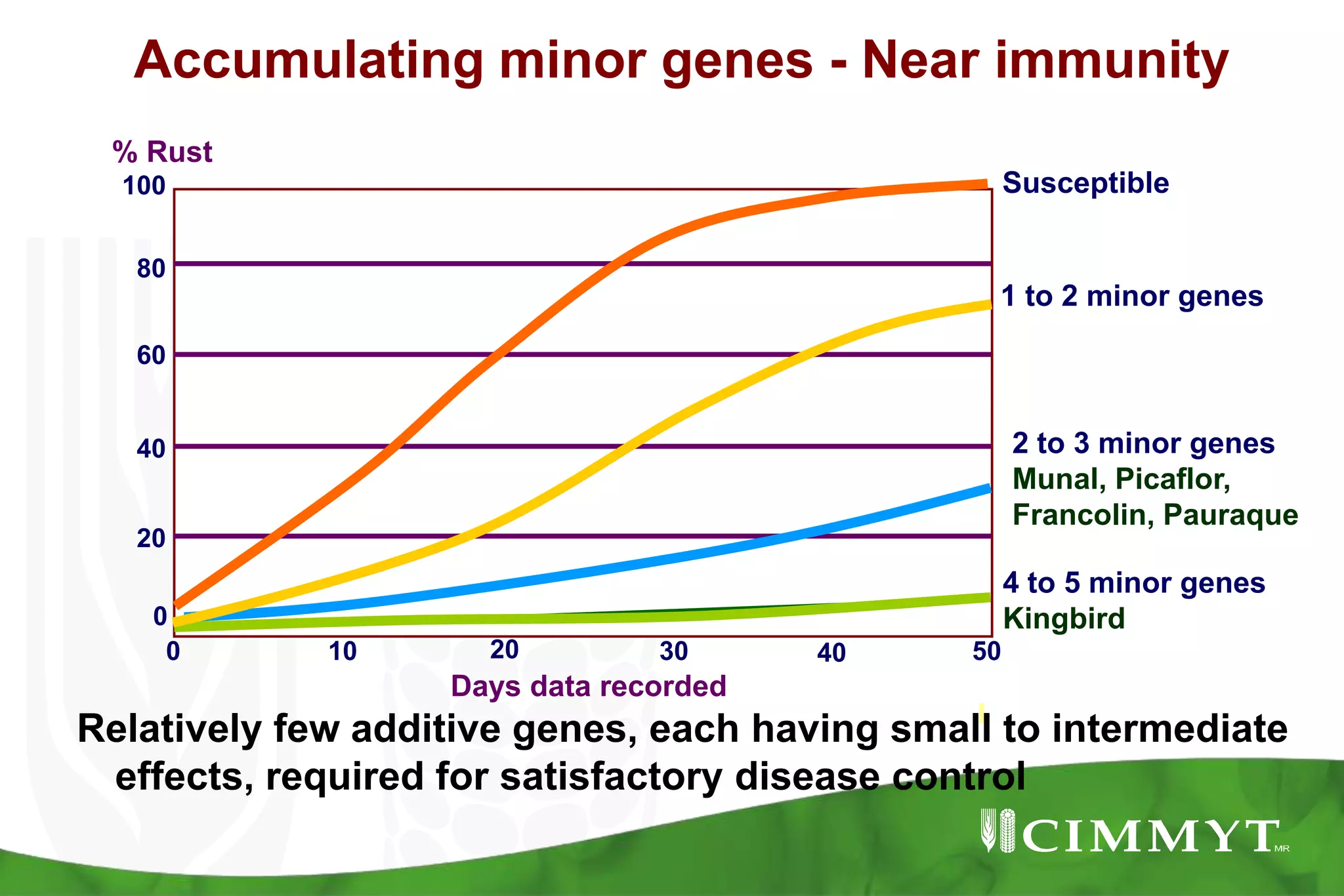
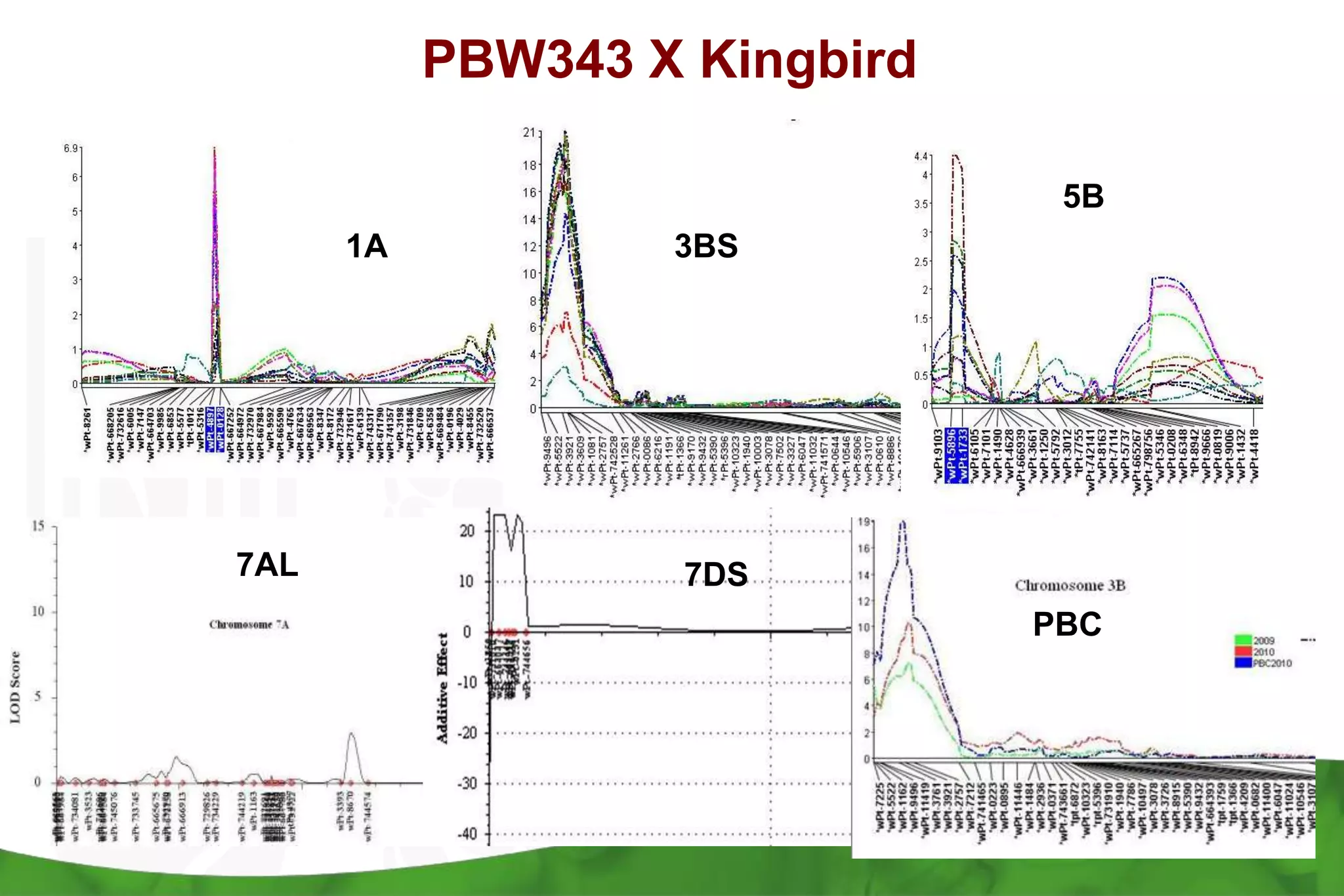
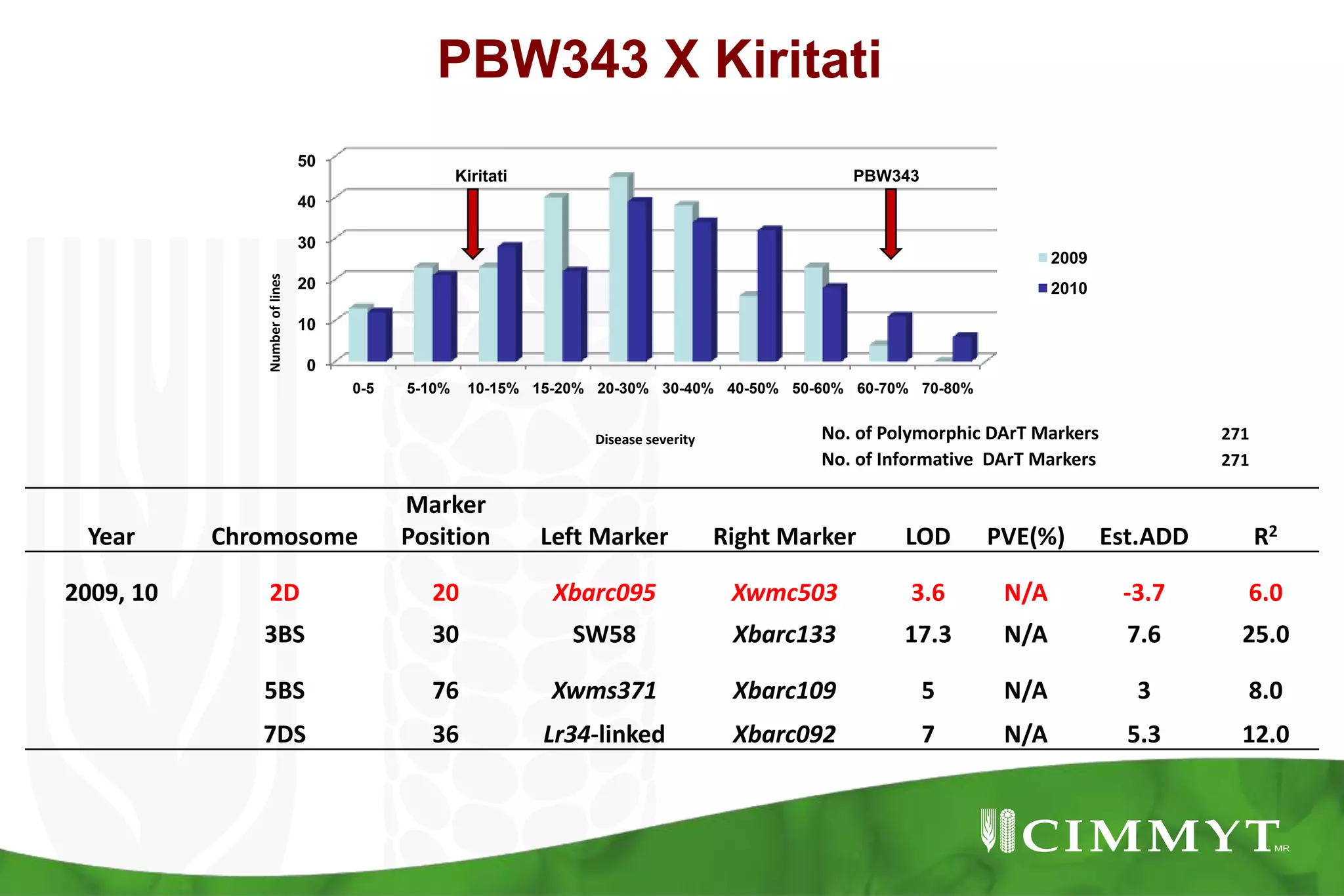
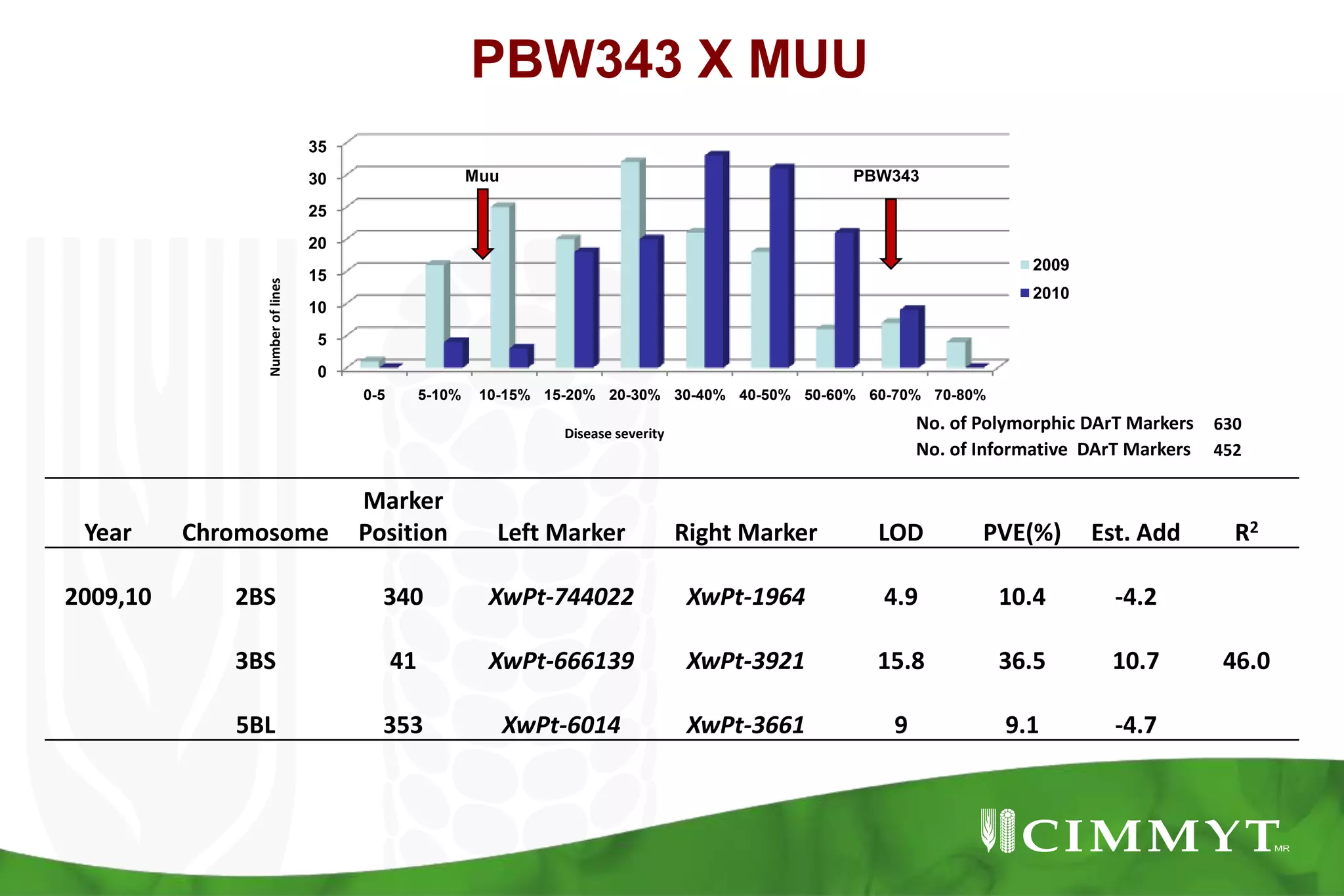
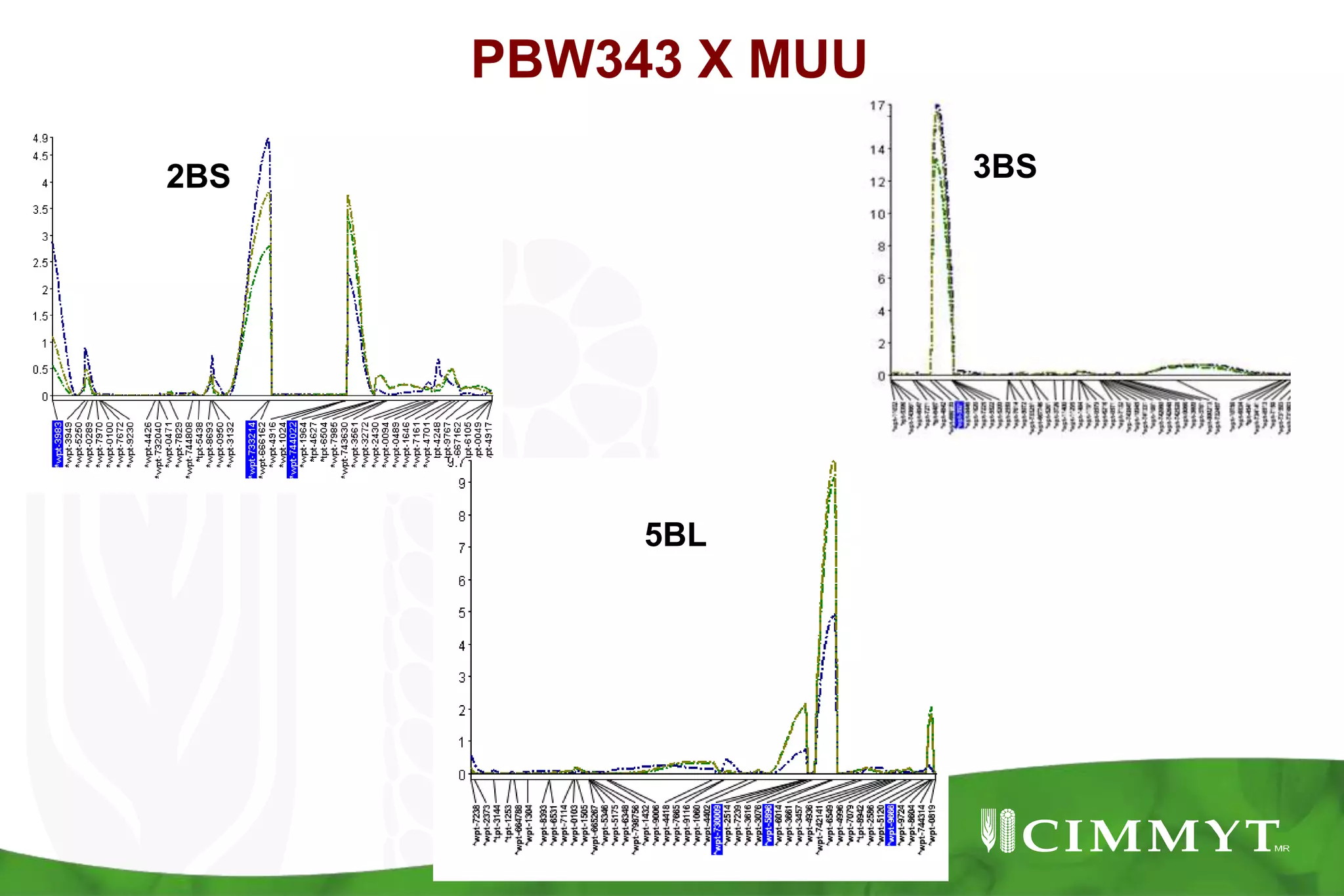
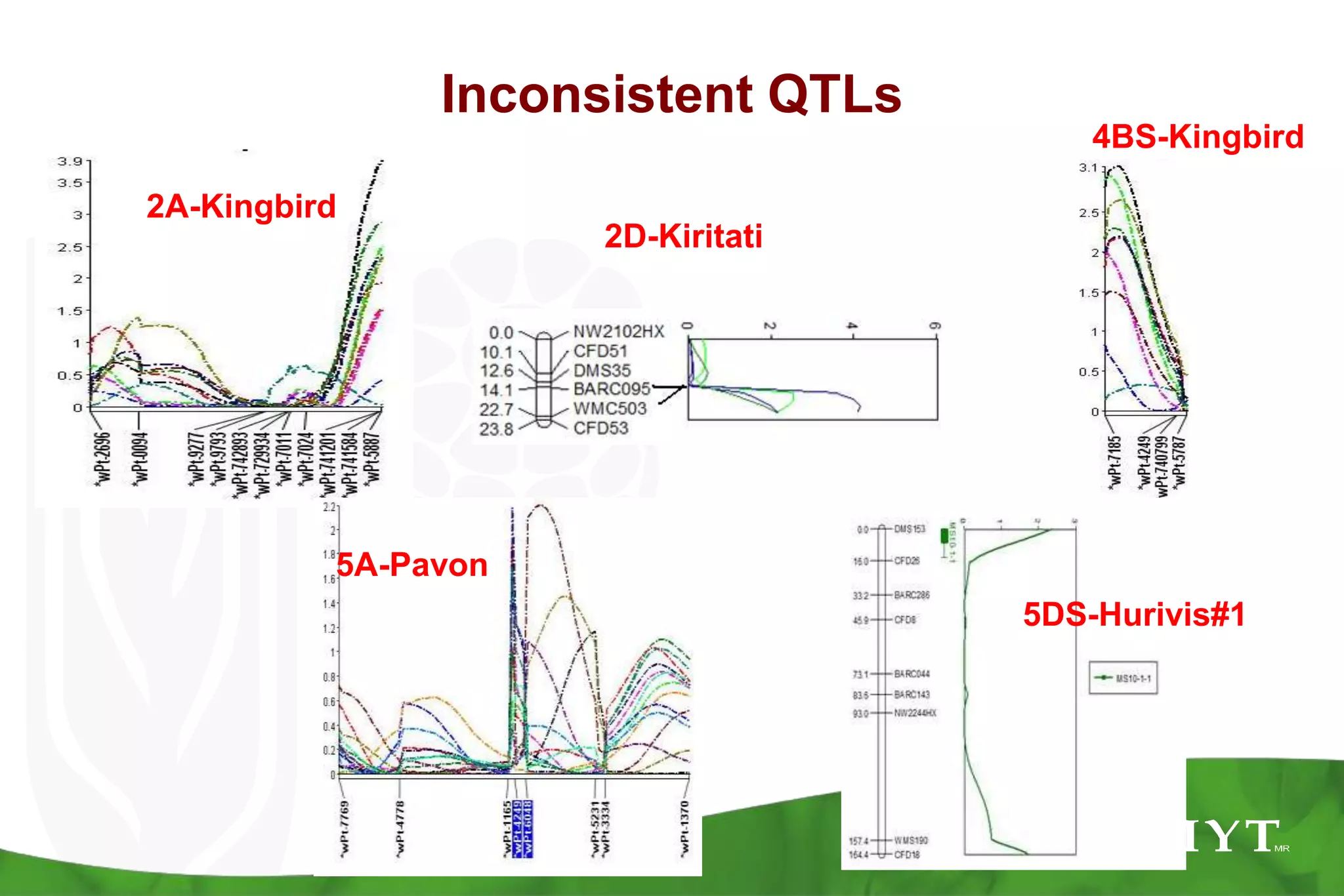
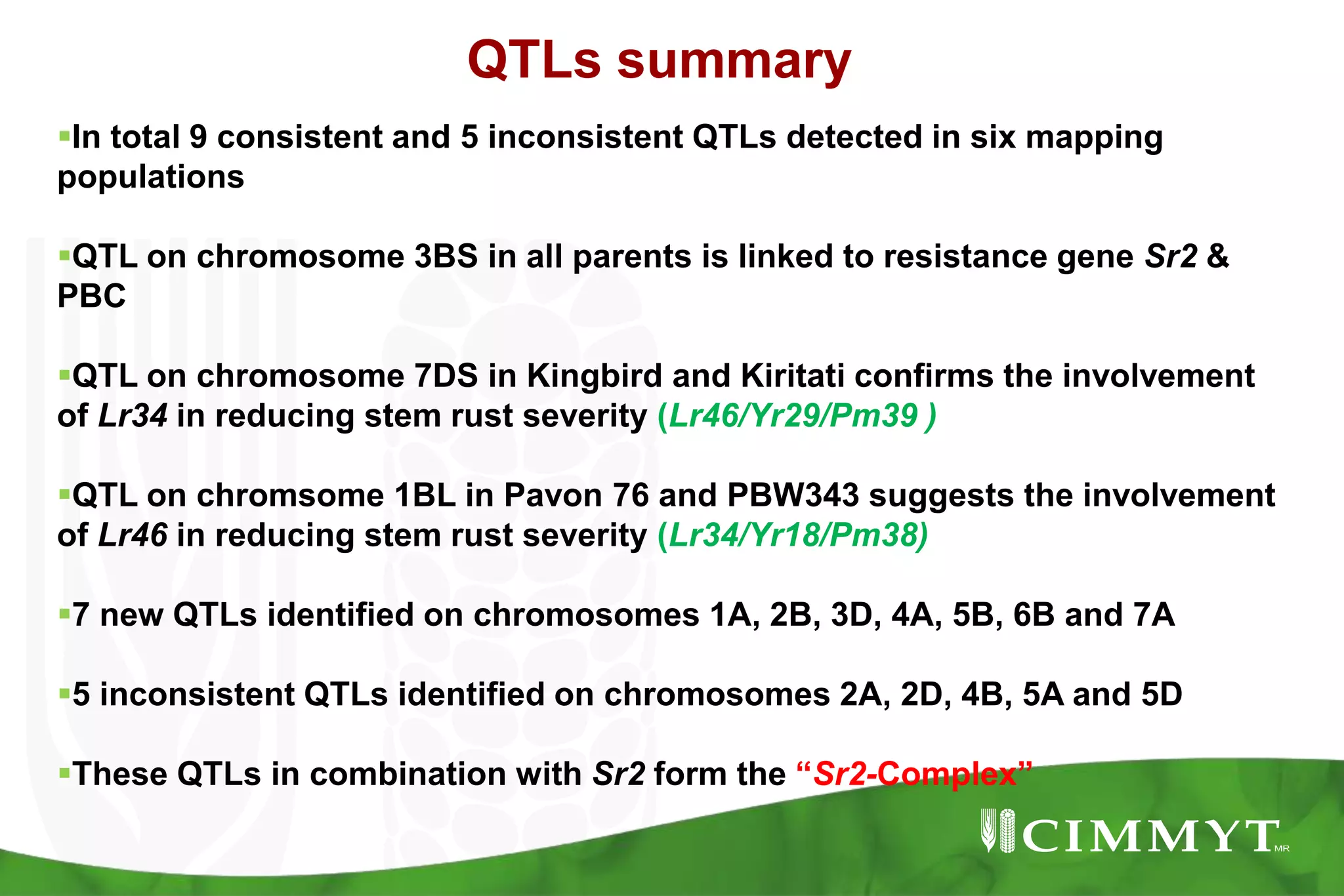
This document summarizes research mapping durable adult plant resistance to stem rust in wheat. Nine consistent and five inconsistent quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were detected across six mapping populations. A QTL on chromosome 3BS was found in all parents and is linked to resistance gene Sr2. A QTL on chromosome 7DS confirms the involvement of gene Lr34. A QTL on chromosome 1BL suggests the involvement of gene Lr46. These QTLs in combination with Sr2 form the "Sr2-Complex" conferring durable adult plant resistance. Future work will include fine mapping of QTLs and pyramiding adult plant resistance with major genes using markers.