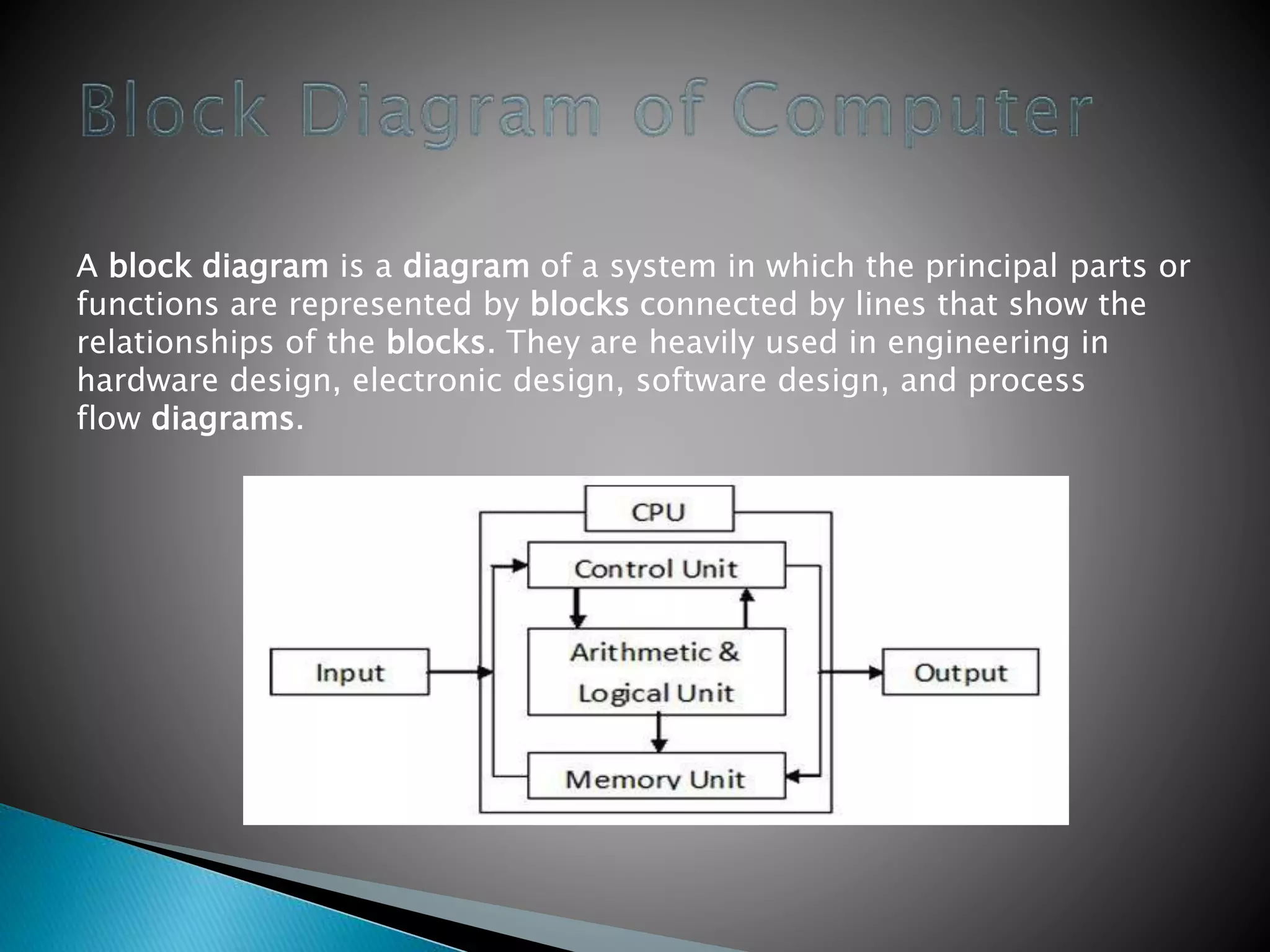
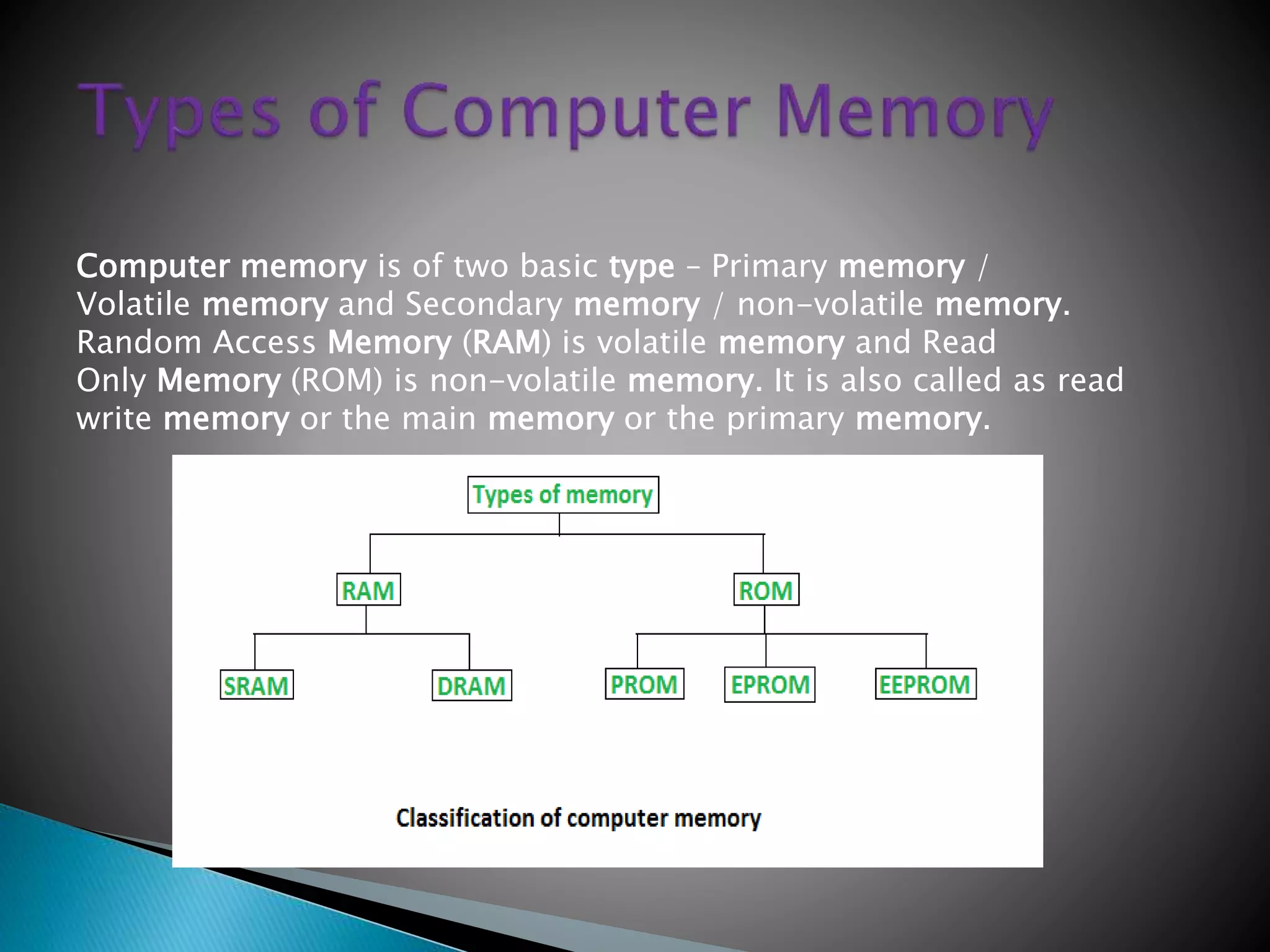
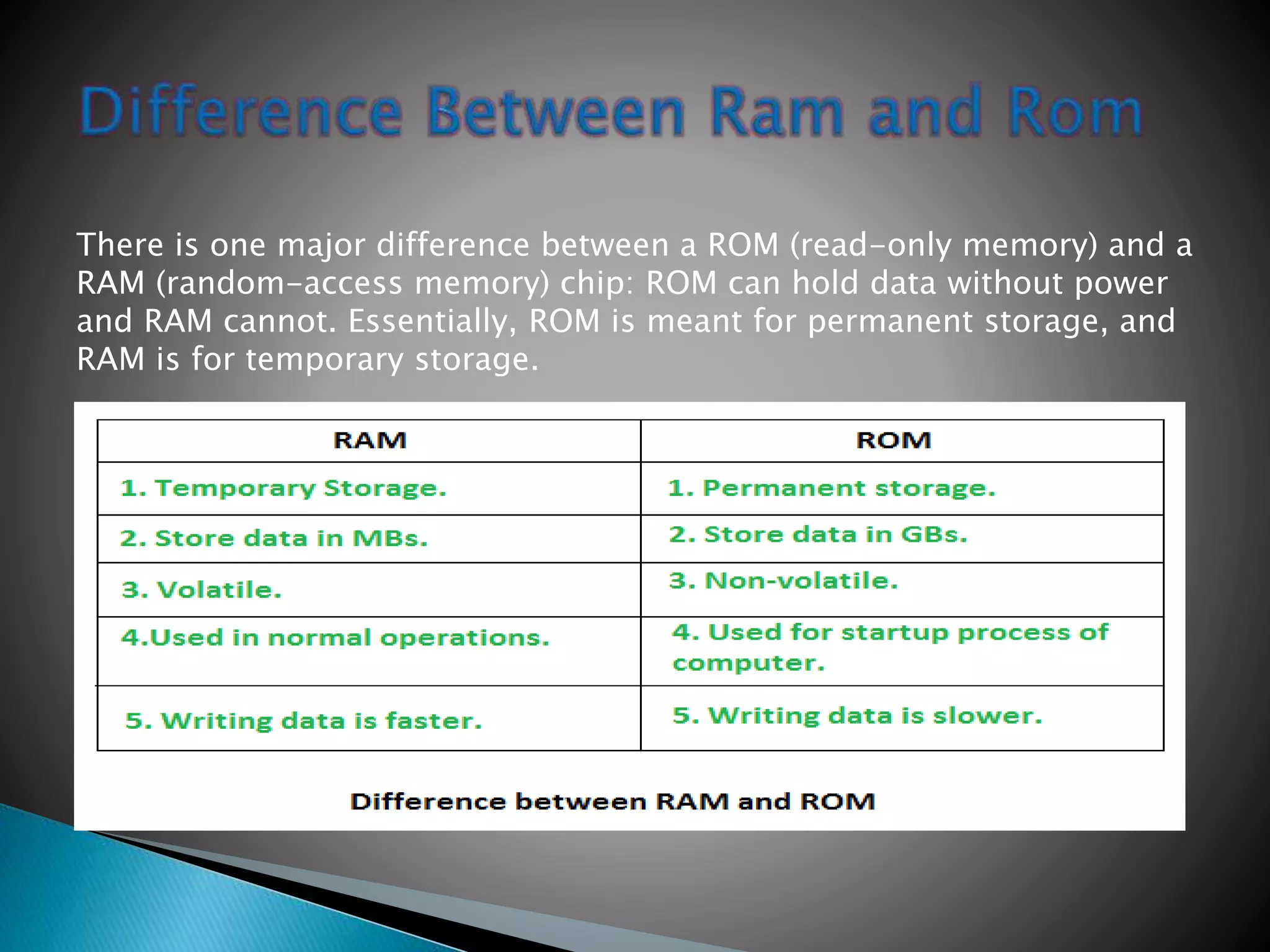
Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive computers, used to solve complex science and engineering problems through parallel processing of up to ten trillion calculations per second. Mainframes are similar but perform many concurrent operations for large organizations, while servers store data and applications to solve smaller problems for many users simultaneously. Workstations are high-end computers for one user for complex science, math, and engineering tasks. Personal computers are smaller computers designed for individual use in homes and small offices. Microcontrollers are embedded processors that control machinery. Smartphones perform computer-like functions with touchscreens and apps.