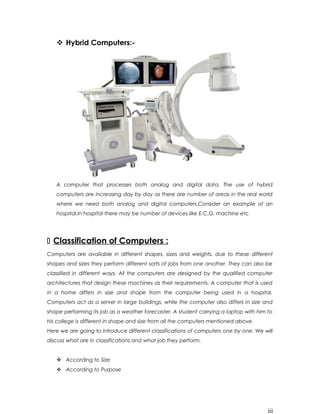
A computer is an electronic machine that accepts information as input, processes it according to programmed instructions, stores the information and output until needed. It cannot think or solve problems on its own. There are four main types of computers - analog, digital, hybrid and mainframe. Analog computers represent data continuously as voltages, digital computers use discrete signals of 1s and 0s, hybrid computers process both analog and digital data, and mainframe computers are large centralized computers used by large organizations. Computers can also be classified by size, from the largest and most powerful supercomputers to mainframes, minicomputers, workstations, and smallest personal computers.