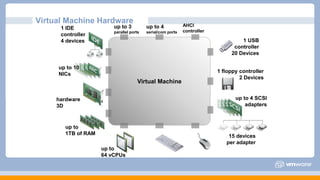
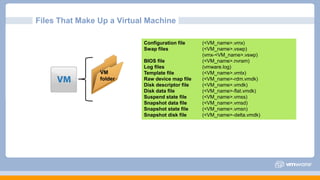
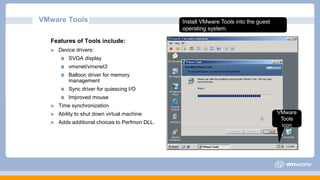
This document discusses virtual machine creation and management topics including vNetwork, vStorage, vMotion, DRS, and high availability (HA). It covers virtual machine hardware configuration, the files that make up a virtual machine, VMware Tools, and virtual machine power options. It also summarizes storage protocols, thin and thick provisioning, methods for migrating virtual machines, and how vMotion and DRS work. Finally, it discusses HA features like protection at different availability levels, using NIC teaming or additional networks for redundancy, and how the HA cluster architecture functions with a master and slave agents.